|
Sergiu Rădăuțanu
Sergiu Rădăuțanu (17 June 1926 – 6 March 1998) was a Moldovan physicist. He was a vice-president of the Academy of Sciences of Moldova and professor at the Technical University of Moldova. Early life Rădăuțanu was born on 17 June 1926 in Chișinău. His parents were both teachers, with his father speaking nine languages and teaching French. Education and early career Rădăuțanu studied at Bogdan Petriceicu Hasdeu High School in Chișinău and graduated from the State University of Moldova in 1955. He earned his PhD in 1959 from the Ioffe Institute in Leningrad, researching solid solutions in semiconductor systems. His habilitation in 1966 at the Peter the Great St. Petersburg Polytechnic University focused on diamond-type semiconductors with defective structures. Key roles and leadership In 1961, Rădăuțanu became the Laboratory Head at the Institute of Applied Physics, where he advanced semiconductor material research. In 1964, he helped found and was a re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supreme Soviet Of The Moldavian SSR
The Supreme Soviet of the Moldavian SSR (, ; ) was the supreme soviet (main Legislature, legislative institution) of the Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic, Moldavian SSR and later the independent Moldova, Republic of Moldova from 1941 to 1993. The last elections of the Supreme Soviet of the Moldavian SSR were held in 1990 and 371 deputies were elected. Convocations On May 23, 1991, the 12th convocation of the Supreme Soviet of the Moldavian SSR became the first Parliament of the Republic of Moldova. * 1st Convocation (1941-1946) * 2nd Convocation (1947-1950) * 3rd Convocation (1951-1954) * 4th Convocation (1955-1959) * 5th Convocation (1959-1962) * 6th Convocation (1963-1966) * 7th Convocation (1967-1970) * 8th Convocation (1971-1974) * 9th Convocation (1975-1979) * 10th Convocation (1980-1984) * 11th Convocation (1985-1989) * 12th Convocation (1990-1993) Chairmen of the Supreme Soviet Chairmen of the Presidium of the Supreme Soviet {, class="wikitable" !Portrait !Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bogdan Petriceicu Hasdeu High School
Bogdan (Cyrillic: Богдан) is a Slavic masculine name that appears in the South Slavic languages and in Polish, Romanian and Moldovan. It is derived from the Slavic words ''Bog'' (Cyrillic: Бог), meaning 'god', and ''dan'' (Cyrillic: дан), meaning 'given'. The name appears to be an early calque from Greek Theódoros (Theodore, Theodosius) or Hebrew Matthew with the same meaning. The name is also used as a surname in Hungary, Romania, Serbia and Croatia. Bogdana is the feminine version of the name. Variations The sound change of 'g' into 'h' (into Bohdan) occurred in the West Slavic languages and in Ukrainian. Both Bogdan and Bohdan are used in Poland. Slavic variants include Bulgarian and Serbo-Croatian Božidar (Божидар) and Polish Bożydar, and diminutive forms and nicknames include Boguś, Bodya, Boca, Boci, Boća, Boša, Bogi, Bo, Boga Boga, Boggie. The feminine form is Bogdana, with variants such as ''Bogdanka''. Names with similar meanings include P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Compound
A coordination complex is a chemical compound consisting of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the periodic table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom through several of the ligand's atoms; ligands with 2, 3, 4 or even 6 bonds to the central atom ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
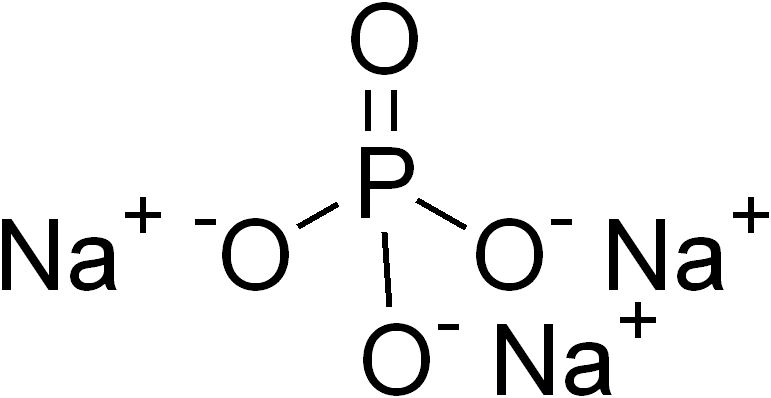
Ternary Compound
In inorganic chemistry and materials chemistry, a ternary compound or ternary phase is a chemical compound containing three different elements. While some ternary compounds are molecular, ''e.g.'' chloroform (), more typically ternary phases refer to extended solids. The perovskites are a famous example. Binary phases, with only two elements, have lower degrees of complexity than ternary phases. With four elements, quaternary phases are more complex. The number of isomers of a ternary compound provide a distinction between inorganic and organic chemistry: "In inorganic chemistry one or, at most, only a few compounds composed of any two or three elements were known, whereas in organic chemistry the situation was very different." Ternary crystalline compounds An example is sodium phosphate, . The sodium ion has a charge of 1+ and the phosphate ion has a charge of 3–. Therefore, three sodium ions are needed to balance the charge of one phosphate ion. Another example of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rector (academia)
A rector (Latin language, Latin for 'ruler') is a senior official in an educational institution, and can refer to an official in either a university or a secondary school. Outside the English-speaking world, the rector is often the most senior official in a university, while in the United States, the equivalent is often referred to as the President (education), president, and in the United Kingdom and Commonwealth of Nations, the equivalent is the Vice-chancellor (education), vice-chancellor. The term and office of a rector can be referred to as a rectorate. The title is used widely in universities in EuropeEuropean nations where the word ''rector'' or a cognate thereof (''rektor'', ''recteur'', etc.) is used in referring to university administrators include Albania, Austria, Benelux, the Benelux, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Italy, Latvia, Malta, Moldova, North Macedonia, Poland, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute Of Applied Physics
An institute is an organizational body created for a certain purpose. They are often research organisations (research institutes) created to do research on specific topics, or can also be a professional body. In some countries, institutes can be part of a university or other institutions of higher education, either as a group of departments or an autonomous educational institution without a traditional university status such as a "university institute", or institute of technology. In some countries, such as South Korea and India, private schools are sometimes referred to as institutes; also, in Spain, secondary schools are referred to as institutes. Historically, in some countries, institutes were educational units imparting vocational training and often incorporating libraries, also known as mechanics' institutes. The word "institute" comes from the Latin word ''institutum'' ("facility" or "habit"), in turn derived from ''instituere'' ("build", "create", "raise" or "educat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamond
Diamond is a Allotropes of carbon, solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Diamond is tasteless, odourless, strong, brittle solid, colourless in pure form, a poor conductor of electricity, and insoluble in water. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the Chemical stability, chemically stable form of carbon at Standard temperature and pressure, room temperature and pressure, but diamond is metastable and converts to it at a negligible rate under those conditions. Diamond has the highest Scratch hardness, hardness and thermal conductivity of any natural material, properties that are used in major industrial applications such as cutting and polishing tools. Because the arrangement of atoms in diamond is extremely rigid, few types of impurity can contaminate it (two exceptions are boron and nitrogen). Small numbers of lattice defect, defects or impurities (about one per million of lattice atoms) can color ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter The Great St
Peter may refer to: People * List of people named Peter, a list of people and fictional characters with the given name * Peter (given name) ** Saint Peter (died 60s), apostle of Jesus, leader of the early Christian Church * Peter (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name) Culture * Peter (actor) (born 1952), stage name Shinnosuke Ikehata, a Japanese dancer and actor * ''Peter'' (1934 film), a film directed by Henry Koster * ''Peter'' (2021 film), a Marathi language film * "Peter" (''Fringe'' episode), an episode of the television series ''Fringe'' * ''Peter'' (novel), a 1908 book by Francis Hopkinson Smith * "Peter" (short story), an 1892 short story by Willa Cather * ''Peter'' (album), a 1972 album by Peter Yarrow * ''Peter'', a 1993 EP by Canadian band Eric's Trip * "Peter", 2024 song by Taylor Swift from '' The Tortured Poets Department: The Anthology'' Animals * Peter (Lord's cat), cat at Lord's Cricket Ground in London * Peter (chief mouser), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Habilitation
Habilitation is the highest university degree, or the procedure by which it is achieved, in Germany, France, Italy, Poland and some other European and non-English-speaking countries. The candidate fulfills a university's set criteria of excellence in research, teaching, and further education, which usually includes a dissertation. The degree, sometimes abbreviated ''Dr. habil''. (), ''dr hab.'' (), or ''D.Sc.'' ('' Doctor of Sciences'' in Russia and some CIS countries), is often a qualification for full professorship in those countries. In German-speaking countries it allows the degree holder to bear the title ''PD'' (for ). In a number of countries there exists an academic post of docent, appointment to which often requires such a qualification. The degree conferral is usually accompanied by a public oral defence event (a lecture or a colloquium) with one or more opponents. Habilitation is usually awarded 5–15 years after a PhD degree or its equivalent. Achieving this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity between that of a conductor and an insulator. Its conductivity can be modified by adding impurities (" doping") to its crystal structure. When two regions with different doping levels are present in the same crystal, they form a semiconductor junction. The behavior of charge carriers, which include electrons, ions, and electron holes, at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors, and most modern electronics. Some examples of semiconductors are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and elements near the so-called " metalloid staircase" on the periodic table. After silicon, gallium arsenide is the second-most common semiconductor and is used in laser diodes, solar cells, microwave-frequency integrated circuits, and others. Silicon is a critical element for fabricating most electronic circuits. Semiconductor devices can display a range of different useful properties, such as passing current more easil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid Solution
A solid solution, a term popularly used for metals, is a homogeneous mixture of two compounds in solid state and having a single crystal structure. Many examples can be found in metallurgy, geology, and solid-state chemistry. The word "solution" is used to describe the intimate mixing of components at the atomic level and distinguishes these homogeneous materials from physical mixtures of components. Two terms are mainly associated with solid solutions – ''solvents'' and ''solutes,'' depending on the relative abundance of the atomic species. In general if two compounds are isostructural then a solid solution will exist between the end members (also known as parents). For example sodium chloride and potassium chloride have the same cubic crystal structure so it is possible to make a pure compound with any ratio of sodium to potassium (Na1-xKx)Cl by dissolving that ratio of NaCl and KCl in water and then evaporating the solution. A member of this family is sold under the bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |