|
Sekhukhune II
Sekhukhune II was the paramount King of the Bapedi and grandson of Sekhukhune I. He reigned during the Second Anglo-Boer War. Sekhukhune's reign marked the final collapse of the Bapedi resistance against the occupation of their land by the South African Republic and the British Empire.Sekhukhune II his heir Thulare II predeceased him and Kgobalale was appointed as a regent instead of his elder brother Seraki. It was the pedi nation as large that turned down the appointment of Seraki due to his unruly behaviour. They believed that if Kgobalale should have a problem he could notify his brother Seraki as he was trusted to when it comes to war. See also * Sekwati * Mampuru II * Sekhukhune I * Pedi people The Pedi or (also known as the Northern Sotho or and the Marota or ) – are a southern African ethnic group that speak Pedi or ''Sepedi'', a dialect belonging to the Sotho-Tswana enthnolinguistic group. Northern Sotho is a term used to ... References {{reflist S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedi People
The Pedi or (also known as the Northern Sotho or and the Marota or ) – are a southern African ethnic group that speak Pedi or ''Sepedi'', a dialect belonging to the Sotho-Tswana enthnolinguistic group. Northern Sotho is a term used to refer to one of South Africa's 11 official languages. Northern Sotho or Sesotho sa Leboa consist of 33 dialects, of which Pedi is one of them. The BaPedi people are almost exclusively found in South Africa's northeastern provinces which are Limpopo, and parts of northern Mpumalanga. There is confusion regarding the distinction between BaPedi people, and tribes referred to Northern Sotho (''Basotho ba Lebowa).'' On the one hand, one military explanation is that the BaPedi people became powerful at one point under a powerful king that ruled over a large piece of land. During this period, a powerful army of the BaPedi conquered smaller tribes, and proclaimed paramountcy over them. On the other hand, another explanation is that after the decl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sekhukhune
Sekhukhune I (Matsebe; circa 1814 – 13 August 1882) was the paramount King of the Marota, more commonly known as the Bapedi, from 21 September 1861 until his assassination on 13 August 1882 by his rival and half-brother, Mampuru II. As the Pedi paramount leader he was faced with political challenges from boer settlers, the independent South African Republic (Dutch: ''Zuid-Afrikaansche Republiek''), the British Empire, and considerable social change caused by Christian missionaries. Sekhukhune was the son of Sekwati I, and succeeded him upon his death in 20 September 1861 after forcibly taking the throne from his half-brother and the heir apparent Mampuru II. His other known siblings were; Legolwana, Johannes Dinkwanyane, and Kgoloko. Sekhukhune married Legoadi IV in 1862, and lived at a mountain, now known as or Leolo Mountains which he fortified. To strengthen his kingdom and to guard against European colonisation, he had his young subjects work in white mines and on farm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
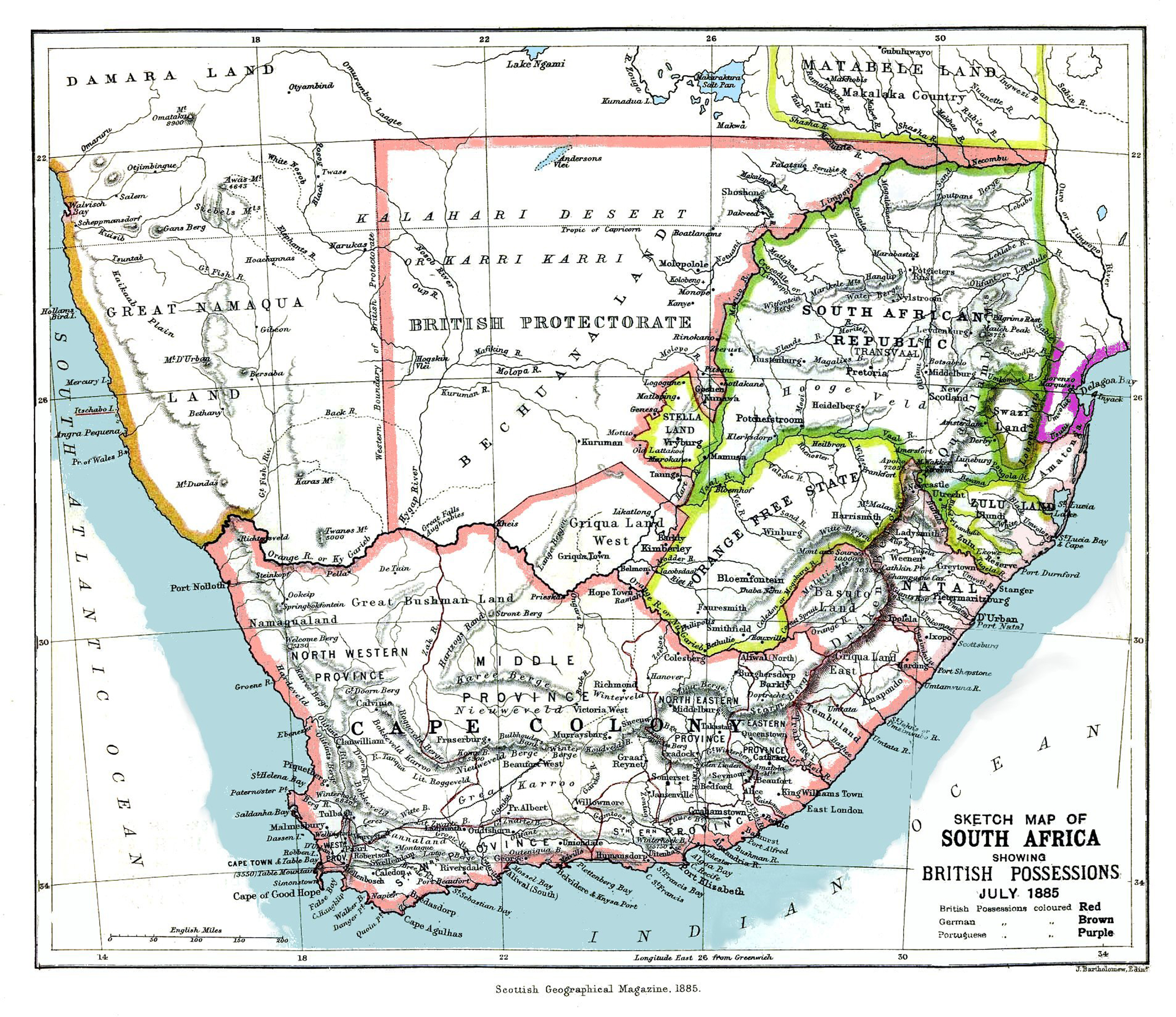
Second Boer War
The Second Boer War ( af, Tweede Vryheidsoorlog, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, the Anglo–Boer War, or the South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer Republics (the South African Republic and the Orange Free State) over the Empire's influence in Southern Africa from 1899 to 1902. Following the discovery of gold deposits in the Boer republics, there was a large influx of "foreigners", mostly British from the Cape Colony. They were not permitted to have a vote, and were regarded as "unwelcome visitors", invaders, and they protested to the British authorities in the Cape. Negotiations failed and, in the opening stages of the war, the Boers launched successful attacks against British outposts before being pushed back by imperial reinforcements. Though the British swiftly occupied the Boer republics, numerous Boers refused to accept defeat and engaged in guerrilla warfare. Eventually, British scorched earth po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sekhukhune
Sekhukhune I (Matsebe; circa 1814 – 13 August 1882) was the paramount King of the Marota, more commonly known as the Bapedi, from 21 September 1861 until his assassination on 13 August 1882 by his rival and half-brother, Mampuru II. As the Pedi paramount leader he was faced with political challenges from boer settlers, the independent South African Republic (Dutch: ''Zuid-Afrikaansche Republiek''), the British Empire, and considerable social change caused by Christian Missionaries, Christian missionaries. Sekhukhune was the son of Sekwati, Sekwati I, and succeeded him upon his death in 20 September 1861 after forcibly taking the throne from his half-brother and the heir apparent Mampuru II. His other known siblings were; Legolwana, Johannes Dinkwanyane, and Kgoloko. Sekhukhune married Legoadi IV in 1862, and lived at a mountain, now known as or Leolo Mountains which he fortified. To strengthen his kingdom and to guard against European colonisation, he had his young subjects wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedi People
The Pedi or (also known as the Marota or ) – are a southern African ethnic group that speak Pedi or ''Sepedi'', a dialect belonging to the Northern Sotho enthnolinguistic group. Sepedi is spoken in Sekhukhuneland (Ga-Sekhukhune) and By 1800 Thulare was the leader of the Pedi Empire in the northeastern Transvaal . His capital Manganeng lay on the Tubatse / Steelpoort River There is confusion regarding the distinction between BaPedi people, and tribes referred to Northern Sotho (''Basotho ba Lebowa).'' On the one hand, one military explanation is that the BaPedi people became powerful at one point under a powerful king that ruled over a large piece of land. During this period, a powerful army of the BaPedi conquered smaller tribes, and proclaimed paramountcy over them. On the other hand, another explanation is that after the decline of one of the BaPedi Kingdom, some tribes separated from the kingship, hence the use of the term Northern Sotho. One reason for separation mig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South African Republic
The South African Republic ( nl, Zuid-Afrikaansche Republiek, abbreviated ZAR; af, Suid-Afrikaanse Republiek), also known as the Transvaal Republic, was an independent Boer Republic in Southern Africa which existed from 1852 to 1902, when it was annexed into the British Empire as a result of the Second Boer War. The ZAR was established as a result of the 1852 Sand River Convention, in which the British government agreed to formally recognise independence of the Boers living north of the Vaal River. Relations between the ZAR and Britain started to deteriorate after the British Cape Colony expanded into the Southern African interior, eventually leading to the outbreak of the First Boer War between the two nations. The Boer victory confirmed the ZAR's independence; however, Anglo-ZAR tensions soon flared up again over various diplomatic issues. In 1899, war again broke out between Britain and the ZAR, which was swiftly occupied by the British military. Many Boer combatant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts established by England between the late 16th and early 18th centuries. At its height it was the largest empire in history and, for over a century, was the foremost global power. By 1913, the British Empire held sway over 412 million people, of the world population at the time, and by 1920, it covered , of the Earth's total land area. As a result, its constitutional, legal, linguistic, and cultural legacy is widespread. At the peak of its power, it was described as " the empire on which the sun never sets", as the Sun was always shining on at least one of its territories. During the Age of Discovery in the 15th and 16th centuries, Portugal and Spain pioneered European exploration of the globe, and in the process established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sekwati
Sekwati was a 19th-century paramount King of the Maroteng or more commonly known as the Bapedi people. His reign focused on rebuilding the Pedi Kingdom on the conclusion of the Mfecane and maintaining peaceful relations with the Boer Voortrekkers and neighbouring chiefdoms in the north-eastern Transvaal. He was the father to rivals Sekhukhune I who took over the Marota/Pedi paramountcy by force and Mampuru II, his rightful successor. By the death of his father Thulare I in 1824, the Marota or Pedi Kingdom was in a state of despair due to the turbulence caused by the Mfecane ("the crushing") or Difeqane ("the scattering") and encroaching white settlers (Boers) into the Transvaal. Sekwati came into power after the death of his older brothers who were killed during raids by Mzilikazi's Matabele. To rebuild the empire he moved his capital from Phiring to Thaba Mosego. Bibliography * Peter Nicholas St. Martin Delius, ''The Pedi Polity Under Sekwati and Sekhukhune, 1828-1880'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mampuru II
Mampuru II (1824 – 22 November 1883) was a king of the Pedi people in southern Africa. Mampuru was a son of the elder brother of Sekwati and claimed he had been designated as his successor. Sekwati died in 1861 and his son, Sekhukhune claimed the throne. Sekhukhune ruled until 1879 when a British-Swazi invasion deposed him and installed Mampuru as king. Mampuru ordered the assassination of Sekhukhune in 1882 for which he was arrested and hanged by the Boer South African Republic the following year. Mampuru is regarded as an early liberation movement icon in South Africa and the prison where he was executed has been renamed in his honour. Early life The king (kgosi) of the Pedi people Sekwati died in 1861 but this resulted in a succession crisis. It was traditional for Pedi rulers to take a ''timamollo'' ("candle wife" or "great wife") in addition to their usual wife. The children of the candle wife would be those who succeeded to the throne, ahead of the other descendants. Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)