|
Serpentinite
Serpentinite is a metamorphic rock composed predominantly of serpentine group minerals formed by serpentinization of mafic or ultramafic rocks. The ancient origin of the name is uncertain; it may be from the similarity of its texture or color to snake skin. Greek pharmacologist Pedanius Dioscorides, Dioscorides (AD 50) recommended this rock to prevent snakebite. Serpentinite has been called ''serpentine'' or ''serpentine rock'', particularly in older geological texts and in wider cultural settings.California Government Code § 425.2; ''see'' Most of the chemical reactions necessary to synthesize acetyl-CoA, essential to basic biochemical pathways of life, take place during serpentinization. Serpentinite thermal vents are therefore considered a candidate for the origin of life on Earth. Formation and mineralogy Serpentinite is formed by near to complete serpentinization of mafic or ultramafic rocks. Serpentinite is formed from mafic rock that is mineral hydration, hydrate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serpentine Subgroup
Serpentine subgroup (part of the kaolinite-serpentine group in the category of phyllosilicates) are greenish, brownish, or spotted minerals commonly found in serpentinite. They are used as a source of magnesium and asbestos, and as decorative stone. The name comes from the greenish color and smooth or scaly appearance from the Latin , meaning "snake-like". Serpentine subgroup is a set of common rock-forming hydrous magnesium iron phyllosilicate () minerals, resulting from the metamorphism of the minerals that are contained in mafic to ultramafic rocks. They may contain minor amounts of other elements including chromium, manganese, cobalt or nickel. In mineralogy and gemology, serpentine may refer to any of the 20 varieties belonging to the serpentine subgroup. Owing to admixture, these varieties are not always easy to individualize, and distinctions are not usually made. There are three important mineral polymorphs of serpentine: antigorite, lizardite and chrysotile. Serpe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serpentine Group
Serpentine subgroup (part of the kaolinite-serpentine group in the category of phyllosilicates) are greenish, brownish, or spotted minerals commonly found in serpentinite. They are used as a source of magnesium and asbestos, and as decorative stone. The name comes from the greenish color and smooth or scaly appearance from the Latin , meaning "snake-like". Serpentine subgroup is a set of common rock-forming hydrous magnesium iron phyllosilicate () minerals, resulting from the metamorphism of the minerals that are contained in mafic to ultramafic rocks. They may contain minor amounts of other elements including chromium, manganese, cobalt or nickel. In mineralogy and gemology, serpentine may refer to any of the 20 varieties belonging to the serpentine subgroup. Owing to admixture, these varieties are not always easy to individualize, and distinctions are not usually made. There are three important mineral polymorphs of serpentine: antigorite, lizardite and chrysotile. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
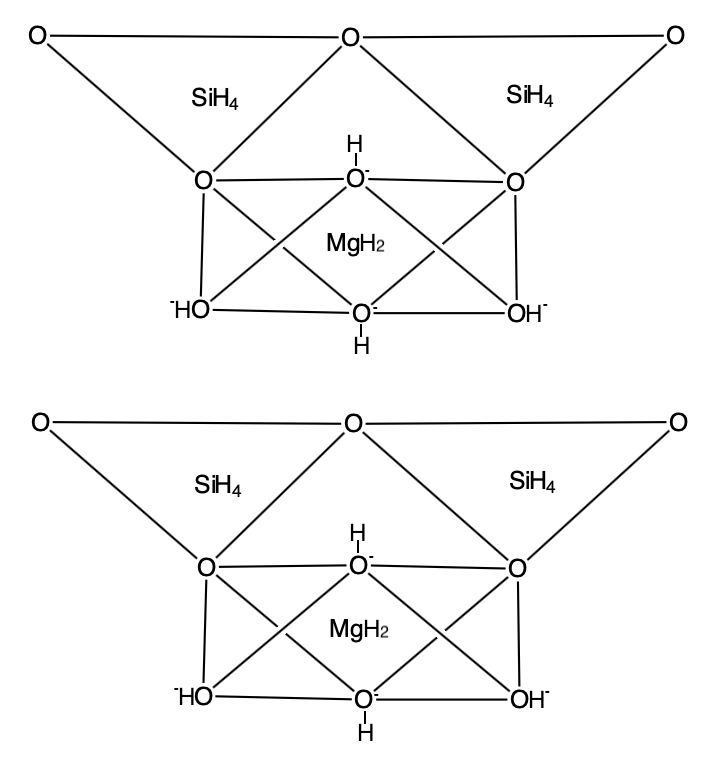
Serpentinization
Serpentinization is a hydration and Metamorphic rock, metamorphic transformation of ferromagnesian minerals, such as olivine and pyroxene, in mafic and ultramafic rock to produce serpentinite. Minerals formed by serpentinization include the Serpentine subgroup, serpentine group minerals (antigorite, lizardite, chrysotile), brucite, talc, Ni-Fe alloys, and magnetite. The mineral alteration is particularly important at the sea floor at plate tectonics, tectonic plate boundaries. Formation and petrology Serpentinization is a form of low-temperature (0 to ~600 °C) metamorphism of ferromagnesian minerals in mafic and ultramafic rocks, such as dunite, harzburgite, or lherzolite. These are rocks low in silica and composed mostly of olivine (), pyroxene (), and chromite (approximately ). Serpentinization is driven largely by Mineral hydration, hydration and oxidation of olivine and pyroxene to serpentine subgroup, serpentine group minerals (antigorite, lizardite, and chrysotile), bru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigorite
Antigorite is a lamellated, monoclinic mineral in the phyllosilicate serpentine subgroup with the ideal chemical formula of (Mg,Fe2+)3Si2O5(OH)4. It is the high-pressure polymorph of serpentine and is commonly found in metamorphosed serpentinites. Antigorite, and its serpentine polymorphs, play an important role in subduction zone dynamics due to their relative weakness and high weight percent of water (up to 13 weight % H2O). It is named after its type locality, the Geisspfad serpentinite, Valle Antigorio in the border region of Italy/Switzerland and is commonly used as a gemstone in jewelry and carvings. Geologic occurrences Antigorite is found in low-temperature, high-pressure (or high-deformation) environments, including both extensional and compressional tectonic regimes. Serpentines are commonly found in the ultramafic greenschist facies of subduction zones, and are visible on the Earth's surface through secondary exhumation. Serpentinites that contain antigorite are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
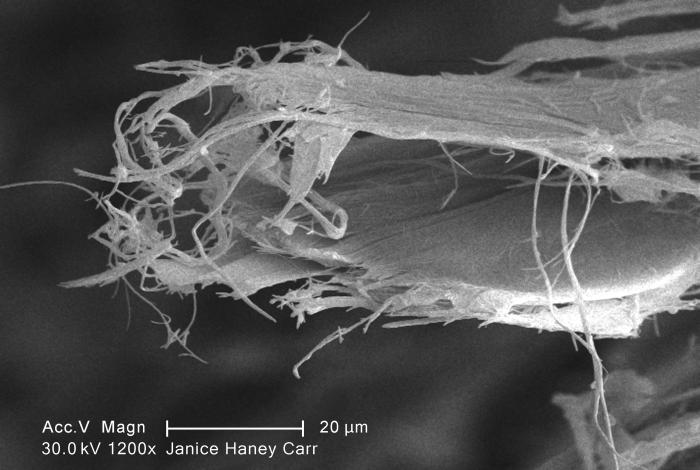
Chrysotile
Chrysotile or white asbestos is the most commonly encountered form of asbestos, accounting for approximately 95% of the asbestos in the United StatesOccupational Safety and Health Administration, U.S. Department of Labor (2007)29 C.F.R. 1910.1001 Appendix J. and a similar proportion in other countries.Institut national de recherche sur la sécurité (1997).Amiante." ''Fiches toxicologiques.'' n° 167. (in French) It is a soft, fibrous silicate mineral in the serpentine subgroup of phyllosilicates; as such, it is distinct from other asbestiform minerals in the amphibole group. Its idealized chemical formula is Mg( Si O)( OH). The material has physical properties which make it desirable for inclusion in building materials, but poses serious health risks when dispersed into air and inhaled. Polytypes Three polytypes of chrysotile are known. These are very difficult to distinguish in hand specimens, and polarized light microscopy must normally be used. Some older publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Awaruite
Awaruite is a naturally occurring alloy of nickel and iron with a composition from Ni2Fe to Ni3Fe. Awaruite occurs in river placer deposits derived from serpentinized peridotites and ophiolites. It also occurs as a rare component of meteorites. It occurs in association with native gold and magnetite in placers; with copper, heazlewoodite, pentlandite, violarite, chromite, and millerite in peridotites; with kamacite, allabogdanite, schreibersite and graphite in meteorites. It was first described in 1885 for an occurrence along Gorge River, near Awarua Bay, South Island, New Zealand, its type locality. Awaruite is also known as ''josephinite'' in an occurrence in Josephine County, Oregon where it is found as placer nuggets in stream channels and masses in serpentinized portions of the Josephine peridotite. Some nuggets contain andradite garnet. An occurrence of awaruite was examined as an ore mineral in a large low grade deposit in central British Columbia, some 90 k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subduction Zone
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere and some continental lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at the convergent boundaries between tectonic plates. Where one tectonic plate converges with a second plate, the heavier plate dives beneath the other and sinks into the mantle. A region where this process occurs is known as a subduction zone, and its surface expression is known as an arc-trench complex. The process of subduction has created most of the Earth's continental crust. Rates of subduction are typically measured in centimeters per year, with rates of convergence as high as 11 cm/year. Subduction is possible because the cold and rigid oceanic lithosphere is slightly denser than the underlying asthenosphere, the hot, ductile layer in the upper mantle. Once initiated, stable subduction is driven mostly by the negative buoyancy of the dense subducting lithosphere. The down-going slab sinks into the mantle largely under its own ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gros Morne Moho
Gros may refer to: People * Gros (surname) * Gross (surname), the German variant of Gros * Le Gros, the Norman variant of Gros Other uses * Gros (coinage), a type of 13th-century silver coinage of France * Gros (grape), another name for Elbling, a variety of white grape * Groș, a village of the city of Hunedoara, Transylvania, Romania * General Register Office for Scotland (GROS) See also * Gros Morne (other) Gros Morne or Gros-Morne may refer to: * Gros-Morne, Artibonite, a commune in the Artibonite department in Haiti * Gros Morne, Grand'Anse, rural settlement in the Moron commune of Haiti * Gros-Morne, Martinique, a commune in the French overseas d ... * * Gross (other) * Grosz (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fayalite
Fayalite (, commonly abbreviated to Fa) is the iron-rich endmember, end-member of the olivine solid solution, solid-solution series. In common with all minerals in the olivine, olivine group, fayalite crystallizes in the orthorhombic system (space group ''Pbnm'') with cell parameters ''a'' = 4.82 Å, ''b'' = 10.48 Å and ''c'' = 6.09 Å. Fayalite forms solid solution series with the magnesium olivine endmember forsterite (Mg2SiO4) and also with the manganese rich olivine endmember tephroite (Mn2SiO4). Iron rich olivine is a relatively common constituent of acidic and Alkaline earth metal, alkaline igneous rocks such as volcanic obsidians, rhyolites, trachytes and phonolites and plutonic quartz syenites where it is associated with amphiboles. Its main occurrence is in ultramafic volcanic and plutonic rocks and less commonly in felsic plutonic rocks and rarely in granite pegmatite. It also occurs in lithophysae in obsidian. It also occurs in medium-grade thermall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brucite
Brucite is the mineral form of magnesium hydroxide, with the chemical formula Magnesium, Mg(hydroxyl, OH)2. It is a common alteration product of periclase in marble; a low-temperature hydrothermal Vein (geology), vein mineral in metamorphosed limestones and Chlorite group, chlorite schists; and formed during serpentinization of dunites. Brucite is often found in association with Serpentine group, serpentine, calcite, aragonite, Dolomite (mineral), dolomite, magnesite, hydromagnesite, artinite, talc and chrysotile. It adopts a layered CdI2-like structure with hydrogen-bonds between the layers. Discovery Brucite was first described in 1824 by François Sulpice Beudant and named for the discoverer, American mineralogist, Archibald Bruce (mineralogist), Archibald Bruce (1777–1818). A fibrous variety of brucite is called nemalite. It occurs in fibers or laths, usually elongated along [1010], but sometimes [1120] Miller index, crystalline directions. Occurrence A notable location i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |