|
Semi-autobiographical
An autobiography, sometimes informally called an autobio, is a self-written account of one's own life, providing a personal narrative that reflects on the author's experiences, memories, and insights. This genre allows individuals to share their unique perspectives and stories, offering readers a glimpse into the author's personal journey and the historical or cultural context in which they lived. The term "autobiography" was first used in 1797, but the practice of writing about one's life dates back to antiquity. Early examples include Saint Augustine's '' Confessions'' (), which is considered one of the first Western autobiographies. Unlike biographies, which are written by someone else, autobiographies are based on the author's memory and personal interpretation of events, making them inherently subjective. This subjectivity can sometimes lead to inaccuracies or embellishments, as the author may recall events differently or choose to present them in a certain light. Autobiog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Taylor (scholar)
William Taylor (7 November 1765 – 5 March 1836), often called William Taylor of Norwich, was a British essayist, scholar and polyglot. He is most notable as a supporter and translator of German romantic literature. Early life He was born in Norwich, Norfolk, England on 7 November 1765, the only child of William Taylor (died 1819), a wealthy Norwich merchant with European trade connections, by his wife Sarah (died 1811), second daughter of John Wright of Diss, Norfolk. William Taylor was taught Latin, French and Dutch by John Bruckner, pastor of the French and Dutch Protestant churches in Norwich, in preparation for continuing his father's continental trading in textiles. In 1774 he was transferred to Palgrave Academy, Suffolk, by Rochemont Barbauld, whose wife Anna Letitia Barbauld Taylor regarded as a strong influence. For three years his school companion was Frank Sayers, who was to be a lifelong friend. In August 1779 his father took him from school. During the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memoir
A memoir (; , ) is any nonfiction narrative writing based on the author's personal memories. The assertions made in the work are thus understood to be factual. While memoir has historically been defined as a subcategory of biography or autobiography since the late 20th century, the genre is differentiated in form, presenting a narrowed focus, usually a particular time phase in someone's life or career. A biography or autobiography tells the story "of a life", while a memoir often tells the story of a particular career, event, or time, such as touchstone moments and turning points in the author's life. The author of a memoir may be referred to as a memoirist or a memorialist. Early memoirs Memoirs have been written since the ancient times, as shown by Julius Caesar's '' Commentarii de Bello Gallico'', also known as ''Commentaries on the Gallic Wars''. In the work, Caesar describes the battles that took place during the nine years that he spent fighting local armies in the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Senate
The Roman Senate () was the highest and constituting assembly of ancient Rome and its aristocracy. With different powers throughout its existence it lasted from the first days of the city of Rome (traditionally founded in 753 BC) as the Senate of the Roman Kingdom, to the Senate of the Roman Republic and Senate of the Roman Empire and eventually the Byzantine Senate of the Eastern Roman Empire, existing well into the post-classical era and Middle Ages. During the days of the Roman Kingdom, the Senate was generally little more than an advisory council to the king. However, as Rome was an electoral monarchy, the Senate also elected new Roman kings. The last king of Rome, Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, was overthrown following a coup d'état led by Lucius Junius Brutus, who founded the Roman Republic. During the early Republic, the Senate was politically weak, while the various executive Roman magistrates who appointed the senators for life (or until expulsion by Roma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
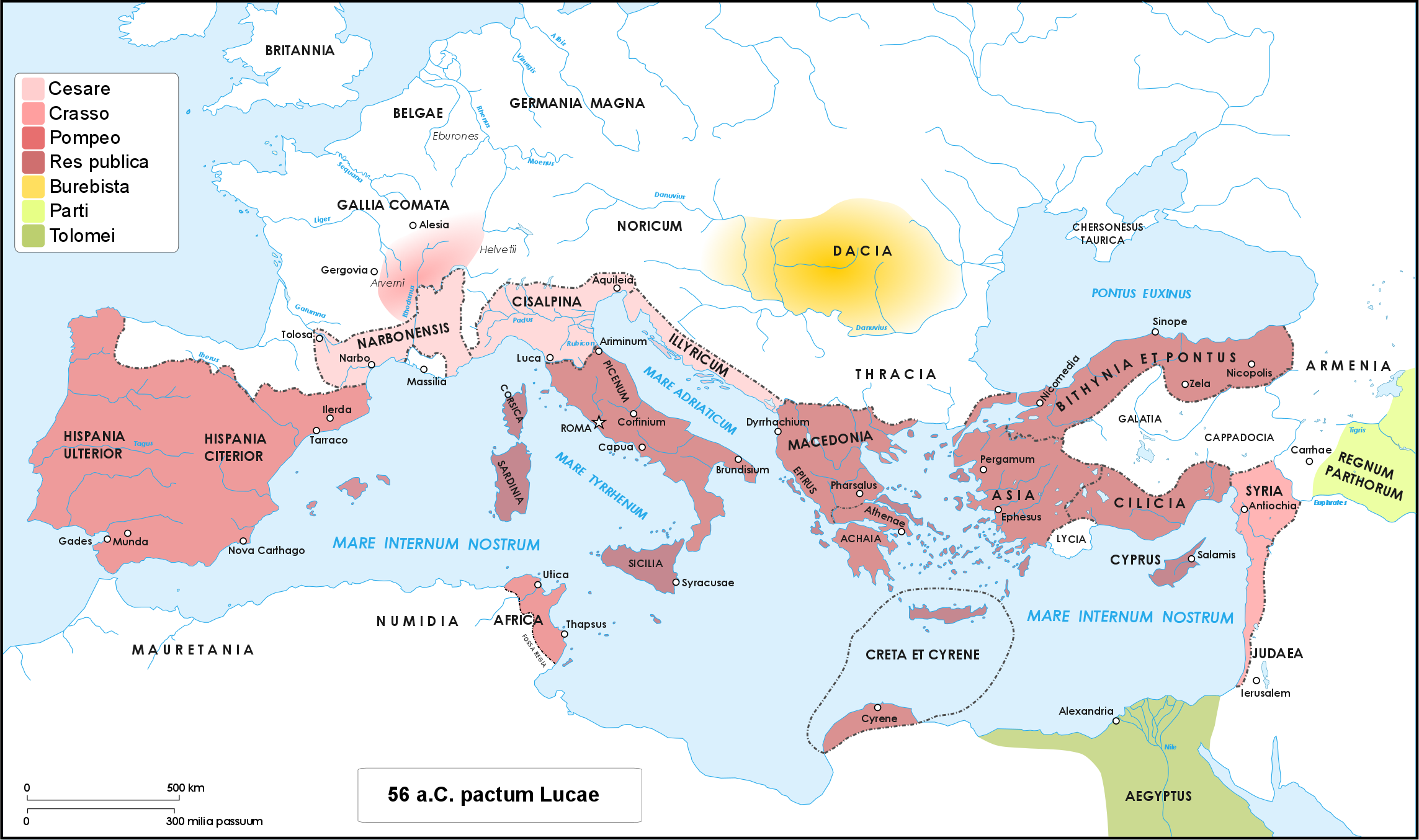
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC – 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey ( ) or Pompey the Great, was a Roman people, Roman general and statesman who was prominent in the last decades of the Roman Republic. As a young man, he was a partisan and protégé of the dictator Sulla, after whose death he achieved much military and political success himself. He was an ally and a rival of Julius Caesar, and died in Caesar's civil war, civil war with him. A member of the senatorial nobility, Pompey entered into a military career while still young. He rose to prominence serving Sulla as a commander in Sulla's civil war, the civil war of 83–81 BC. Pompey's success as a general while young enabled him to advance directly to his first Roman consul, consulship without following the traditional ''cursus honorum'' (the required steps to advance in a political career). He was elected as consul on three occasions (70, 55, 52 BC). He celebrated th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesar's Civil War
Caesar's civil war (49–45 BC) was a civil war during the late Roman Republic between two factions led by Julius Caesar and Pompey. The main cause of the war was political tensions relating to Caesar's place in the Republic on his expected return to Rome on the expiration of his Lex Vatinia, governorship in Roman Gaul, Gaul. Before the war, Caesar had led an Gallic Wars, invasion of Gaul for almost ten years. A build-up of tensions starting in late 50 BC, with both Caesar and Pompey refusing to back down, led to the outbreak of civil war. Pompey and his allies induced the Roman Senate, Senate to demand Caesar give up his provinces and armies in the opening days of 49 BC. Caesar refused and instead Crossing the Rubicon, marched on Rome. The war was fought in Italy, Illyria, Greece in the Roman era, Greece, Ptolemaic Egypt, Egypt, Africa (Roman province), Africa, and Hispania. The decisive events occurred in Greece in 48 BC: Pompey defeated Caesar at the Battle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commentarii De Bello Civili
'' Commentarii de Bello Civili'' (''Commentaries on the Civil War''), or ''Bellum Civile'', is an account written by Julius Caesar of his war against Gnaeus Pompeius and the Roman Senate. It consists of three books covering the events of 49–48 BC, from shortly before Caesar's invasion of Italy to Pompey's defeat at the Battle of Pharsalus and flight to Egypt. It was preceded by the much longer account of Caesar's campaigns in Gaul and was followed by similar works covering the ensuing wars against the remnants of Pompey's armies in Egypt, North Africa, and Spain. Caesar's authorship of the ''Commentarii de Bello Civili'' is not disputed, while the three later works are believed to have been written by contemporaries of Caesar. Title The Latin title ''Commentarii de Bello Civili'' is often retained as the title of the book in English translations of the work. The title itself is Latin for "Commentaries on the Civil War". It is sometimes shortened to just "Civil Wars", "Abou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
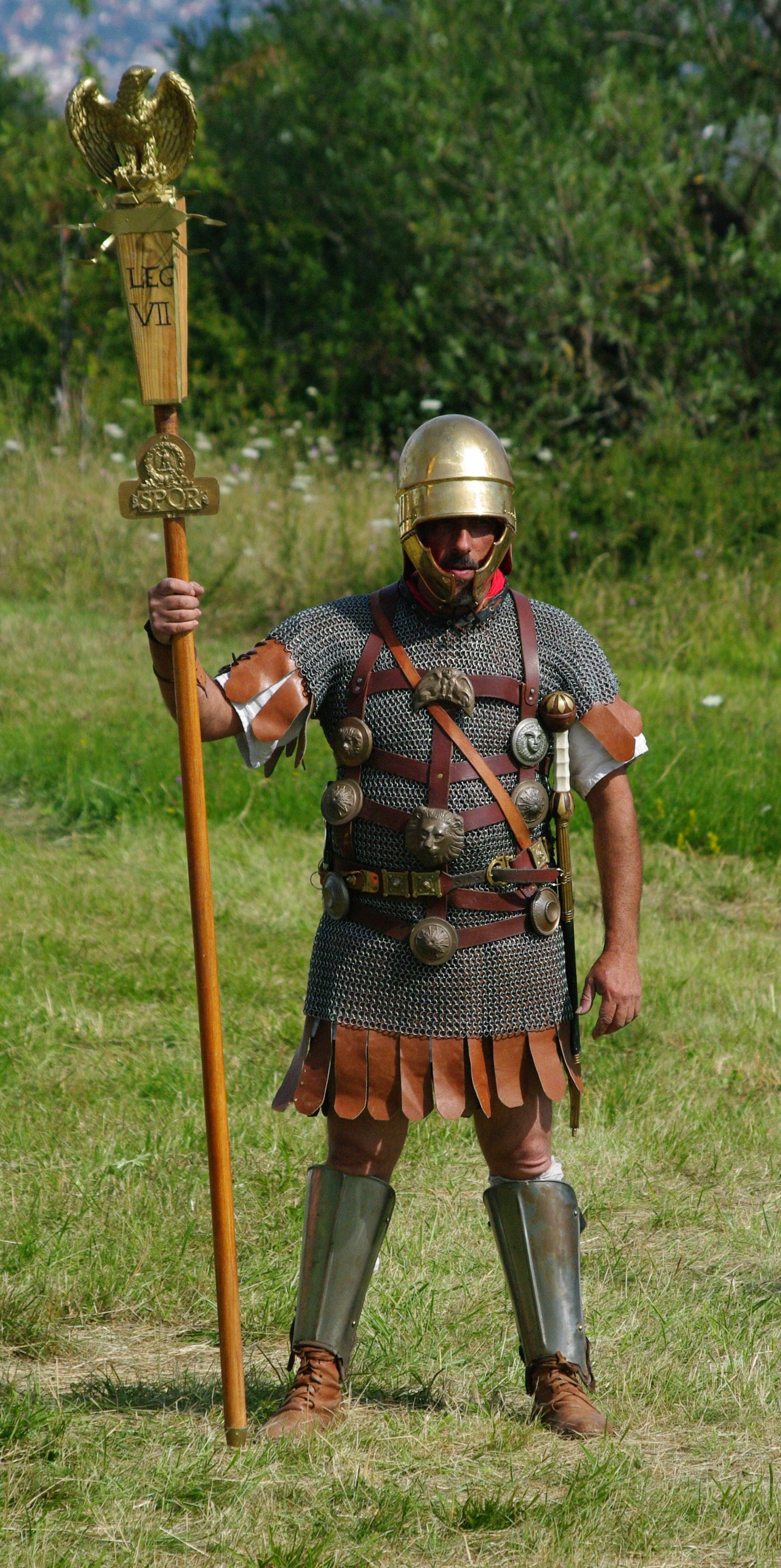
Gallic Wars
The Gallic Wars were waged between 58 and 50 BC by the Roman general Julius Caesar against the peoples of Gaul (present-day France, Belgium, and Switzerland). Gauls, Gallic, Germanic peoples, Germanic, and Celtic Britons, Brittonic tribes fought to defend their homelands against an aggressive Roman Military campaign, campaign. The Wars culminated in the decisive Battle of Alesia in 52 BC, in which a complete Roman victory resulted in the expansion of the Roman Republic over the whole of Gaul. Though the collective Gallic armies were as strong as the Roman forces, the Gallic tribes' internal divisions eased victory for Caesar. Gallic chieftain Vercingetorix's attempt to unite the Gauls under a single banner came too late. Caesar portrayed the invasion as being a preemptive and defensive action, but historians agree that he fought the wars primarily to boost his political career and to pay off his debts. Still, Gaul was of significant military importance to the Romans. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commentarii De Bello Gallico
''Commentarii de Bello Gallico'' (; ), also ''Bellum Gallicum'' (), is Julius Caesar's first-hand account of the Gallic Wars, written as a third-person narrative. In it, Caesar describes the battles and intrigues that took place in the nine years he spent fighting the Celtic and Germanic peoples in Gaul who opposed Roman conquest. The "Gaul" to which Caesar refers is ambiguous, as the term had various connotations in Roman writing and discourse during Caesar's time. Generally, Gaul included all of the regions primarily inhabited by Celts, aside from the province of Gallia Narbonensis (modern-day Provence and Languedoc-Roussillon), which had already been conquered in Caesar's time, therefore encompassing the rest of modern France, Belgium, Western Germany, and parts of Switzerland. As the Roman Republic made inroads deeper into Celtic territory and conquered more land, the definition of "Gaul" shifted. Concurrently, "Gaul" was also used in common parlance as a synonym for "unc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caesar's civil war, a civil war. He subsequently became Roman dictator, dictator from 49 BC until Assassination of Julius Caesar, his assassination in 44 BC. Caesar played a critical role in Crisis of the Roman Republic, the events that led to the demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire. In 60 BC, Caesar, Marcus Licinius Crassus, Crassus, and Pompey formed the First Triumvirate, an informal political alliance that dominated Roman politics for several years. Their attempts to amass political power were opposed by many in the Roman Senate, Senate, among them Cato the Younger with the private support of Cicero. Caesar rose to become one of the most powerful politicians in the Roman Republic through a string of military victories in the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Ghazali
Al-Ghazali ( – 19 December 1111), archaically Latinized as Algazelus, was a Shafi'i Sunni Muslim scholar and polymath. He is known as one of the most prominent and influential jurisconsults, legal theoreticians, muftis, philosophers, theologians, logicians and mystics in Islamic history. He is considered to be the 11th century's '' mujaddid'',William Montgomery Watt, ''Al-Ghazali: The Muslim Intellectual'', p. 180. Edinburgh University Press, 1963. a renewer of the faith, who, according to the prophetic hadith, appears once every 100 years to restore the faith of the Islamic community.Dhahabi, Siyar, 4.566 Al-Ghazali's works were so highly acclaimed by his contemporaries that he was awarded the honorific title "Proof of Islam" ('' Ḥujjat al-Islām''). Al-Ghazali was a prominent mujtahid in the Shafi'i school of law. Much of Al-Ghazali's work stemmed around his spiritual crises following his appointment as the head of the Nizamiyya University in Baghdad - which was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Elk Speaks
''Black Elk Speaks'' is a 1932 book by John G. Neihardt, an American poet and writer, who relates the story of Black Elk, an Oglala Lakota medicine man. Black Elk spoke in Lakota and Black Elk's son, Ben Black Elk, who was present during the talks, translated his father's words into English. Neihardt made notes during these talks which he later used as the basis for his book. The prominent psychologist Carl Jung read the book in the 1930s and urged its translation into German; in 1955, it was published as ''Ich rufe mein Volk'' (''I Call My People''). Reprinted in the US in 1961, with a 1988 edition named ''Black Elk Speaks: Being the Life Story of a Holy Man of the Oglala Sioux, as told through John G. Neihardt (Flaming Rainbow)'' and a State University of New York Press 2008 Premier Edition annotated by Lakota scholar Raymond DeMallie, the book has found an international audience. However, the book has come under fire for what critics describe as inaccurate representa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |