|
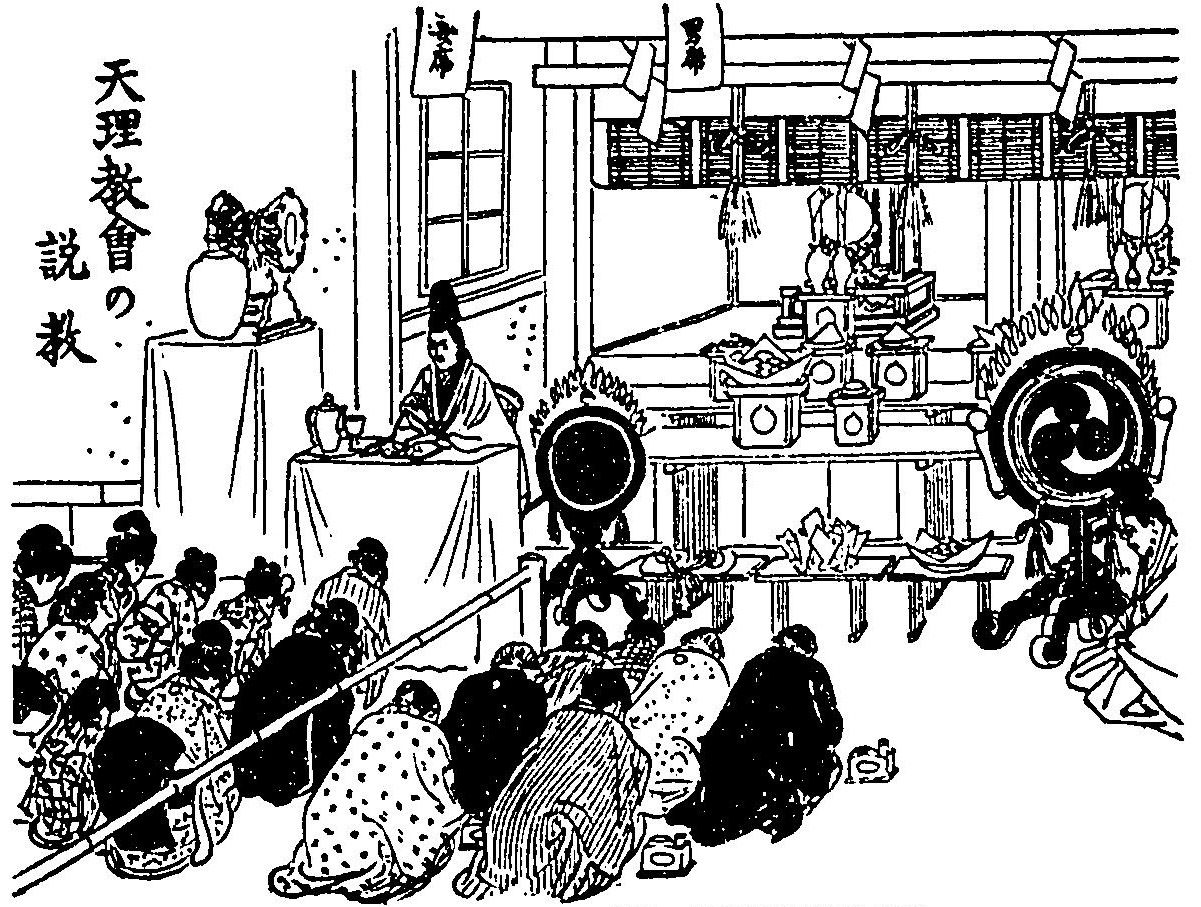
Service (Tenrikyo)
In the Tenrikyo religion, the , also known as the Tsutome, is the most important prayer ritual, along with the Sazuke. The Service comes in fundamental forms (i.e. the Kagura Service and Teodori) and several variant forms (such as the Morning and Evening Service). The text to the Service is the '' Mikagura-uta,'' one of the three scriptures of Tenrikyo. In Japanese, using kanji, ''Otsutome'' can be written as or . However, in Tenrikyo publications, it is typically written using only hiragana. Kagura Service The most important Service is the . This service is the masked dance that is exclusively performed around the Kanrodai where Tenrikyo Church Headquarters – located in Tenri City, Japan – is situated. In Shinto, the ''kagura'' is a ceremonial dance; in Tenrikyo, it is considered to be the religion's most sacred dance. Hashimoto cites three meanings behind the performance of the Kagura Service–to represent God's creative power at the time of human conception and thus i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenrikyo
is a Japanese new religion which is neither strictly monotheistic nor pantheistic, originating from the teachings of a 19th-century woman named Nakayama Miki, known to her followers as "Oyasama". Followers of Tenrikyo believe that God of Origin, God in Truth, known by several names including "Tsukihi," " Tenri-Ō-no-Mikoto" and "Oyagamisama" revealed divine intent through Miki Nakayama as the Shrine of God and to a lesser extent the roles of the Honseki Izo Iburi and other leaders. Tenrikyo's worldly aim is to teach and promote the Joyous Life, which is cultivated through acts of charity and mindfulness called . The primary operations of Tenrikyo today are located at Tenrikyo Church Headquarters, which supports 16,833 locally managed churches in Japan,Japanese Ministry of Education. ''Shuukyou Nenkan, Heisei 14-nen'' (宗教年鑑平成14年). 2002. the construction and maintenance of the and various community-focused organisations. It has 1.75 million followers in Japan a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cymbals
A cymbal is a common percussion instrument. Often used in pairs, cymbals consist of thin, normally round plates of various alloys. The majority of cymbals are of indefinite pitch, although small disc-shaped cymbals based on ancient designs sound a definite note (such as crotales). Cymbals are used in many ensembles ranging from the orchestra, percussion ensembles, jazz bands, heavy metal bands, and marching groups. Drum kits usually incorporate at least a crash, ride, or crash/ride, and a pair of hi-hat cymbals. A player of cymbals is known as a cymbalist. Etymology and names The word cymbal is derived from the Latin , which is the latinisation , which in turn derives . In orchestral scores, cymbals may be indicated by the French ; German , , , or ; Italian or ; and Spanish . Many of these derive from the word for plates. History Cymbals have existed since ancient times. Representations of cymbals may be found in reliefs and paintings from Armenian Highlands (7 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taiko
are a broad range of Traditional Japanese musical instruments, Japanese percussion instruments. In Japanese language, Japanese, the term refers to any kind of drum, but outside Japan, it is used specifically to refer to any of the various Japanese drums called and to the form of ensemble drumming more specifically called . The process of constructing varies between manufacturers, and the preparation of both the drum body and skin can take several years depending on the method. have a mythological origin in Japanese folklore, but historical records suggest that were introduced to Japan through China, Chinese and Korean cultural influence as early as the 6th century CE; pottery from the Haniwa period depicting drums has also been found. Some are similar to instruments originating from India. Archaeological evidence also supports the view that were present in Japan during the 6th century in the Kofun period. Their function has varied throughout history, ranging from com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenrikyo Homeshrine
is a Japanese new religion which is neither strictly monotheistic nor pantheistic, originating from the teachings of a 19th-century woman named Nakayama Miki, known to her followers as "Oyasama". Followers of Tenrikyo believe that God of Origin, God in Truth, known by several names including "Tsukihi," "Tenri-Ō-no-Mikoto" and "Oyagamisama" revealed divine intent through Miki Nakayama as the Shrine of God and to a lesser extent the roles of the Honseki Izo Iburi and other leaders. Tenrikyo's worldly aim is to teach and promote the Joyous Life, which is cultivated through acts of charity and mindfulness called . The primary operations of Tenrikyo today are located at Tenrikyo Church Headquarters, which supports 16,833 locally managed churches in Japan,Japanese Ministry of Education. ''Shuukyou Nenkan, Heisei 14-nen'' (宗教年鑑平成14年). 2002. the construction and maintenance of the and various community-focused organisations. It has 1.75 million followers in Japan and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiba (Tenrikyo)
In the Tenrikyo religion, the Jiba (Japanese: ぢば, 地場, 中心), also known as the , is the ''axis mundi'' where adherents believe that God created humankind. The spot is located in the center of the main sanctuary at Tenrikyo Church Headquarters, located in Tenri, Nara, Japan (coordinates: ). It is marked by a sacred wooden pillar called the ''Kanrodai'' (甘露台). In Japanese, using kanji, ''Jiba'' can be written as , and ''Ojiba'' as . However, in Tenrikyo publications, it is typically written using only hiragana. History Miki Nakayama originally identified the location of the Jiba in 1875 (May 26 according to the lunar calendar; June 29 according to the Gregorian calendar). As stated in this following except from Chapter 6 in '' The Life of Oyasama'': Significance The significance of the ''Jiba'' is described in all three Tenrikyo scriptures – the ''Ofudesaki'', the ''Mikagura-uta'', and the ''Osashizu''. Phrases in the scriptures define ''Jiba'' as simply "the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmological
Cosmology () is a branch of physics and metaphysics dealing with the nature of the universe, the cosmos. The term ''cosmology'' was first used in English in 1656 in Thomas Blount's ''Glossographia'', with the meaning of "a speaking of the world". In 1731, German philosopher Christian Wolff used the term cosmology in Latin (''cosmologia'') to denote a branch of metaphysics that deals with the general nature of the physical world. Religious or mythological cosmology is a body of beliefs based on mythological, religious, and esoteric literature and traditions of creation myths and eschatology. In the science of astronomy, cosmology is concerned with the study of the chronology of the universe. Physical cosmology is the study of the observable universe's origin, its large-scale structures and dynamics, and the ultimate fate of the universe, including the laws of science that govern these areas. It is investigated by scientists, including astronomers and physicists, as we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liturgy
Liturgy is the customary public ritual of worship performed by a religious group. As a religious phenomenon, liturgy represents a communal response to and participation in the sacred through activities reflecting praise, thanksgiving, remembrance, supplication, or repentance. It forms a basis for establishing a relationship with God. Technically speaking, liturgy forms a subset of ritual. The word ''liturgy'', sometimes equated in English as " service", refers to a formal ritual enacted by those who understand themselves to be participating in an action with the divine. Etymology The word ''liturgy'' (), derived from the technical term in ancient Greek (), ''leitourgia'', which means "work or service for the people" is a literal translation of the two affixes λήϊτος, "leitos", derived from the Attic form of λαός ("people, public"), and ἔργον, "ergon", meaning "work, service". In origin, it signified the often expensive offerings wealthy Greeks made in serv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kokyū
The is the only traditional Japanese string instrument played with a bow (music), bow. A variant of the instrument also exists in Okinawa Prefecture, Okinawa, called () in Okinawan language, Okinawan. The , like the , has its origins in Okinawa. Although it is similar to Chinese , it actually came to Okinawa via the from Indonesia and Malaysia. The is similar in construction to the , appearing as a smaller version of that instrument. In Okinawa, the body is round, while in mainland Japan, it is square like a . It has three (or, more rarely, four) strings and is played upright, with a horsehair-strung bow bowing the strings. It is often tuned the same as a but an octave higher. In central Japan, the was formerly used as an integral part of the ensemble, along with the and , but beginning in the 20th century the began to play the role previously filled by the . Since Shinei Matayoshi, a and musician and maker, invented and popularized a four-stringed version of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shamisen
The , also known as or (all meaning "three strings"), is a three-stringed traditional Japanese musical instrument derived from the Chinese instrument . It is played with a plectrum called a bachi. The Japanese pronunciation is usually but sometimes when used as a suffix, according to regular rendaku, sound change (e.g. ). In Western Japanese dialects and several Edo period sources, it is both written and pronounced as . The construction of the varies in shape, depending on the genre in which it is used. The instrument used to accompany kabuki has a thin neck, facilitating the agile and virtuosic requirements of that genre. The one used to accompany Bunraku, puppet plays and Min'yo, folk songs has a longer and thicker neck instead, to match the more robust music of those genres. Construction The is a plucked stringed instrument. Its construction follows a model similar to that of a guitar or a banjo, with a neck and strings stretched across a resonating body. The nec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koto (instrument)
The is a Japanese plucked half-tube zither instrument, and the national instrument of Japan. It is derived from the Chinese and , and similar to the Mongolian , the Korean and , the Vietnamese , the Sundanese and the Kazakh . Koto are roughly in length, and made from Paulownia wood ('' Paulownia tomentosa'', known as ). The most common type uses 13 strings strung over movable bridges used for tuning, different pieces possibly requiring different tuning. Seventeen-string koto are also common, and act as bass in ensembles. Koto strings are generally plucked using three fingerpicks (), worn on the first three fingers of the right hand. Names and types The character for ''koto'' is , although is often used. However, (''koto'') is the general term for all string instruments in the Japanese language,(jaKotobank koto/ref> including instruments such as the , , , , , and so on. When read as , it indicates the Chinese instrument . The term is used today in the same way. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fue (flute)
is the Japanese word for bamboo flute, and refers to a class of flutes native to Japan. come in many varieties, but are generally high-pitched and made of a bamboo called . The most popular of the is the . Categorization are traditionally broken up into two basic categories – the transverse flute and the end-blown flute. Transverse flutes are held to the side, with the musician blowing across a hole near one end; end-blown flutes are held vertically and the musician blows into one end. History The earliest may have developed from pitch pipes known as in Chinese language, Chinese.Malm, William P. Traditional Japanese Music and Musical Instruments. 1959. Rev. ed. Otowa: Kodansha International, 2000. The instrument eventually made its way over to Japan from China in the 5th century, becoming prevalent during the Nara Period. Soon after the introduction of instruments, Komusō, members of the Fuke-shū, Fuke sect of Zen Buddhism made normal use of the . These "priests of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |