|
Selonian Language
Selonian was an East Baltic language, which was spoken by the East Baltic tribe of the Selonians, who until the 15th century lived in Selonia, a territory in southeastern Latvia and northeastern Lithuania. The language persisted until the 16th century. History Traces of the Selonian language can still be found in the territories the Selonians inhabited, especially in the accent and phonetics of the so-called Selonian dialect of the Latvian language. There are some traces of the Selonian language in the northeastern sub-dialects of the Aukštaitian dialect of the Lithuanian language, mostly in the lexicon. Classification It is considered that the Selonian language retained the Proto-Baltic sonorant diphthongs *an, *en, *in, *unlike the Lithuanian language, but like the Latvian language Latvian (, ), also known as Lettish, is an East Baltic languages, East Baltic language belonging to the Indo-European language family. It is spoken in the Baltic region, and is the language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Selonia
Selonia (; ), also known as Augšzeme (the "Highland"), is one of the Historical Latvian Lands encompassing the eastern part of the historical region of Semigallia () as well as a portion of northeastern Lithuania. Its main city and cultural center is Jēkabpils. The Selonian language has become extinct, though some of the inhabitants still speak a Selonian subdialect. History The territory of Selonia is defined by Latvian law as follows: the part of Aizkraukle city on the left bank of the Daugava, Daudzese Parish, Jaunjelgava Parish, Jaunjelgava city, Nereta Parish, Mazzalve Parish, Pilskalne Parish, Sece Parish, Sērene Parish, Staburags Parish, Sunākste Parish, Zalve Parish, Bebrene Parish, Demene Parish, Dviete Parish, Eglaine Parish, Ilūkste city, Kalkūne Parish, Laucesa Parish, Medumi Parish, Pilskalne Parish, Prode Parish, Saliena Parish, Skrudaliena Parish, Subate city, Svente Parish, Šēdere Parish, Tabore Parish, Vecsaliena Parish, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Selonians
The Selonians (; , from – "highlanders") were a tribe of Baltic peoples. They lived until the 15th century in Selonia, located in southeastern Latvia and northeastern Lithuania. They eventually merged with neighbouring tribes, contributing to the ethnogenesis of modern Latvians and Lithuanians. They spoke the Eastern Baltic Selonian language. History Little is known about the Selonians. There is little archaeological evidence and in historic sources the region is often described as a "scarcely populated land". In written sources they are mentioned only few times. Archeological data can trace the Selonians back to the beginning of 1st millennium AD when they lived on both sides of the Daugava River. But since the 6th and 7th centuries their settlements can be traced only on the left bank of the river. Selonian culture had a very strong Latgalian influence. Selonian and Latgalian burial traditions show little difference. Some scholars speculate that during the late Iron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Latvia
Latvia, officially the Republic of Latvia, is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is one of the three Baltic states, along with Estonia to the north and Lithuania to the south. It borders Russia to the east and Belarus to the southeast, and shares a Maritime boundary, maritime border with Sweden to the west. Latvia covers an area of , with a population of 1.9million. The country has a Temperate climate, temperate seasonal climate. Its capital and List of cities and towns in Latvia, largest city is Riga. Latvians, who are the titular nation and comprise 65.5% of the country's population, belong to the ethnolinguistic group of the Balts and speak Latvian language, Latvian. Russians in Latvia, Russians are the most prominent minority in the country, at almost a quarter of the population; 37.7% of the population speak Russian language, Russian as their native tongue. After centuries of State of the Teutonic Order, Teutonic, Swedish Livonia, Swedish, Inflanty Voi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, Poland to the south, and the Russian exclave, semi-exclave of Kaliningrad Oblast to the southwest, with a Maritime boundary, maritime border with Sweden to the west. Lithuania covers an area of , with a population of 2.89 million. Its capital and largest city is Vilnius; other major cities include Kaunas, Klaipėda, Šiauliai and Panevėžys. Lithuanians who are the titular nation and form the majority of the country's population, belong to the ethnolinguistic group of Balts and speak Lithuanian language, Lithuanian. For millennia, the southeastern shores of the Baltic Sea were inhabited by various Balts, Baltic tribes. In the 1230s, Lithuanian lands were united for the first time by Mindaugas, who formed the Kingdom of Lithuania on 6 July ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Balto-Slavic Languages
The Balto-Slavic languages form a branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European family of languages, traditionally comprising the Baltic languages, Baltic and Slavic languages. Baltic and Slavic languages share several linguistic traits not found in any other Indo-European branch, which points to a period of common development and origin. A Proto-Balto-Slavic language is reconstructable by the comparative method, descending from Proto-Indo-European language, Proto-Indo-European by means of well-defined Sound change, sound laws, and from which modern Slavic and Baltic languages descended. One particularly innovative dialect separated from the Balto-Slavic dialect continuum and became ancestral to the Proto-Slavic language, from which all Slavic languages descended. While the notion of a Balto-Slavic unity was previously contested largely due to political controversies, there is now a general consensus among academic specialists in Indo-European linguistics that Baltic an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
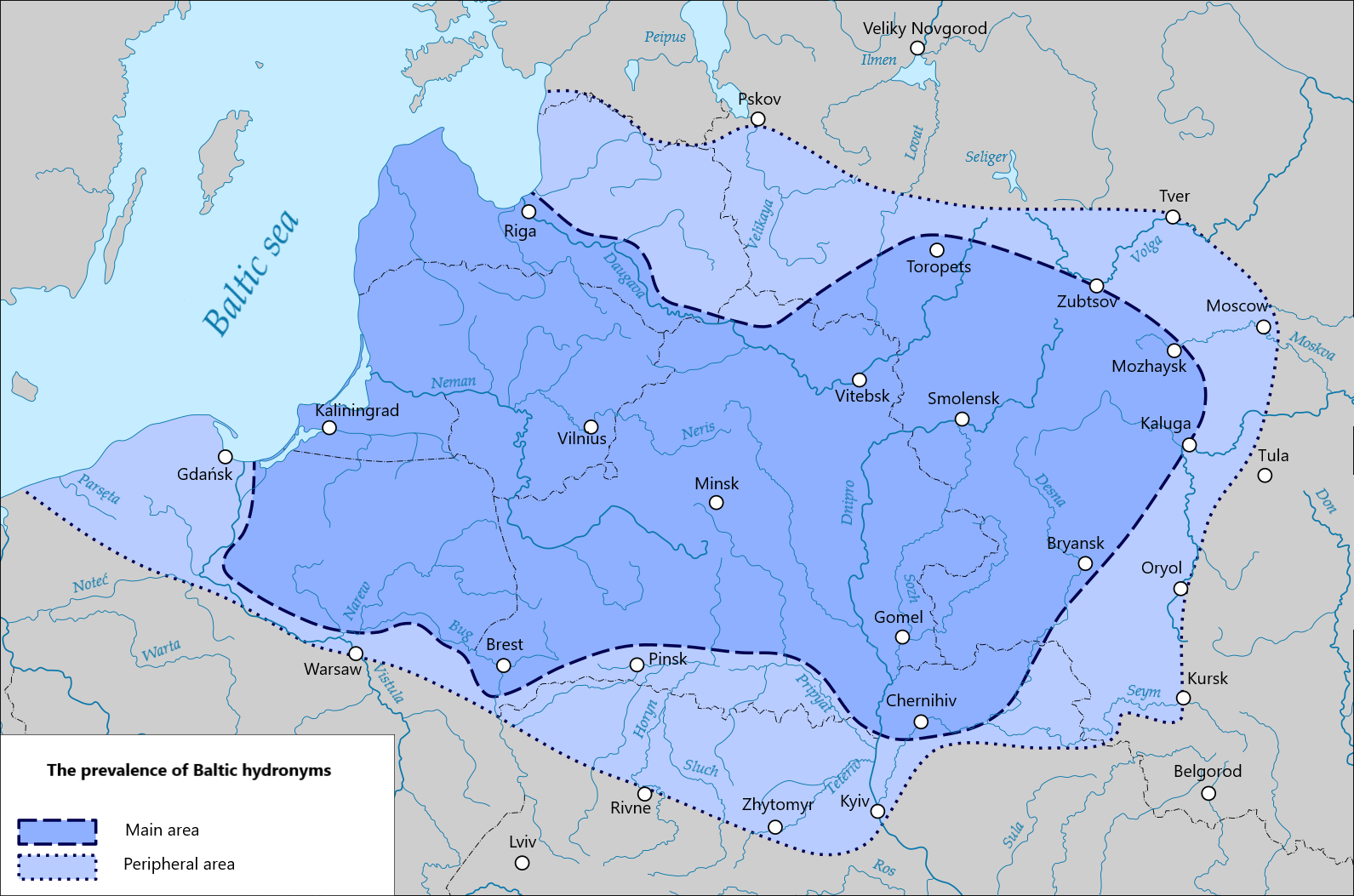
East Baltic Languages
The East Baltic languages are a group of languages that along with the extinct West Baltic languages belong to the Baltic branch of the Indo-European language family. The East Baltic branch primarily consists of two extant languages— Latvian and Lithuanian. Occasionally, Latgalian and Samogitian are viewed as distinct languages, though they are traditionally regarded as dialects. It also includes now-extinct Selonian, Semigallian, and possibly Old Curonian. Lithuanian is the most-spoken East Baltic language, with more than 3 million speakers worldwide, followed by Latvian, with 1.75 million native speakers, then Samogitan with 500,000 native speakers, and lastly Latgalian with 150,000 native speakers. History Originally, East Baltic was presumably native to the north of Eastern Europe, which included modern Latvia, Lithuania, northern parts of current European Russia and Belarus. Dnieper Balts lived in the current territory of Moscow, which was the furthest undisput ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Baltic Tribes C 1200
Baltic may refer to: Peoples and languages *Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian *Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originating from the Baltic countries *Baltic Germans, historical ethnic German minority in Latvia and Estonia *Baltic Finnic peoples, the Finnic peoples historically inhabiting the area on the northeastern side of the Baltic sea Places Northern Europe * Baltic Sea, in Europe * Baltic region, an ambiguous term referring to the general area surrounding the Baltic Sea * Baltic states (also Baltic countries, Baltic nations, Baltics), a geopolitical term, currently referring to Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania * Baltic Provinces or governorates, former parts of the Swedish Empire and then Russian Empire (in modern Latvia, Estonia) * Baltic Shield, the exposed Precambrian northwest segment of the East European Craton * Baltic Plate, an ancient tectonic p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Balts
The Balts or Baltic peoples (, ) are a group of peoples inhabiting the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea who speak Baltic languages. Among the Baltic peoples are modern-day Lithuanians (including Samogitians) and Latvians (including Latgalians (modern), Latgalians) — all East Balts — as well as the Old Prussians, Curonians, Sudovians, Skalvians, Yotvingians and Galindians — the West Balts — whose languages and cultures are now extinct, but made a large influence on the living branches, especially on literary Lithuanian language. The Balts are descended from a group of Proto-Indo-Europeans, Proto-Indo-European tribes who settled the area between the lower Vistula and southeast shore of the Baltic Sea and upper Daugava and Dnieper rivers, and which over time became differentiated into West and East Balts. In the fifth century CE, parts of the eastern Baltic coast began to be settled by the ancestors of the Western Balts, whereas the East Balts lived in modern-day Belarus, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Latvian Language
Latvian (, ), also known as Lettish, is an East Baltic languages, East Baltic language belonging to the Indo-European language family. It is spoken in the Baltic region, and is the language of the Latvians. It is the official language of Latvia as well as one of the official languages of the European Union. There are about 1.5 million native Latvian speakers in Latvia and 100,000 abroad. Altogether, 2 million, or 80% of the population of Latvia, spoke Latvian in the 2000s, before the total number of inhabitants of Latvia slipped to 1.8 million in 2022. Of those, around 1.16 million or 62% of Latvia's population used it as their primary language at home, though excluding the Latgale Planning Region, Latgale and Riga Planning Region, Riga regions it is spoken as a native language in villages and towns by over 90% of the population. As a Baltic languages, Baltic language, Latvian is most closely related to neighboring Lithuanian language, Lithuanian (as well as Old Prussian language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Aukštaitian Dialect
Aukštaitian () is one of the dialects of the Lithuanian language, spoken in the ethnographic regions of Aukštaitija, Dzūkija and Suvalkija. It became the basis for the standard Lithuanian language. Classification Revised classification of the dialects, proposed in 1965 by linguists Zigmas Zinkevičius and Aleksas Girdenis, divides the Aukštaitian dialect into three sub-dialects based on pronunciation of the mixed diphthongs ''an'', ''am'', ''en'', ''em'' and the ogonek The tail or ( ; Polish: , "little tail", diminutive of ) is a diacritic hook placed under the lower right corner of a vowel in the Latin alphabet used in several European languages, and directly under a vowel in several Native American langu ... vowels ''ą'' and ''ę'': Western Aukštaitianmost similar to standard Lithuanianpreserves both the diphthongs and the vowels. It is further subdivided into two sub-dialects: * The Kaunas sub-dialect is spoken mostly in Suvalkija. This sub-dialect separ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Lithuanian Language
Lithuanian (, ) is an East Baltic languages, East Baltic language belonging to the Baltic languages, Baltic branch of the Indo-European language family. It is the language of Lithuanians and the official language of Lithuania as well as one of the official languages of the European Union. There are approximately 2.8 million native Lithuanian speakers in Lithuania and about 1 million speakers elsewhere. Around half a million inhabitants of Lithuania of non-Lithuanian background speak Lithuanian daily as a second language. Lithuanian is closely related to neighbouring Latvian language, Latvian, though the two languages are not mutually intelligible. It is written in a Latin script. In some respects, some linguists consider it to be the most conservative (language), conservative of the existing Indo-European languages, retaining features of the Proto-Indo-European language that had disappeared through development from other descendant languages. History Among Indo-European languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Medieval Languages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of World history (field), global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early Middle Ages, Early, High Middle Ages, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralised authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |