|
Sethians
The Sethians (Greek: Σηθιανοί) were one of the main currents of Gnosticism during the 2nd and 3rd century AD, along with Valentinianism and Basilideanism. According to John D. Turner, it originated in the 2nd century AD as a fusion of two distinct Hellenistic Judaic philosophies and was influenced by Christianity and Middle Platonism. However, the exact origin of Sethianism is not properly understood. History Mentions The Sethians (Latin ''Sethoitae'') are first mentioned, alongside the Ophites, in the 2nd century, by Irenaeus (who was antagonistic towards Gnosticism) and in Pseudo-Tertullian (Ch. 30). According to Frederik Wisse, all subsequent accounts appear to be largely dependent on Irenaeus. Hippolytus repeats information from Irenaeus. According to Epiphanius of Salamis (c. 375), Sethians were in his time found only in Egypt and Palestine, but fifty years earlier, they had been found as far away as Greater Armenia. Philaster's (4th century AD) ''Catalogue o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gnosticism
Gnosticism (from Ancient Greek language, Ancient Greek: , Romanization of Ancient Greek, romanized: ''gnōstikós'', Koine Greek: Help:IPA/Greek, [ɣnostiˈkos], 'having knowledge') is a collection of religious ideas and systems that coalesced in the late 1st century AD among Early Christianity, early Christian sects. These diverse groups emphasized personal spiritual knowledge (''gnosis'') above the Proto-orthodox Christianity, proto-orthodox teachings, traditions, and authority of religious institutions. Generally, in Gnosticism, the Monad (Gnosticism), Monad is the supreme God who emanates divine beings; one, Sophia (Gnosticism), Sophia, creates the flawed demiurge who makes the material world, trapping souls until they regain divine knowledge. Consequently, Gnostics considered material existence flawed or evil, and held the principal element of salvation to be direct knowledge of the hidden divinity, attained via mystical or esoteric insight. Many Gnostic texts deal not in co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophites
The Ophites, also called Ophians (Ancient Greek, Greek Ὀφιανοί ''Ophianoi'', from ὄφις ''ophis'' "snake"), were a Christian Gnosticism, Gnostic sect depicted by Hippolytus of Rome (170–235) in a lost work, the ''Syntagma'' ("arrangement"). It is now thought that later accounts of these "Ophites" by Pseudo-Tertullian, Philastrius and Epiphanius of Salamis are all dependent on the lost ''Syntagma'' of Hippolytus. It is possible that, rather than an actual sectarian name, Hippolytus may have invented "Ophite" as a generic term for what he considered heretical speculations concerning the Serpents in the Bible, serpent of Genesis or Moses. Apart from the sources directly dependent on Hippolytus (Pseudo-Tertullian, Philastrius and Epiphanius), Origen and Clement of Alexandria also mention the group. The group is mentioned by Irenaeus in ''On the Detection and Overthrow of the So-Called Gnosis, Adversus Haereses''1:30. Pseudo-Tertullian Pseudo-Tertullian (probably the La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seth
Seth, in the Abrahamic religions, was the third son of Adam and Eve. The Hebrew Bible names two of his siblings (although it also states that he had others): his brothers Cain and Abel. According to , Seth was born after Abel's murder by Cain, and Eve believed that God had appointed him as a replacement for Abel. Genesis According to the Book of Genesis, Seth was born when Adam was 130 years old (according to the Masoretic Text), or 230 years old (according to the Septuagint), "a son in his likeness and image". The genealogy repeated at . states that Adam fathered "sons and daughters" before his death, aged 930 years. According to Genesis, Seth died at the age of 912 (that is, 14 years before Noah's birth). Jewish tradition Seth figures in the biblical texts of the ''Life of Adam and Eve'' (the ''Apocalypse of Moses''). It recounts the lives of Adam and Eve from after their expulsion from the Garden of Eden to their deaths. While the surviving versions were composed from the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
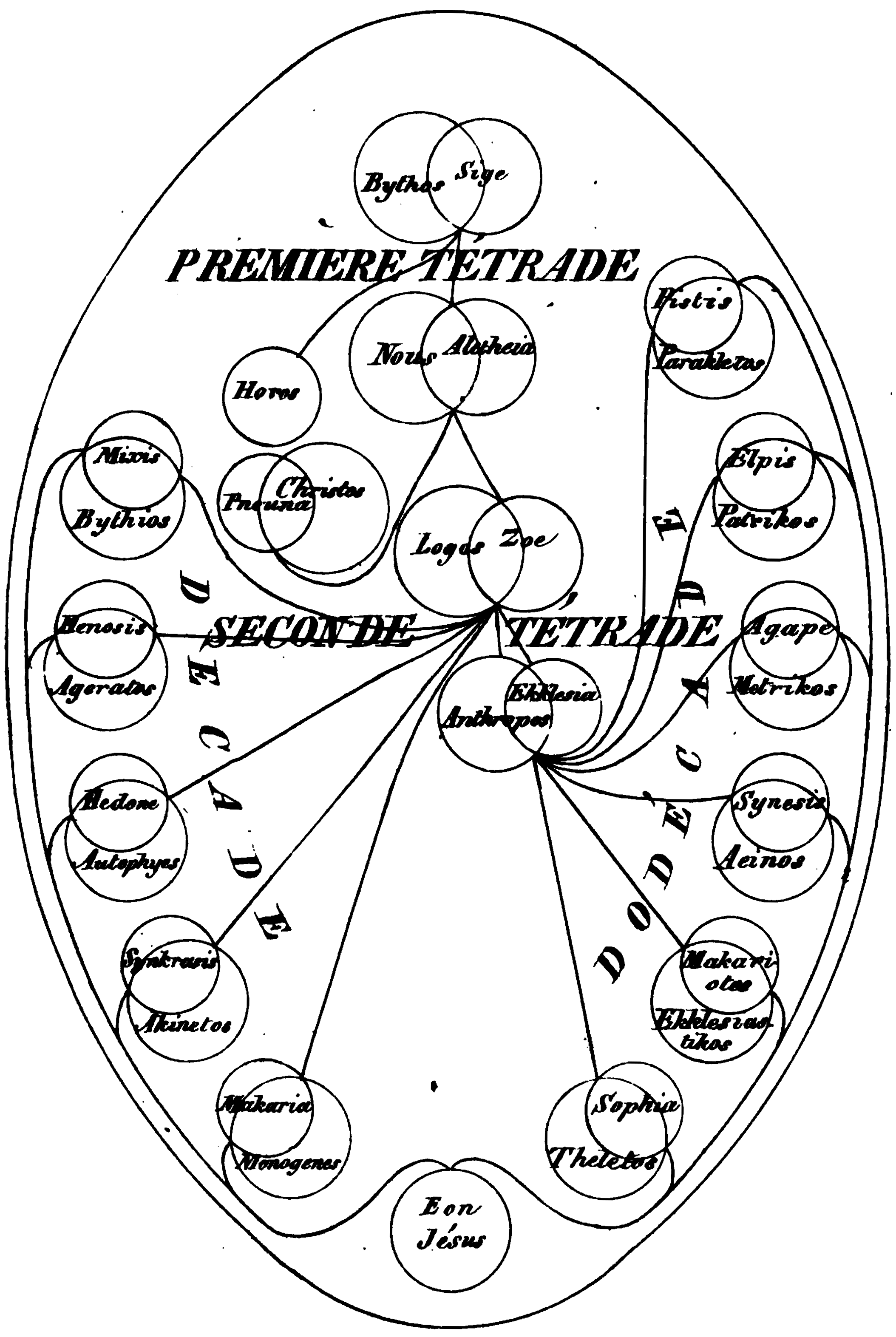
Valentinianism
Valentinianism was one of the major Gnostic Christian movements. Founded by Valentinus ( CE – CE) in the 2nd century, its influence spread widely, not just within the Roman Empire but also from northwest Africa to Egypt through to Asia Minor and Syria in the east. Later in the movement's history, it broke into Eastern and a Western schools. The Valentinian movement remained active until the 4th century, declining after Emperor Theodosius I issued the Edict of Thessalonica in 380, which established Nicene Christianity as the state religion of the Roman Empire. No evidence exists that Valentinus was labeled a heretic during his lifetime. Irenaeus of Lyons, who was the first patristic source to describe Valentinus's teachings—though likely incompletely and with a bias toward the time's proto-orthodox Christianity—did not finish his apologetic work '' Against Heresies'' until the later 2nd century, likely sometime after Valentinus's death. The rapid growth of the Vale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cainites
The Cainites or Cainians (, ''Kainoi'', and , ''Kaianoi'') were a heresy allegedly venerating Cain and celebrating him for his sins, described by Irenaeus. Irenaeus asserts in his ''Against Heresies''. i. 31 that the Cainites are enemies of the God of Israel and venerated everyone who opposed him, including Cain. They would claim fellowship with Esau, Korah, and the men of Sodom. Liberation would be achieved by committing sins against the Creator. He further asserts that their holy scripture is the Gospel of Judas, which he believed to teach immorality. However, since the discovery of primary sources in the Nag Hammadi library, the descriptions by Irenaeus do not match the actual sources, and there is no reference to Cain in the sole extant manuscript of the Gospel of Judas. Although some descriptions attributed to Cainites bear resemblences to certain Gnostic sects, no Gnostic sect held a positive depiction of Cain or encouraged sins. In none of the known Gnostic sources has C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Setianism
The Temple of Set (ToS) is an Occultism, occult religious organization founded in 1975. A new religious movement and form of Western esotericism, the Temple espouses a religion known as Setianism, whose practitioners are called Setians. This is sometimes identified as a form of Satanism. The Temple was established in the United States in 1975 by Michael Angelo Aquino, Michael Aquino, an American political science, political scientist, military officer, and a high-ranking member of Anton LaVey's Church of Satan. Dissatisfied with LaVey's Materialism, materialistic approach, abolition of regional groups, and commercialization of Church degrees, Aquino resigned and – according to his own claim – embarked on a ritual to invoke Satan, who revealed to him a sacred text called ''The Book of Coming Forth by Night''. According to Aquino, in this work Satan revealed his true name to be that of Set (deity), Set, which had been the name used by his followers in ancient Egyp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbelo
Barbēlō (Greek: Βαρβηλώ) refers to the first emanation of God in several forms of Gnostic cosmogony. Barbēlō is often depicted as a supreme female principle, the single passive antecedent of creation in its manifold. This figure is also variously referred to as 'Mother-Father' (hinting at her apparent androgyny), 'The Triple Androgynous Name', or 'Eternal Aeon'. So prominent was her place amongst some Gnostics that some schools were designated as ''Barbeliotae'', Barbēlō worshippers or Barbēlō gnostics. The nature of Barbēlō Nag Hammadi Library In the ''Apocryphon of John'', a tractate in the Nag Hammadi Library containing the most extensive recounting of the Sethian Gnostic creation myth, the Barbēlō is described as "the first power, the glory, Barbēlō, the perfect glory in the aeons, the glory of the revelation". All subsequent acts of creation within the divine sphere (save, crucially, that of the lowest aeon Sophia) occurs through her coaction with Go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autogenes
In Sethian Gnosticism, Autogenes (Meaning "Self-Born One" in Greek) is an emanation or son of Barbelo (along with Kalyptos and Protophanes according to '' Zostrianos''). Autogenes is mentioned in Nag Hammadi texts such as '' Zostrianos'', ''The Three Steles of Seth'', '' Allogenes the Stranger'', and '' Marsanes''. Autogenes in Gnosticism is roughly parallel to the Platonic soul. See also *Aeon (Gnosticism) *Plato's theory of soul Plato's theory of the soul, which was inspired variously by the teachings of Socrates, considered the psyche () to be the essence of a person, being that which decides how people behave. Plato considered this essence to be an incorporeal, etern ... References Gnostic deities {{Gnosticism-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anointing
Anointing is the ritual, ritual act of pouring aromatic oil over a person's head or entire body. By extension, the term is also applied to related acts of sprinkling, dousing, or smearing a person or object with any perfumed oil, milk, butter, or other fat. Scented oils are used as perfumes and sharing them is an act of #Hospitality, hospitality. Their use to #Religion, introduce a divine influence or presence is recorded from the earliest times; anointing was thus used as #Health, a form of medicine, thought to rid persons and things of dangerous spirits and demons which were believed to cause disease. In present usage, "anointing" is typically used for ceremonial blessings such as the #Royalty, coronation of European monarchs. This continues an #Judaism, earlier Hebrew practice most famously observed in the anointings of Aaron as high priest and both Saul and David by the prophet Samuel (Bible), Samuel. The concept is important to the figure of the Messiah or the Christ (Hebre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Docetism
In the history of Christianity, docetism (from the ''dokeĩn'' "to seem", ''dókēsis'' "apparition, phantom") was the doctrine that the phenomenon of Jesus, his historical and bodily existence, and above all the human form of Jesus, was mere semblance without any true reality. Broadly, it is taken as the belief that Jesus only seemed to be human, and that his human form was an illusion. The word ''Dokētaí'' ("Illusionists") referring to early groups who denied Jesus's humanity, first occurred in a letter by Bishop Serapion of Antioch (197–203), who discovered the doctrine in the Gospel of Peter, during a pastoral visit to a Christian community using it in Rhosus, and later condemned it as a forgery. It appears to have arisen over theological contentions concerning the meaning, figurative or literal, of a sentence from the Gospel of John: "the Word was made Flesh". Docetism was unequivocally rejected at the First Council of Nicaea in 325. and is regarded as heretical by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nag Hammadi Library
The Nag Hammadi library (also known as the Chenoboskion Manuscripts and the Gnostic Gospels) is a collection of early Christian and Gnostic texts discovered near the Upper Egyptian town of Nag Hammadi in 1945. Thirteen leather-bound papyrus codices buried in a sealed jar were found by a local farmer named Muhammed al-Samman. The writings in these codices comprise 52 mostly Gnostic treatises, but they also include three works belonging to the '' Corpus Hermeticum'' and a partial translation/alteration of Plato's ''Republic''. In his introduction to ''The Nag Hammadi Library in English'', James Robinson suggests that these codices may have belonged to a nearby Pachomian monastery and were buried after Saint Athanasius condemned the use of non-canonical books in his Festal Letter of 367 A.D. The Pachomian hypothesis has been further expanded by Lundhaug & Jenott (2015, 2018) and further strengthened by Linjamaa (2024). In his 2024 book, Linjamaa argues that the Nag Hammadi l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |