|
Semi-Arianism
Semi-Arianism was a position regarding the relationship between God the Father and the Son of God, adopted by some 4th-century Christians. Though the doctrine modified the teachings of Arianism, it still rejected the doctrine that Father, Son, and Holy Spirit are co-eternal, and of the same substance, or consubstantial, and was therefore considered to be heretical by many contemporary Christians."semi-Arianism." Encyclopædia Britannica. Encyclopædia Britannica Ultimate Reference Suite. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica, 2012. Arius held that the Father, Son, and Holy Spirit were three separate essences or substances (ousia) and that the Son and Spirit derived their divinity from the Father, were created, and were inferior to the Godhead of the Father. Semi-Arians asserted that the Son was "of a similar substance" (homoiousios) as the Father but not "of the same substance" (homoousios). History Arianism was the view of Arius and his followers, the Arians, that Jesus was su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arianism
Arianism (, ) is a Christology, Christological doctrine which rejects the traditional notion of the Trinity and considers Jesus to be a creation of God, and therefore distinct from God. It is named after its major proponent, Arius (). It is considered Heresy in Christianity, heretical by most modern mainstream branches of Christianity. It is held by a minority of modern denominations, although some of these denominations hold related doctrines such as Socinianism, and some shy away from use of the term Arian due to the term's historically negative connotations. Modern denominations sometimes connected to the teaching include Jehovah's Witnesses, some individual churches within the Churches of Christ (including the movement's founder Barton W. Stone), as well as some Hebrew Roots Christians and Messianic Judaism, Messianic Jews (although many Messianic Jews also follow Nicene Christianity). It is first attributed to Arius (), a Christian presbyter who preached and studied in Ale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valens Of Mursa
Valens of Mursa was bishop of Mursa (Osijek in modern Croatia) and a supporter of Homoian theology, which is often labelled as a form of Arianism, although semi-Arianism is probably more accurate. Life Valens and his fellows were seen by contemporaneous and later Church historical sources, to vacillate according to the political winds, being 'always inclined to side with the dominant party. Synod of Tyre He was one of a group of Bishops including Ursacius of Singidunum (Belgrade) who made accusations of impropriety against Athanasius of Alexandria resulting in the First Synod of Tyre. Ursacius and Valens next appear in 342 at Constantinople assisting with the consecration of Macedonius as bishop of the metropolis. In 346, Valens and Ursacius, recanted both of their previous hostility to Athanasius and to his Trinitarian theology. Accordingly, they journeyed to Rome, presenting a written recantation to its bishop, Julius, and wrote to Athanasius, expressing their willingnes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arians
Arianism (, ) is a Christological doctrine which rejects the traditional notion of the Trinity and considers Jesus to be a creation of God, and therefore distinct from God. It is named after its major proponent, Arius (). It is considered heretical by most modern mainstream branches of Christianity. It is held by a minority of modern denominations, although some of these denominations hold related doctrines such as Socinianism, and some shy away from use of the term Arian due to the term's historically negative connotations. Modern denominations sometimes connected to the teaching include Jehovah's Witnesses, some individual churches within the Churches of Christ (including the movement's founder Barton W. Stone), as well as some Hebrew Roots Christians and Messianic Jews (although many Messianic Jews also follow Nicene Christianity). It is first attributed to Arius (), a Christian presbyter who preached and studied in Alexandria, Egypt, although it developed out of v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
God The Father
God the Father is a title given to God in Christianity. In mainstream trinitarian Christianity, God the Father is regarded as the first Person of the Trinity, followed by the second person, Jesus Christ the Son, and the third person, God the Holy Spirit. Since the second century, Christian creeds included affirmation of belief in "God the Father ( Almighty)", primarily in his capacity as "Father and creator of the universe". Christians take the concept of God as the father of Jesus Christ metaphysically further than the concept of God as the creator and father of all people, as indicated in the Apostles' Creed where the expression of belief in the "Father almighty, creator of heaven and earth" is immediately, but separately followed by in "Jesus Christ, his only Son, our Lord", thus expressing both senses of fatherhood. Christianity Overview In much of modern Christianity, God is addressed as the Father, in part because of his active interest in human affairs on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homoean
The Acacians (), or perhaps better described as the Homoians (from gr. hómoios) or Homoeans (), were a non-Nicene branch of Christianity that dominated the church during much of the fourth-century Arian Controversy. They declared that the Son was similar to God the Father, without reference to substance (essence). Homoians played a major role in the Christianization of the Goths in the Danubian provinces of the Roman Empire. "Though Homoian Arianism derived from the thought both of Eusebius of Caesarea and of Arius, we cannot with confidence detect it before the year 357, when it appears in the Second Sirmian Creed." Supporters Homoian theology “was a development of the theology of Eusebius of Caesarea.” * “Homoian Arianism derived from the thought both of Eusebius of Caesarea and of Arius.” * "Akakius of Caesarea is usually regarded as the leader of the Homoian Arians ''par excellence.'' He succeeded Eusebius as bishop of that see in 339 or 340 and remained there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
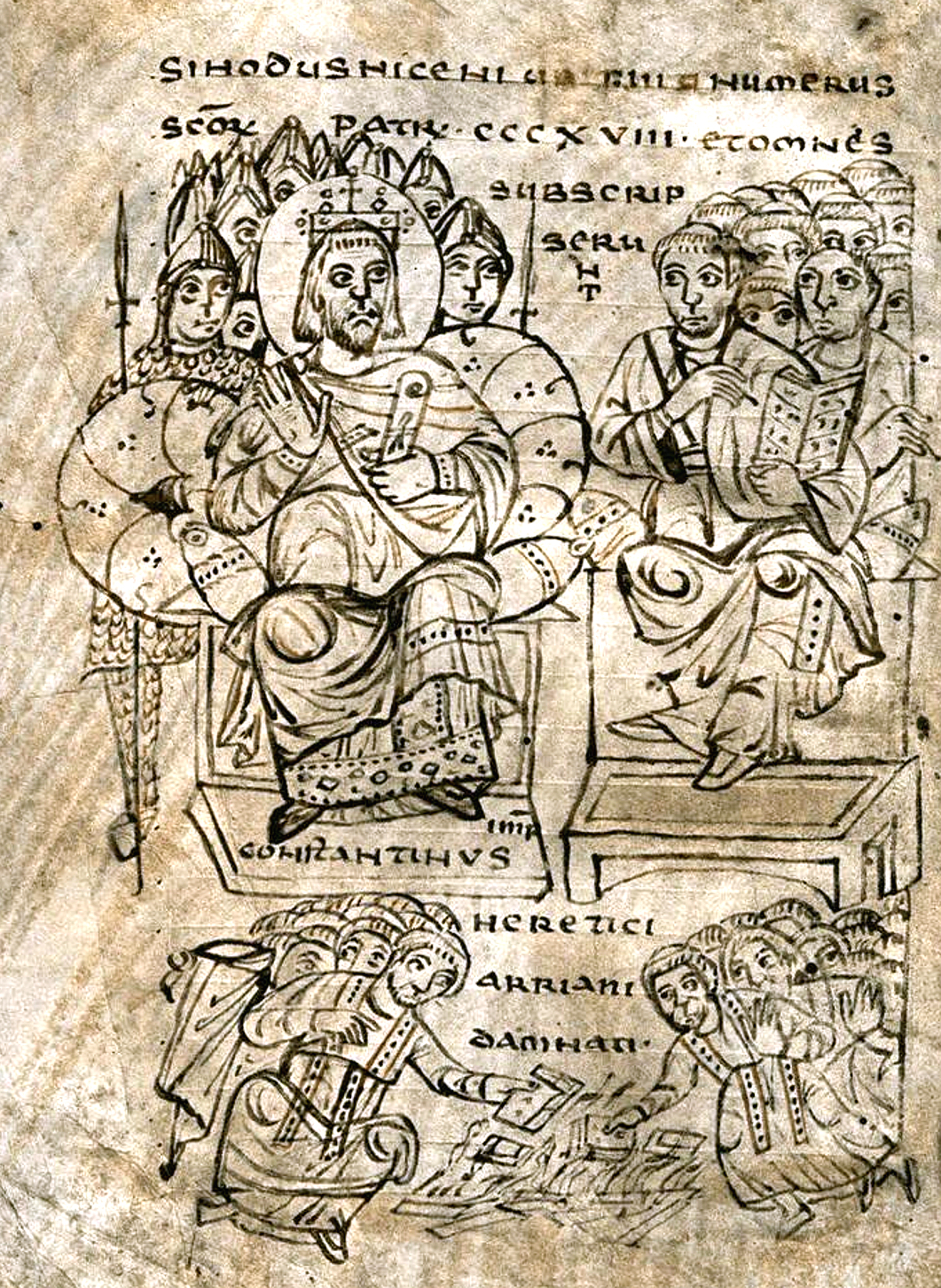
Constantius II
Constantius II (; ; 7 August 317 – 3 November 361) was Roman emperor from 337 to 361. His reign saw constant warfare on the borders against the Sasanian Empire and Germanic peoples, while internally the Roman Empire went through repeated civil wars, court intrigues, and usurpations. His religious policies inflamed domestic conflicts that would continue after his death. Constantius was a son of Constantine the Great, who elevated him to the imperial rank of '' Caesar'' on 8 November 324 and after whose death Constantius became ''Augustus'' together with his brothers, Constantine II and Constans on 9 September 337. He promptly oversaw the massacre of his father-in-law, an uncle, and several cousins, consolidating his hold on power. The brothers divided the empire among themselves, with Constantius receiving Greece, Thrace, the Asian provinces, and Egypt in the east. For the following decade a costly and inconclusive war against Persia took most of Constantius's time and at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germinius Of Sirmium
Germinius, born in Cyzicus, was bishop of Sirmium, (today the town Sremska Mitrovica, in the territory of Srem in Serbia) and a supporter of Homoian theology, which is often labelled as a form of Arianism. Background Along with Valens of Mursa and Ursacius of Singidunum he was responsible for drafting the theological statement known as the Blasphemy of Sirmium in 357. He also appears in the ''Altercatio Heracliani laici cum Germinio episcopo Sirmiensi'', which purports to be the minutes of a public disputation between Germinius and a Nicene layman called Heraclianus in January 366.This document mention one more heresiarch among the bishops of Sirmium (metropolitan bishops of Pannonia Secunda), Photinus Photinus (Greek: Φωτεινός; died 376) was a Christian bishop of Sirmium in Pannonia Secunda (today the town Sremska Mitrovica in Serbia), best known for denying the incarnation of Christ, thus being considered a heresiarch by both the Ca .... For Photinus of Sirmium and h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ursacius Of Singidunum
Ursacius ( 335–346) was the bishop of Singidunum (the ancient city which was to become Belgrade), during the middle of the 4th century. He played an important role during the evolving controversies surrounding the legacies of the Council of Nicaea and the theologian Arius, acting frequently in concert with his fellow bishops of the Diocese of Pannonia (or "Illyria"), Germinius of Sirmium and Valens of Mursa. Found at various times during their episcopal careers staking positions on both sides of the developing theological debate and internal Church politicking, Ursacius and his fellows were seen to vacillate according to the political winds. __TOC__ Early life Born at the latest 300, little is known of Ursacius' early career, but he appears already to have become bishop of Singidunum by 335, in which capacity he formed part of the group of bishops empanelled at the Synod of Tyre to investigate the veracity of accusations of impropriety made against Athanasius of Alexandria. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eusebius Of Nicomedia
Eusebius of Nicomedia (; ; died 341) was an Arian priest who baptised Constantine the Great on his deathbed in 337. A fifth-century legend evolved that Pope Sylvester I was the one to baptise Constantine, but this is dismissed by scholars as a forgery "to amend the historical memory of the Arian baptism that the emperor received at the end of his life, and instead to attribute an unequivocally orthodox baptism to him". He was a bishop of Berytus (modern-day Beirut) in Phoenicia. He was later made the bishop of Nicomedia, where the Imperial court resided. He lived finally in Constantinople from 338 up to his death. Influence in the Imperial family and the Imperial court Distantly related to the imperial family of Constantine the Great, he owed his progression from a less significant Levantine bishopric to the most important episcopal see to his influence at court and the great power he wielded in the church was derived from that source. In fact, during his time in the imper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eustathius Of Sebaste
Eustathius of Sebaste (. after 377) was bishop of Sebastia in Armenia (modern Sivas, Turkey) during the fourth century. He is known for his asceticism, his early opposition to slavery, and his friendship with Basil of Caesarea. Eustathius was son of the Arian bishop Eulalius of Sebaste and was born sometime around 300 AD. He was originally a monk, and is said to have been the first who acquainted the Armenians with an ascetic life. For this reason some persons ascribed to him the work on Ascetics, which is usually regarded as the production of Saint Basil of Caesarea. Basil was a close friend and student of Eustathius, looking up to him from a young age; Eustathius greatly influenced Basil, including inspiring him to pursue the monastic life instead of studying in Athens. Eustathius was one of the few patristic authors to endorse the complete abolition of slavery, and possibly the first person to reject slavery entirely. Eustathius was the teacher of Macrina, Basil, Naucratiu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Of Laodicea
George (Greek: Γεώργιος; died 359) was the bishop of Laodicea in Syria from 335 until his deposition in 347. He took part in the Trinitarian controversies of the fourth century. At first an ardent admirer of the teaching of Arius and associated with Eusebius of Nicomedia, he subsequently became a semi-Arian, but seems ultimately to have united with the Anomoeans, whose uncompromising opponent he had once been, and to have died professing their tenets. George was a native of Alexandria in Roman Egypt. In early life he devoted himself with considerable distinction to the study of philosophy.Philost. ''H. E.'' viii. 17. He was ordained a presbyter by Bishop Alexander I of Alexandria. Having gone to Antioch, he endeavoured to mediate between Arius and the orthodox catholic church. To the Arians he shewed how, by a sophistical evasion based on (''τὰ δὲ πάντα ἐκ τοῦ Θεοῦ''), they might accept the orthodox test (''Θεὸν ἐκ Θεοῦ''). The attem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dedication Council Of Antioch
Beginning with three synods convened between 264 and 269 in the matter of Paul of Samosata, more than thirty councils were held in Antioch in ancient times. Most of these dealt with phases of the Arian and of the Christological controversies. For example, the ''Catholic Encyclopedia'' article on Paul of Samosata states: The most celebrated convened in the summer of 341 at the dedication of the Domus Aurea, and is therefore called ' or dedication council. Nearly a hundred Eastern bishops were present, but the bishop of Rome was not represented. The emperor Constantius II attended in person. The Synods of Antioch in 264-269 The first Synod of Antioch, which took place between 264 and 269, was one of the early significant ecclesiastical councils in the Christian Church. This synod was primarily convened to address the teachings of Paul of Samosata, who was the Bishop of Antioch. Paul of Samosata had introduced a doctrine that was considered heretical by the mainstream Church, par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |