|
Seki Kazumasa
was a Japanese ''daimyō'' of the late Sengoku period through early Edo period, who was a retainer of the Oda and Toyotomi clans. His court title was . Kazumasa took part in many of the major campaigns of the Toyotomi clan, serving as a yoriki under his brother-in-law Gamō Ujisato. In the early Edo period, he served under the Tokugawa clan at the Sieges of Osaka. His domain of Kurosaka was confiscated in 1618, due to internal disturbances. Kazumasa died in 1625, but his nephew and adoptive son Ujimori was granted 5,000 '' koku'' and allowed to succeed to family headship as a high-ranking hatamoto A was a high ranking samurai in the direct service of the Tokugawa shogunate of feudal Japan. While all three of the shogunates in Japanese history had official retainers, in the two preceding ones, they were referred to as ''gokenin.'' Howev .... References *Fukuda, Chizuru (2005). ''Oie-sōdō''. Tokyo: Chūōkōron-shinsha. "Ise-Kameyama han" on ''Edo 300 HTML''(19 February 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daimyō
were powerful Japanese magnates, feudal lords who, from the 10th century to the early Meiji period in the middle 19th century, ruled most of Japan from their vast, hereditary land holdings. They were subordinate to the shogun and nominally to the emperor and the '' kuge''. In the term, means 'large', and stands for , meaning 'private land'. From the '' shugo'' of the Muromachi period through the Sengoku to the ''daimyo'' of the Edo period, the rank had a long and varied history. The backgrounds of ''daimyo'' also varied considerably; while some ''daimyo'' clans, notably the Mōri, Shimazu and Hosokawa, were cadet branches of the Imperial family or were descended from the ''kuge'', other ''daimyo'' were promoted from the ranks of the samurai, notably during the Edo period. ''Daimyo'' often hired samurai to guard their land, and they paid the samurai in land or food as relatively few could afford to pay samurai in money. The ''daimyo'' era ended soon after the Meiji R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
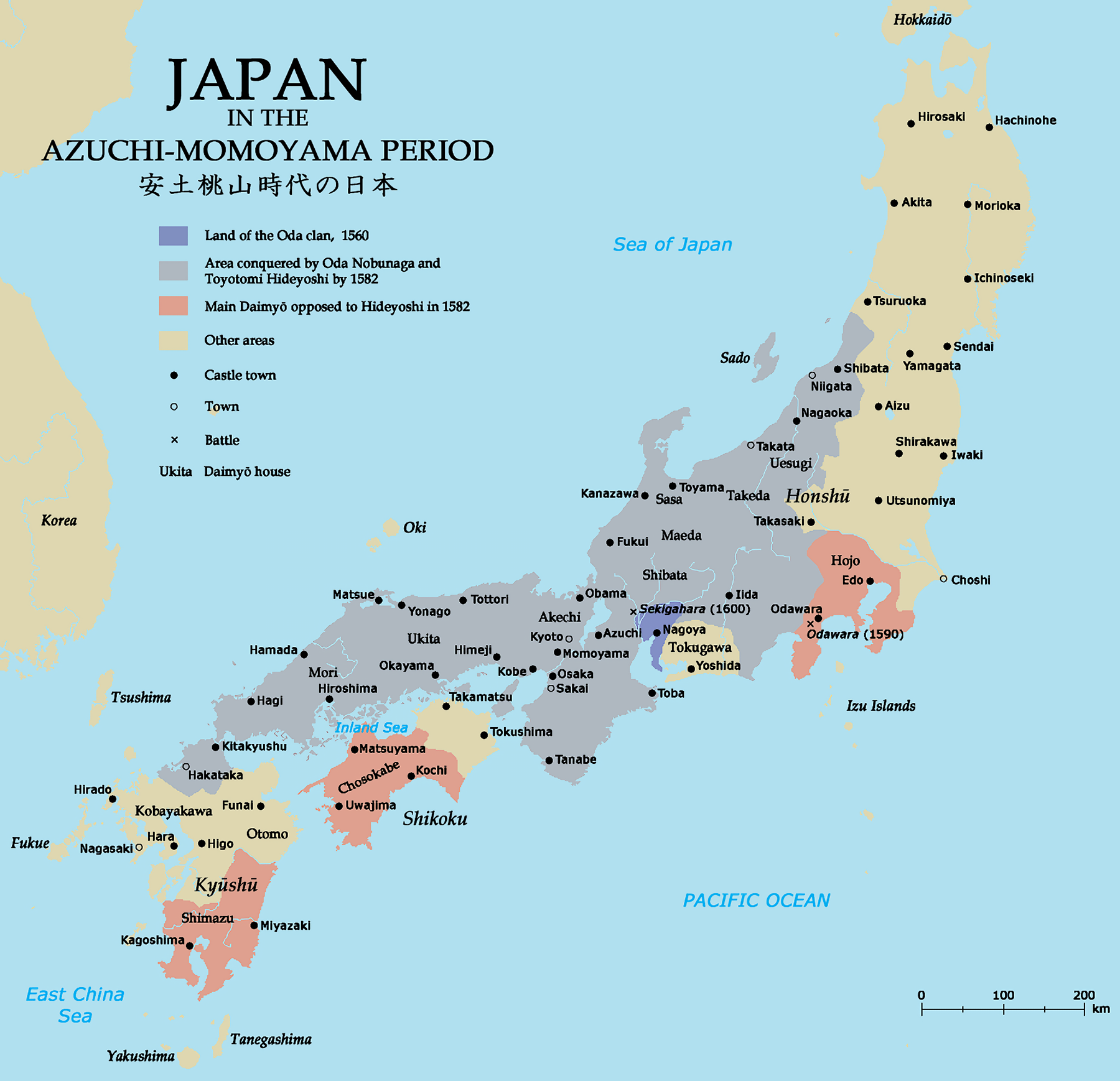
Sengoku Period
The was a period in Japanese history of near-constant civil war and social upheaval from 1467 to 1615. The Sengoku period was initiated by the Ōnin War in 1467 which collapsed the feudal system of Japan under the Ashikaga shogunate. Various samurai warlords and clans fought for control over Japan in the power vacuum, while the emerged to fight against samurai rule. The arrival of Europeans in 1543 introduced the arquebus into Japanese warfare, and Japan ended its status as a tributary state of China in 1549. Oda Nobunaga dissolved the Ashikaga shogunate in 1573 and launched a war of political unification by force, including the Ishiyama Hongan-ji War, until his death in the Honnō-ji Incident in 1582. Nobunaga's successor Toyotomi Hideyoshi completed his campaign to unify Japan and consolidated his rule with numerous influential reforms. Hideyoshi launched the Japanese invasions of Korea in 1592, but their eventual failure damaged his prestige before his death in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edo Period
The or is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's 300 regional ''daimyo''. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was characterized by economic growth, strict social order, isolationist foreign policies, a stable population, perpetual peace, and popular enjoyment of arts and culture. The period derives its name from Edo (now Tokyo), where on March 24, 1603, the shogunate was officially established by Tokugawa Ieyasu. The period came to an end with the Meiji Restoration and the Boshin War, which restored imperial rule to Japan. Consolidation of the shogunate The Edo period or Tokugawa period is the period between 1603 and 1867 in the history of Japan, when Japan was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and the country's regional ''daimyo''. A revolution took place from the time of the Kamakura shogunate, which existed with the Tennō's court, to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kokushi (officials)
were provincial officials in Classical Japan. They were nobles sent from the central government in Kyoto to oversee a province, a system that was established as part of the Taika Reform in 645, and enacted by the ''Ritsuryō'' system. There were four classes of ''kokushi'', from the highest to the lowest: ''Kami'' (守), ''Suke'' (介), ''Jō'' (掾), and ''Sakan'' (目). In the Middle Ages, an acting governor called ''mokudai'', the ''daikan'' of the ''kokushi'', took over the local government of the province, while the ''kokushi'' returned to the capital to take on a supervising role. History The oldest reference to the term ''kokushi'' appears on the Seventeen-article constitution from 604. As part of the Taika Reform in 645, a new system of provincial government was established, marking the beginning of the ''kokushi''. Before this, the governors were called ''mikotomochi'' (宰 or 使者). This term was replaced with the ''kanji'' characters 国 (province) and 司 (govern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoriki
were members of the '' samurai'' class of feudal Japan. ''Yoriki'' literally means ''helper'' (ru - помощник) or ''assistant'' (ru - ассистент). Description and history ''Yoriki'' assisted '' daimyō'' (feudal lords) or their designated commanders during military campaigns in the Kamakura is a city in Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan. Kamakura has an estimated population of 172,929 (1 September 2020) and a population density of 4,359 persons per km² over the total area of . Kamakura was designated as a city on 3 November 1939. Kamak ... and Muromachi periods. In the Edo period, ''yoriki'' provided administrative assistance at governmental offices. Among different ''yorikis'' were the ''machikata yoriki'', who were in charge of police under the command of the '' machi-bugyō''. Below the ''yoriki'' were the ''dōshin''. In the city of Edo there were about 25 ''yorikis'' working each for the two ''machi-bugyō'' offices. References * Cunningham, Don (2004). 'Tai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gamō Ujisato
or Gamō Yasuhide was a Japanese ''daimyō'' of the Sengoku and Azuchi–Momoyama periods. He was heir and son of Gamō Katahide, lord of Hino Castle in Ōmi Province, he later held Matsusaka ( Ise Province) and finally Aizuwakamatsu Castle in Mutsu Province. He also controlled Obama Castle through one of his retainers, Gamō Chūzaemon. Early life and rise Ujisato, known in his childhood as , was born in Hino, in the Gamō district of Ōmi Province in 1556. In 1568, Oda Nobunaga, who was en route to Kyoto, defeated the Rokkaku clan, who were the masters of Tsuruchiyo's father, . Upon the Rokkaku clan's defeat, Katahide as a former influential vassal, pledged loyalty to Nobunaga, and became an Oda retainer. However, the price of Katahide's pledge was giving up his son as a hostage, and so Tsuruchiyo was taken to Gifu, then the Oda clan's headquarters. Tsuruchiyo's sagacity impressed Nobunaga, and soon, the young man had his manhood rite in Gifu, taking the name .DF 7 of 80/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sieges Of Osaka
The was a series of battles undertaken by the Japanese Tokugawa shogunate against the Toyotomi clan, and ending in that clan's destruction. Divided into two stages (winter campaign and summer campaign), and lasting from 1614 to 1615, the siege put an end to the last major armed opposition to the shogunate's establishment. The end of the conflict is sometimes called the , because the era name was changed from Keichō to Genna immediately following the siege. Background When Toyotomi Hideyoshi died in 1598, Japan came to be governed by the Council of Five Elders, among whom Tokugawa Ieyasu possessed the most authority. After defeating Ishida Mitsunari in the battle of Sekigahara in 1600, Ieyasu essentially seized control of Japan for himself, and abolished the Council. In 1603, the Tokugawa shogunate was established, with its capital at Edo. Hideyori and his mother Yodo-dono were allowed to stay at Osaka Castle, a fortress that had served as Hideyoshi's residence and he found h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koku
The is a Chinese-based Japanese unit of volume. 1 koku is equivalent to 10 or approximately , or about . It converts, in turn, to 100 shō and 1000 gō. One ''gō'' is the volume of the "rice cup", the plastic measuring cup that is supplied with commercial Japanese rice cookers. The ''koku'' in Japan was typically used as a dry measure. The amount of rice production measured in ''koku'' was the metric by which the magnitude of a feudal domain ('' han'') was evaluated. A feudal lord was only considered '' daimyō'' class when his domain amounted to at least 10,000 ''koku''. As a rule of thumb, one ''koku'' was considered a sufficient quantity of rice to feed one person for one year. The Chinese equivalent or cognate unit for capacity is the ''shi'' or ''dan'' ( also known as ''hu'' (), now approximately 103 litres but historically about . Chinese equivalent The Chinese ''shi'' or ''dan'' is equal to 10 ''dou'' () " pecks", 100 ''sheng'' () " pints". While the current ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hatamoto
A was a high ranking samurai in the direct service of the Tokugawa shogunate of feudal Japan. While all three of the shogunates in Japanese history had official retainers, in the two preceding ones, they were referred to as ''gokenin.'' However, in the Edo period, ''hatamoto'' were the upper vassals of the Tokugawa house, and the ''gokenin'' were the lower vassals. There was no precise difference between the two in terms of income level, but a hatamoto had the right to an audience with the ''shōgun'', whereas gokenin did not.Ogawa, p. 43. The word ''hatamoto'' literally means "origin of the flag", with the sense of 'around the flag', it is described in Japanese as 'those who guard the flag' (on the battlefield) and is often translated into English as "bannerman". Another term for the Edo-era ''hatamoto'' was , sometimes rendered as "direct shogunal ''hatamoto''", which serves to illustrate the difference between them and the preceding generation of ''hatamoto'' who served var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tara Domain
Tara may refer to: Arts and entertainment Film and television * ''Tara'' (1992 film), an Indian film directed by Bijaya Jena * ''Tara'' (2001 film), an American film, also known as ''Hood Rat'', directed by Leslie Small * ''Tara'' (2010 film), a Bengali film directed by Bratyo Basu * ''Tara'' (2013 film), an Indian film directed by Kumar Raj * ''Tara'' (TV series), soap opera that aired on Zee TV *TARA, acronym for '' The Amazing Race Asia'', a reality game show on the AXN network Music * T-ara, a South Korean girl music group * Tara Music, a label featuring traditional Irish music * ''Tara'' (Absu album) * "Tara" (song), a song on Moya Brennan's 2003 album ''Two Horizons'' * ''Tara'' (Yano album) * "Tara", a song by Roxy Music on the 1982 album ''Avalon'' (Roxy Music album) Fictional settings * Tara (plantation), fictional home of Scarlett O'Hara in ''Gone with the Wind'' *Tara, a planet, setting of the ''Doctor Who'' serial '' The Androids of Tara'' *Tara, a fictional town, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ise-Kameyama Domain
was a feudal domain under the Tokugawa shogunate of Edo period Japan, located in Ise Province in what is part of now modern-day Kameyama, Mie. It was centered around Ise-Kameyama Castle. Ise-Kameyama Domain was controlled by '' fudai daimyō'' clans throughout most its history. History The Ise-Kamayama area of northern Ise Province was controlled in the Sengoku period by Seki Morinobu. Under Toyotomi Hideyoshi, his son Seki Kazumasa was relocated to Mino Province and replaced by Hideyoshi's general Okamoto Yoshikatsu as part of a 22,000 '' koku'' fief. Okamoto Yoshikatsu rebuilt Kameyama Castle and laid out the foundations for the castle town. However, he sided with the pro-Toyotomi Western Army at the 1600 Battle of Sekigahara and was dispossessed by the victorious Tokugawa Ieyasu, who restored Seki Kazumasa to his former domains with an increase in ''kokudaka'' to 30,000 ''koku''. Under Seki Kazumasa, Kameyama-juku, the post station on the Tōkaidō was repaired and exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |