|
Serrasalminae
The Serrasalmidae (serrasalmids) are a family of characiform fishes, recently elevated to family status. It includes more than 90 species. The name means "serrated salmon family", which refers to the serrated keel running along the belly of these fish. Fish classified as Serrasalmidae are also known by these common names: pacu, piranha, and silver dollar. These common names generally designate differing dental characteristics and feeding habits. Description Serrasalmids are medium- to large-sized characiform fishes that reach about long, generally characterized by a deep, laterally compressed body with a series of midventral abdominal spines or scutes, and a long dorsal fin (over 16 rays). Most species also possess an anteriorly directed spine just before the dorsal fin extending from a supraneural bone; exceptions include members of the genera '' Colossoma'', ''Piaractus'', and ''Mylossoma''. Most serrasalmids have about 60 chromosomes, ranging from 54 to 62.''Metynnis'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piranha
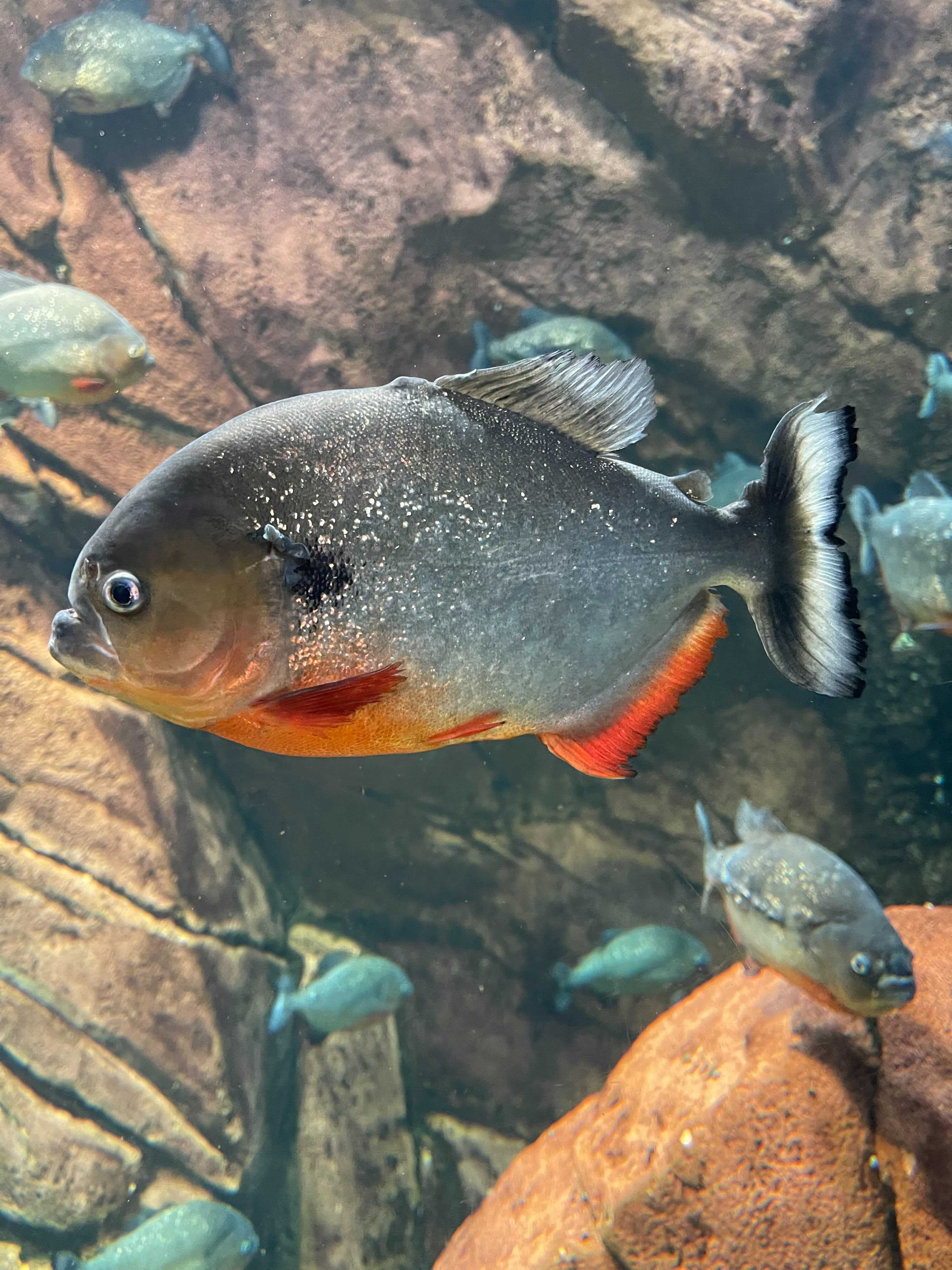
A piranha or piraña (, , or ; or , ) is one of a number of freshwater fish in the family Serrasalmidae, or the subfamily Serrasalminae within the tetra family, Characidae in order Characiformes. These fish inhabit South American rivers, floodplains, lakes and reservoirs. Although often described as extremely predatory and mainly feeding on fish, their dietary habits vary extensively, and they will also take plant material, leading to their classification as omnivorous. Etymology The name originates from the indigenous Tupi people and their respective Tupi language. It is formed from two words, meaning fish and meaning tooth; the same word is used by Indians to describe a pair of scissors. Another possible derivation is from , probably literally "biting-fish". In the mid 18th century the Portuguese merged the word into . Finally, the word may also come from the combination of meaning fish and meaning cut (which also meant "bad" or "devil" in Tupi-Guarani). Taxonomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tometes
''Tometes'' is a genus of fish in the family Serrasalmidae found in fast-flowing rivers in northern South America. Adults of all seven species in this genus are phytophagous, feeding primarily on aquatic plants in the family Podostemaceae. The genus name ''Tometes'' was coined in 1850 by Valenciennes in reference to the incisiform teeth. When the type species of the genus, ''T. trilobatus'', was described in 1850, it was placed in synonym with ''Myleus setiger'', the type species of the genus ''Myleus'', which is why ''Tometes'' and ''Myleus'' were considered to be the same genus for a long time. It was just later that the two genera were revalitated and other specimen could be categorized in the genus ''Tometes''. Taxonomy Even today the taxonomic classification of the Serrasalmidae is not an easy task. Many names are placed in synonymy due to a lack of information and insufficient data bases. It was not long ago when it was discovered that ''Tometes'' and ''Myleus'' are two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver Dollar (fish)
Silver dollar is a common name given to a number of species of fishes, mostly in the genus ''Metynnis'', tropical fish belonging to the family Characidae which are closely related to piranha and pacu. Native to South America, these somewhat round-shaped silver fish are popular with fish-keeping hobbyists. The silver dollar is a peaceful schooling species that spends most of its time in the mid- to upper-level of the water. Its average lifespan is less than ten years but can live longer in captivity. A chin-layer, the adult fish will spawn around 2,000 eggs. This breeding occurs in soft, warm water in low light. Silver dollars natively live in a tropical climate in the sides of weedy rivers. They prefer water with a pH of 5–7, a water hardness of up to 15 dGH, and an ideal temperature range of 24–28 °C (75–82 °F). Their diet is almost exclusively vegetarian and in captivity they will often eat all the plants in a tank. They will also eat worms and small insects. Fish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacu
Pacu () is a common name used to refer to several species of omnivorous South American freshwater serrasalmid fish that are related to the piranha. Pacu and piranha do not have similar teeth, the main difference being jaw alignment; piranha have pointed, razor-sharp teeth in a pronounced underbite, whereas pacu have squarer, straighter teeth and a less severe underbite, or a slight overbite. Pacu, unlike piranha, mainly feed on plant material and not flesh or scales. Additionally, the pacu can reach much larger sizes than piranha, at up to in total length and in weight. Name The common name ''pacu'' is generally applied to fish classified under the below listed genera. Among these, several genera contain species where commonly used English names include the word ''pacu'', as listed. *'' Colossoma'' – black pacu, black-finned pacu, giant pacu *''Metynnis'' *'' Mylesinus'' (''Myloplus'') *''Mylossoma '' *'' Ossubtus'' – parrot pacu, eaglebeak pacu *''Piaractus'' – red-be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pristobrycon
''Pristobrycon'' is a genus of piranhas from the Orinoco and Amazon Basins, as well as rivers in the Guianas. ''Pristobrycon'' is not monophyletic. No single morphological feature has been found that completely diagnoses this genus. ''P. striolatus'' is very different from other species of this genus. The genus ''Pristobrycon'' was created by Eigenmann to include species which have intermediate characters between "the fierce ''Rooseveltiella'' Pygocentrus_nattereri.html" ;"title="''Pygocentrus nattereri">''Pygocentrus nattereri''without palatine teeth, and the less blood-thirsty ''Serrasalmus'' with a series of permanent teeth along the palatine". The author designed ''P. calmoni'' as the type species of the genus. Two groups are included in this genus. One group is characterized by presence of the preanal spine (only ''P. calmoni'') and the other group including the rest of the species assigned (''P. careospinus'', ''P. maculipinnis'' and ''P. striolatus'') (Fink & Machado-All ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ossubtus
''Ossubtus'' is a genus of fish in the family Serrasalmidae. It contains a single species, ''Ossubtus xinguense'', the parrot pacu or eaglebeak pacu, The species is endemic to rapids in the Xingu River basin in the Brazilian Amazon.Andrade, M.C., Sousa, L.M., Ota, R.P., Jégu, M. & Giarrizzo, T. (2016)Redescription and Geographical Distribution of the Endangered Fish ''Ossubtus xinguense'' Jégu 1992 (Characiformes, Serrasalmidae) with Comments on Conservation of the Rheophilic Fauna of the Xingu River.''PLoS ONE, 11 (9): e0161398.'' This endangered species is primarily a herbivore. Description The body of ''Ossubtus xinguense'' is ovoid in shape. The profile of the snout is blunt. In young fish, the mouth is terminal (pointing forward); however, as the fish grows, the mouth turns downward and becomes strictly ventral in individuals longer than . This gives the mouth a beak-like appearance. It reaches up to in total length and about in weight. Range and habitat ''Ossubtus xin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
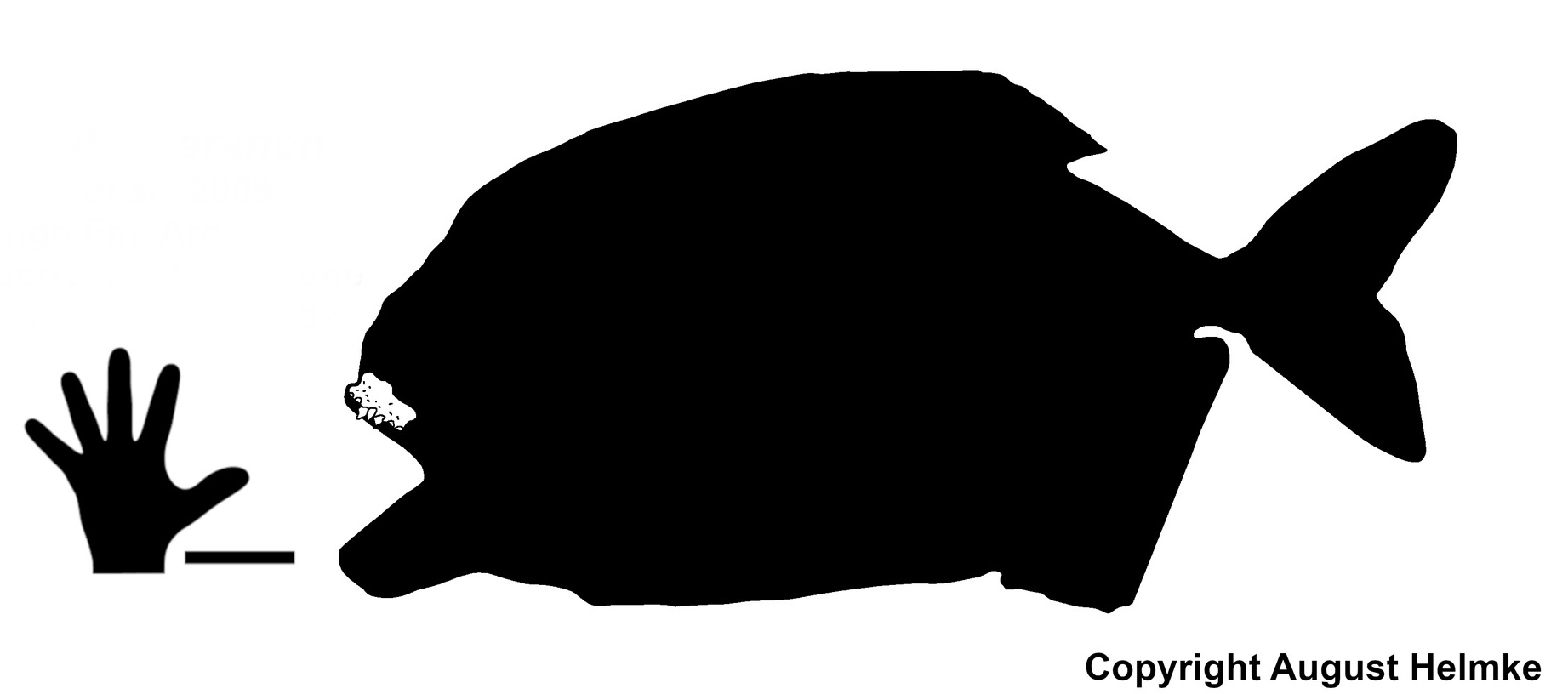
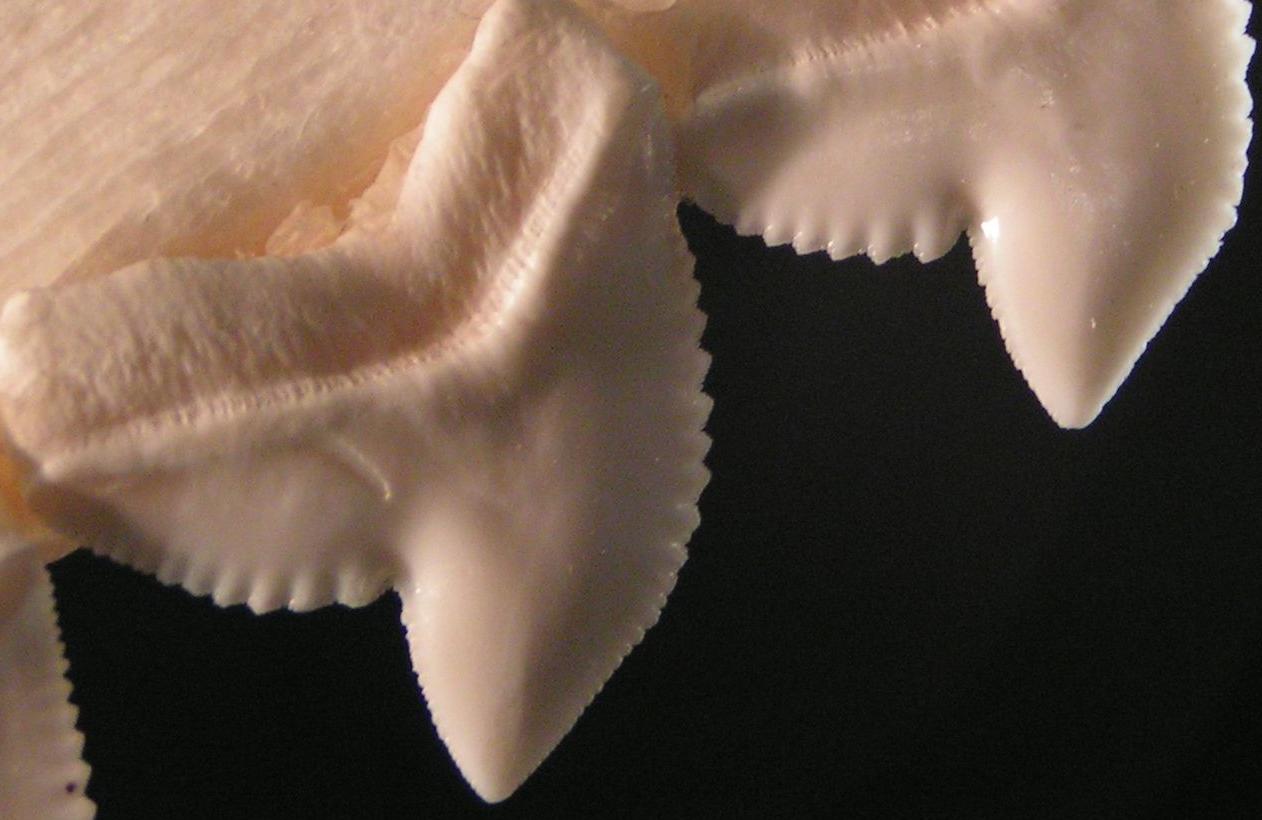
Megapiranha
''Megapiranha'' is an extinct serrasalmid characin fish from the Late Miocene (8–10 million years ago) Ituzaingó Formation of Argentina, described in 2009. The type species is ''M. paranensis''.''Megapiranha'' at .org It is thought to have been about in length and in weight. The consists only of e and a zigzag tooth row; the rest of its body is unknown. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Characiform
Characiformes is an order of ray-finned fish, comprising the characins and their allies. Grouped in 18 recognized families, more than 2000 different species are described, including the well-known piranha and tetras.; Buckup P.A.: "Relationships of the Characidiinae and phylogeny of characiform fishes (Teleostei: Ostariophysi)", ''Phylogeny and Classification of Neotropical Fishes'', L.R. Malabarba, R.E. Reis, R.P. Vari, Z.M. Lucena, eds. (Porto Alegre: Edipucr) 1998:123-144. Taxonomy The Characiformes form part of a series called the Otophysi within the superorder Ostariophysi. The Otophysi contain three other orders, Cypriniformes, Siluriformes, and Gymnotiformes. The Characiformes form a group known as the Characiphysi with the Siluriformes and Gymnotiformes. The order Characiformes is the sister group to the orders Siluriformes and Gymnotiformes, though this has been debated in light of recent molecular evidence. Originally, the characins were all grouped within a single ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salmon
Salmon () is the common name In biology, a common name of a taxon or organism (also known as a vernacular name, English name, colloquial name, country name, popular name, or farmer's name) is a name that is based on the normal language of everyday life; and is often contra ... for several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family (biology), family Salmonidae, which are native to tributary, tributaries of the North Atlantic (genus ''Salmo'') and North Pacific (genus ''Oncorhynchus'') basin. Other closely related fish in the same family include trout, Salvelinus, char, Thymallus, grayling, Freshwater whitefish, whitefish, lenok and Hucho, taimen. Salmon are typically fish migration, anadromous: they hatch in the gravel stream bed, beds of shallow fresh water streams, migrate to the ocean as adults and live like sea fish, then return to fresh water to reproduce. However, populations of several spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serration
Serration is a saw-like appearance or a row of sharp or tooth-like projections. A serrated cutting edge has many small points of contact with the material being cut. By having less contact area than a smooth blade or other edge, the applied pressure at each point of contact is greater and the points of contact are at a sharper angle to the material being cut. This causes a cutting action that involves many small splits in the surface of the material being cut, which cumulatively serve to cut the material along the line of the blade. In nature, serration is commonly seen in the cutting edge on the teeth of some species, usually sharks. However, it also appears on non-cutting surfaces, for example in botany where a toothed leaf margin or other plant part, such as the edge of a carnation petal, is described as being serrated. A serrated leaf edge may reduce the force of wind and other natural elements. Probably the largest serrations on Earth occur on the skylines of mountains ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene is preceded by the Oligocene and is followed by the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by a single distinct global event but consist rather of regionally defined boundaries between the warmer Oligocene and the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, the Arabian Peninsula collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Ocean, and allowing a faunal interchange to occur between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans into Eurasia. During the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentition
Dentition pertains to the development of teeth and their arrangement in the mouth. In particular, it is the characteristic arrangement, kind, and number of teeth in a given species at a given age. That is, the number, type, and morpho-physiology (that is, the relationship between the shape and form of the tooth in question and its inferred function) of the teeth of an animal. Animals whose teeth are all of the same type, such as most non-mammalian vertebrates, are said to have '' homodont'' dentition, whereas those whose teeth differ morphologically are said to have ''heterodont'' dentition. The dentition of animals with two successions of teeth (deciduous, permanent) is referred to as ''diphyodont'', while the dentition of animals with only one set of teeth throughout life is ''monophyodont''. The dentition of animals in which the teeth are continuously discarded and replaced throughout life is termed ''polyphyodont''. The dentition of animals in which the teeth are set in soc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |