|
Sepioteuthis
''Sepioteuthis'', commonly known as reef squids or oval squids, is a genus of pencil squid. Reef squids are easily recognizable by their large rounded fins that extend along almost the entire length of their mantle (mollusc), mantles, giving them a superficial resemblance to cuttlefish. Species Three species are currently recognized, though ''S. australis'' and ''S. lessoniana'' are believed to be cryptic species complexes. :*''Sepioteuthis australis'', southern reef squid or southern calamary :*''Sepioteuthis lessoniana'', bigfin reef squid or northern calamary :*''Sepioteuthis sepioidea'', Caribbean reef squid An additional species, ''Sepioteuthis loliginiformis, S. loliginiformis'', was described in 1828, but its validity is questionable. However, if the species turns out to be the same as ''S. australis'' or ''S. lessoniana'', ''S. loliginiformis'' would be the senior synonym and replace the younger name currently in use. References External links Tree of Life web project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sepioteuthis Lessoniana
''Sepioteuthis lessoniana'', commonly known as the bigfin reef squid, tiger squid, glitter squid, oval squid, or northern calamari, is a species of Loliginidae, loliginid squid. It is one of the three currently recognized species belonging to the genus ''Sepioteuthis''. Studies in 1993, however, have indicated that bigfin reef squids may comprise a cryptic species complex. The species is likely to include several very similar and closely related species. Bigfin reef squids are characterised by a large oval fin that extends throughout the margins of its Mantle (mollusc), mantle, giving them a superficial similarity to cuttlefish. They are small to medium-sized squids, averaging in length. They exhibit elaborate mating displays and usually spawn (biology), spawn in May, but it can vary by location. The paralarvae resemble miniature adults and are remarkable for already having the capability to change body colouration upon hatching. Bigfin reef squids have the fastest recorded gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sepioteuthis Sepioidea
The Caribbean reef squid (''Sepioteuthis sepioidea''), commonly called the reef squid, is a species of small, torpedo-shaped squid with undulating fins that extend nearly the entire length of the body, approximately 20 cm (8 in) in length. They are most commonly found in the Caribbean Sea in small schools. As part of the Cephalopod class of Molluscs, these organisms exhibit specific characteristics to help them in their environment, such as tentacles for movement and feeding and color pigments that reflect their behavioral conditions. History and phylogeny The reef squid is included in the monophyletic family ''Loliginidae,'' which houses a discovered twenty-six species. The origin of the family is the geographical Cretaceous period within the Indo-Pacific sea region. In 2001, marine biologist Silvia Maciá discovered that squid were able to propel themselves up out of the water about 2 m (6.6 ft) and fly approximately 10 m (33 ft) before re-entry; a discovery which led to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
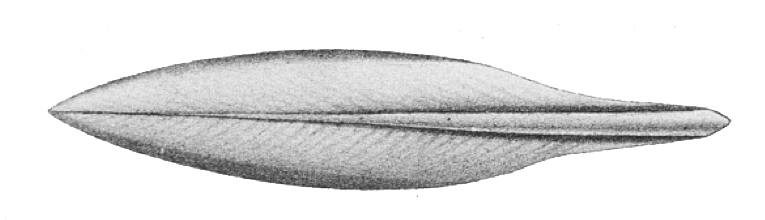
Sepioteuthis Loliginiformis
''Sepioteuthis'', commonly known as reef squids or oval squids, is a genus of pencil squid. Reef squids are easily recognizable by their large rounded fins that extend along almost the entire length of their mantle (mollusc), mantles, giving them a superficial resemblance to cuttlefish. Species Three species are currently recognized, though ''S. australis'' and ''S. lessoniana'' are believed to be cryptic species complexes. :*''Sepioteuthis australis'', southern reef squid or southern calamary :*''Sepioteuthis lessoniana'', bigfin reef squid or northern calamary :*''Sepioteuthis sepioidea'', Caribbean reef squid An additional species, ''Sepioteuthis loliginiformis, S. loliginiformis'', was described in 1828, but its validity is questionable. However, if the species turns out to be the same as ''S. australis'' or ''S. lessoniana'', ''S. loliginiformis'' would be the senior synonym and replace the younger name currently in use. References External links Tree of Life web project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sepioteuthis Australis
''Sepioteuthis australis'', commonly known as the southern calamari or the southern reef squid, is a species of reef squid that is native to oceans off the coast of Australia and New Zealand. This species is caught commercially by trawling, as bycatch in the prawn fishing industry and by recreational anglers. Description The maximum length of this squid is about , with a maximum weight of around . The mantle is robust and tapers bluntly to a point. The eight arms have three rings of suckers with up to thirty hooks, and the two tentacles have long clubs with moderate-sized suckers and further hooks around the suckers. The diamond-shaped fins, which extend for almost the whole length of the mantle are widest in the middle, and are more than half as wide as they are long. The colour of this squid in life is semi-transparent, but if caught and removed from the sea, it will soon change to a uniform orangish-brown or rust colour. The base of the fin has a white or bluish luminescent str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pencil Squid
Loliginidae, commonly known as pencil squids, is an aquatic Family (biology), family of squid classified in the order Myopsida. Taxonomy The family Loliginidae was formerly classified in the order Teuthida. Taxonomic list The classification below (including 47 species) follows Vecchione ''et al.'' (2005) and the Tree of Life Web Project (2010).Vecchione, M. & R.E. Young. (2010)Loliginidae Lesueur, 1821 The Tree of Life Web Project. Several doubtfully distinct species have also been described; see the genus articles for these. *Genus ''Afrololigo'' **''Afrololigo mercatoris'', Guinean thumbstall squid *Genus ''Alloteuthis'' **''Alloteuthis africana'', African squid **''Alloteuthis media'', midsize squid **''Alloteuthis subulata'', European common squid *Genus ''Doryteuthis'' **Subgenus ''Amerigo'' ***''Doryteuthis gahi'', Patagonian squid ***''Doryteuthis ocula'', bigeye inshore squid ***''Doryteuthis opalescens'', opalescent inshore squid ***''Doryteuthis pealeii'', longfi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuttlefish
Cuttlefish, or cuttles, are Marine (ocean), marine Mollusca, molluscs of the order (biology), suborder Sepiina. They belong to the class (biology), class Cephalopoda which also includes squid, octopuses, and nautiluses. Cuttlefish have a unique internal mollusc shell, shell, the cuttlebone, which is used for control of buoyancy. Cuttlefish have large, W-shaped pupils, eight Cephalopod arm, arms, and two tentacles furnished with :wikt:denticulate, denticulated suckers, with which they secure their prey. They generally range in size from , with Cephalopod size, the largest species, the giant cuttlefish (''Sepia apama''), reaching in mantle (mollusc), mantle length and over in mass. Cuttlefish eat small molluscs, crabs, shrimp, fish, octopuses, worms, and other cuttlefish. Their predators include dolphins, larger fish (including sharks), seals, seabirds, and other cuttlefish. The typical life expectancy of a cuttlefish is about 1–2 years. Studies are said to indicate cuttlefis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henri Marie Ducrotay De Blainville
Henri Marie Ducrotay de Blainville (; 12 September 1777 – 1 May 1850) was a French zoologist and anatomist. Life Blainville was born at Arques-la-Bataille, Arques, near Dieppe, Seine-Maritime, Dieppe. As a young man, he went to Paris to study art, but ultimately devoted himself to natural history. He attracted the attention of Georges Cuvier, for whom he occasionally substituted as lecturer at the Collège de France and at the Athenaeum Club, London. In 1812, he was aided by Cuvier in acquiring the position of assistant professor of anatomy and zoology in the Faculty of Sciences at Paris. Eventually, relations between the two men soured, a situation that ended in open enmity. In 1819, Blainville was elected a member of the American Philosophical Society in Philadelphia. In 1825, he was admitted a member of the French Academy of Sciences; and in 1830, he was appointed to succeed Jean-Baptiste Lamarck in the chair of natural history at the museum. Two years later, on the death of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species
A species () is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. It is the basic unit of Taxonomy (biology), classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology (biology), morphology, behaviour, or ecological niche. In addition, palaeontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. About 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a binomial nomenclature, two-part name, a "binomen". The first part of a binomen is the name of a genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name (zoology), specific name or the specific ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus (; : genera ) is a taxonomic rank above species and below family (taxonomy), family as used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. Phylogeneti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantle (mollusc)
The mantle (also known by the Latin language, Latin word pallium meaning mantle, robe or cloak, adjective pallial) is a significant part of the anatomy of molluscs: it is the dorsum (biology), dorsal body wall which covers the visceral mass and usually protrudes in the form of flaps well beyond the visceral mass itself. In many species of molluscs the Epidermis (skin), epidermis of the mantle secretes calcium carbonate and conchiolin, and creates a mollusc shell, shell. In sea slugs there is a progressive loss of the shell and the mantle becomes the dorsal surface of the animal. The words mantle and pallium both originally meant ‘cloak’ or ‘cape’; see mantle (vesture). This anatomical structure in molluscs often resembles a cloak because in many groups the edges of the mantle, usually referred to as the ''mantle margin'', extend far beyond the main part of the body, forming flaps, double-layered structures which have been adapted for many different uses, including for e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptic Species Complex
In biology, a species complex is a group of closely related organisms that are so similar in appearance and other features that the boundaries between them are often unclear. The taxa in the complex may be able to hybridize readily with each other, further blurring any distinctions. Terms that are sometimes used synonymously but have more precise meanings are cryptic species for two or more species hidden under one species name, sibling species for two (or more) species that are each other's closest relative, and species flock for a group of closely related species that live in the same habitat. As informal taxonomic ranks, species group, species aggregate, macrospecies, and superspecies are also in use. Two or more taxa that were once considered conspecific (of the same species) may later be subdivided into infraspecific taxa (taxa within a species, such as plant varieties), which may be a complex ranking but it is not a species complex. In most cases, a species complex is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senior Synonym
In taxonomy, the scientific classification of living organisms, a synonym is an alternative scientific name for the accepted scientific name of a taxon. The botanical and zoological codes of nomenclature treat the concept of synonymy differently. * In botanical nomenclature, a synonym is a scientific name that applies to a taxon that now goes by a different scientific name. For example, Linnaeus was the first to give a scientific name (under the currently used system of scientific nomenclature) to the Norway spruce, which he called '' Pinus abies''. This name is no longer in use, so it is now a synonym of the current scientific name, ''Picea abies''. * In zoology, moving a species from one genus to another results in a different binomen, but the name is considered an alternative combination rather than a synonym. The concept of synonymy in zoology is reserved for two names at the same rank that refers to a taxon at that rank – for example, the name ''Papilio prorsa'' Linnaeus, 17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |