|
Seemanchal Express
The 12487 / 12488 Seemanchal Express is a Superfast train belonging to Northern Railway zone that runs between and in India. It is currently being operated with 12487/12488 train numbers on a daily basis. Service The 12487/Seemanchal Express has an average speed of 55 km/hr and covers 1397 km in 24h 55m. The 12488/Seemanchal Express has an average speed of 55 km/hr and covers 1397 km in 24h 55m. Route & Halts The important halts of the train are: Coach composition The train has modern LHB rakes with max speed of 110 kmph. The train consists of 22 coaches: * 1 Second Tier AC * 3 Third Tier AC * 1 Third Tier AC Economy * 9 Sleeper Class * 6 General Unreserved * 1 Seating cum Luggage Rake * 1 EOG Traction Both trains are hauled by a Siliguri-based WDP-4 / WDP-4B / WDP-4D diesel locomotive from Jogbani to . From Katihar Junction the train is hauled by a Ghaziabad-based WAP-7 electric locomotive and vice versa. Incident On February 3, 2019, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superfast Express Trains In India
Express trains are express rail services of India. Express trains make a small number of stops, unlike ordinary passenger or local trains. Because of their limited stops, these trains are able to obtain the highest speeds of any trains in India. An express train is one where the average speed, excluding halts, is greater than 42 km/h. Including halts the average speed often is below 42 km/h. Although this is pretty slow as compared to international standards, the "Express" trains here mean faster than the ordinary passenger and local trains. In some cases, trains run express where there is an overlapping passenger train service available, and run as passenger train, where there is no supplemental passenger service. Superfast Superfast trains are express trains which make still fewer stops, as compared to ordinary express trains, achieving still shorter journey times. Tickets cost more than ordinary express trains as they have "superfast surcharge" added to them. Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Indian Express
''The Indian Express'' is an English-language Indian daily newspaper founded in 1932. It is published in Mumbai by the Indian Express Limited, Indian Express Group. In 1999, eight years after the group's founder Ramnath Goenka's death in 1991, the group was split between the family members. The southern editions took the name ''The New Indian Express'', while the northern editions, based in Mumbai, retained the original ''Indian Express'' name with ''"The"'' prefixed to the title. History In 1932, the ''Indian Express'' was started by an Ayurvedic doctor, P. Varadarajulu Naidu, at Chennai, being published by his "Tamil Nadu" press. Soon under financial difficulties, he sold the newspaper to Swaminathan Sadanand, the founder of ''The Free Press Journal'', a national news agency. In 1933, the ''Indian Express'' opened its second office in Madurai, launching the Tamil language, Tamil edition, ''Dinamani''. Sadanand introduced several innovations and reduced the price of the newspa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rail Transport In Delhi
Rail or rails may refer to: Rail transport *Rail transport and related matters * Rail (rail transport) or railway lines, the running surface of a railway Arts and media Film * ''Rails'' (film), a 1929 Italian film by Mario Camerini * ''Rail'' (1967 film), a film by Geoffrey Jones for British Transport Films *''Mirattu'' or ''Rail'', a Tamil-language film and its Telugu dub Magazines * ''Rail'' (magazine), a British rail transport periodical * ''Rails'' (magazine), a former New Zealand based rail transport periodical Other arts * The Rails, a British folk-rock band *Rail (theater) or batten, a pipe from which lighting, scenery, or curtains are hung Technology * Rails framework or Ruby on Rails, a web application framework * Rail system (firearms), a mounting system for firearm attachments * Front engine dragster *Runway alignment indicator lights, a configuration of an approach lighting system *Rule Augmented Interconnect Layout, a specification for expressing guidelines for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
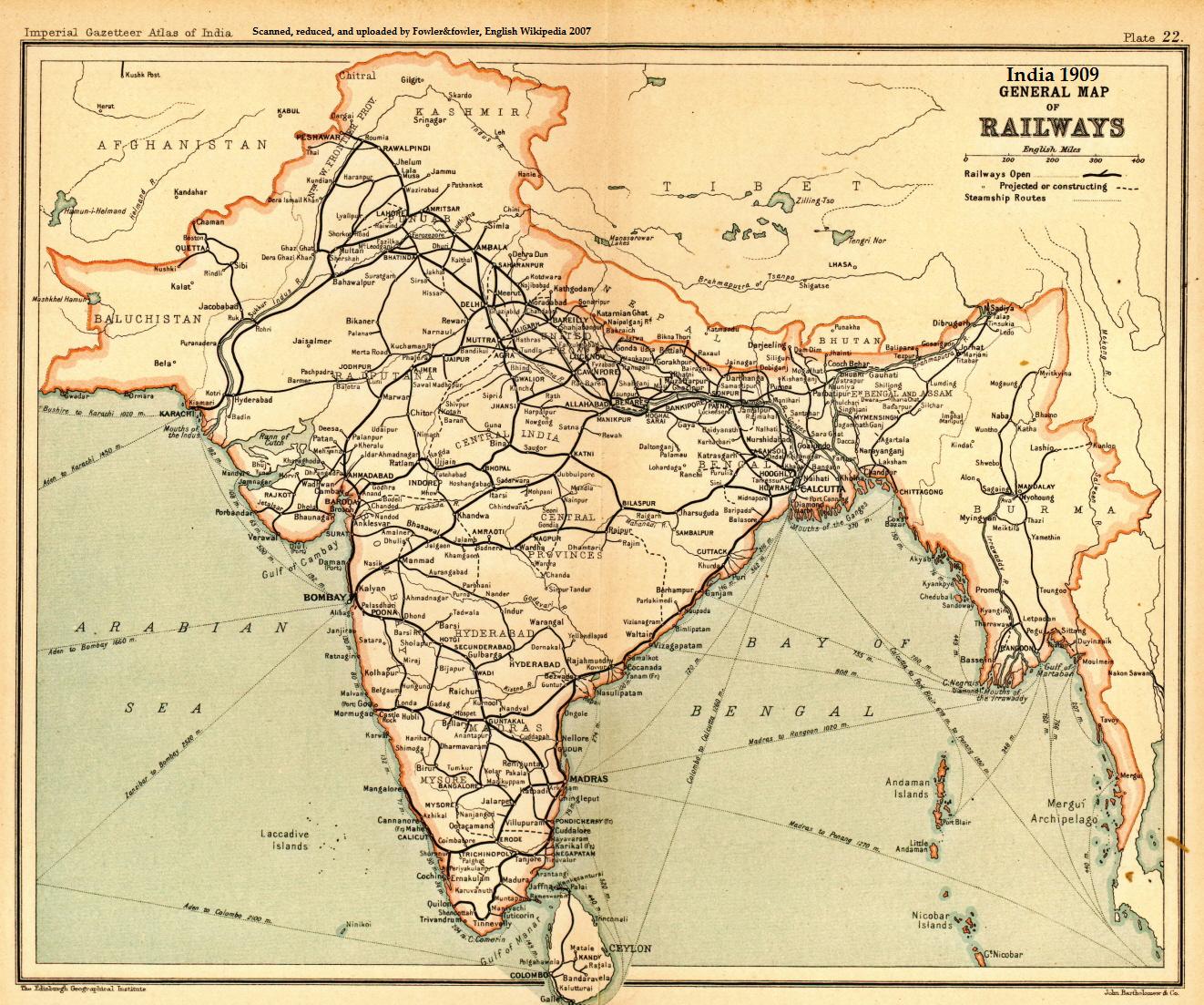
Rail Transport In Bihar
This article deals with the system of transport in Bihar, both public and private. Road transport Bihar has national highways with total length of and state highways with total length of . Also. Bihar has of proposed Expressways. Expressways National Highways State Highways Rail transport The railway network in Bihar is excellent and provides first-rate citizen centric railway services to the people. Most of the cities have a railway junction that facilitates railway travel across the state. You can easily travel from one part of the state to the other by trains. Urban Rail * Patna Metro - Under construction *Patna Monorail - Proposed * Patna tram - defunct since 1903 Water transport Bihar is connected by National Waterways No. 1 which established in October 1986. This National Waterways has fixed terminals at Haldia, BISN (Kolkata), Pakur, Farrakka and Patna. This National Waterways has also floating terminals facilities at Haldia, Kolkata, Diamon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Express Trains In India
Express trains are express rail services of India. Express trains make a small number of stops, unlike ordinary passenger or local trains. Because of their limited stops, these trains are able to obtain the highest speeds of any trains in India. An express train is one where the average speed, excluding halts, is greater than 42 km/h. Including halts the average speed often is below 42 km/h. Although this is pretty slow as compared to international standards, the "Express" trains here mean faster than the ordinary passenger and local trains. In some cases, trains run express where there is an overlapping passenger train service available, and run as passenger train, where there is no supplemental passenger service. Superfast Superfast trains are express trains which make still fewer stops, as compared to ordinary express trains, achieving still shorter journey times. Tickets cost more than ordinary express trains as they have "superfast surcharge" added to them. Tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transport In Delhi
Delhi has significant reliance on its transport infrastructure. The city has developed a highly efficient public transport system with the introduction of the Delhi Metro, which is undergoing a rapid modernization and expansion since 2006. There are 16.6 million registered vehicles in the city as of 30 June 2014, which is the highest in the world among all cities, most of which do not follow any pollution emission norm (within municipal limits), while the Delhi metropolitan region (NCR Delhi) has 11.2 million vehicles. Delhi and NCR lose nearly 42 crore (420 million) man-hours every month while commuting between home and office through public transport, due to the traffic congestion. Therefore, serious efforts, including a number of transport infrastructure projects, are under way to encourage usage of public transport in the city. History Prior to independence in the 1940s, public transport in the city was in private hands, with people relying mainly on tongas and the bus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kolkata–Jogbani Express
The Kolkata–Jogbani Express is an Express trains in India, Express train belonging to Eastern Railway zone that runs between and in India. It is currently being operated with 13159/13160 train numbers on twice in a week basis. Service The 13159/Kolkata–Jogbani Express has an average speed of 38 km/hr and covers 547 km in 14h 20m. The 13160/Jogbani–Kolkata Express has an average speed of 43 km/hr and covers 547 km in 12h 45m. Route and halts The important halts of the train are: * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Coach composition The train has standard ICF rakes with max speed of 110 kmph. The train consists of 20 coaches: * 2 AC II Tier cum AC III Tier * 2 AC III Tier * 8 Sleeper coaches * 6 General * 2 Seating cum Luggage Rake Traction Both trains are hauled by an Electric Loco Shed, Howrah-based WAP-4 from Kolkata till after which a Diesel Loco Shed, Siliguri-based WDP-4 took charge for rest of the journey till Jogbani. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anand Vihar Terminal Railway Station
Anand Vihar Terminal (station code: ANVT) is a railway station in the Anand Vihar locality of Delhi, India. It is under the administrative control of the Delhi Division of the Northern Railway zone of the Indian Railways. This station was officially inaugurated on 19 December 2009 by the then Union Railway minister Mamata Banerjee, and Chief Minister of Delhi Sheila Dixit. The terminal, spread over , is one of the largest railway stations and will cater to all East–bound trains from Delhi after the second phase becomes operational. History Anand Vihar Terminal railway station is developed as a terminal station of New Delhi. Delhi Sarai Rohilla Terminal and Hazrat Nizamuddin Terminal are two more railway terminals in the city of Delhi from where many regional and long-distance trains originate. Background The city of Delhi heavily depends on the rail transport to cater for the increasing load of passengers to their destinations. The long-distance trains from Delhi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jogbani Railway Station
Jogbani railway station serves Jogbani in Araria district in the Indian state of Bihar. See also *Indian Railways Indian Railways (IR) is a statutory body under the ownership of Ministry of Railways, Government of India that operates India's national railway system. It manages the fourth largest national railway system in the world by size, with a tot ... References Railway junction stations in Bihar Railway stations in Araria district {{Bihar-railstation-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Central Railway Zone
The East Central Railway (abbreviated ECR) is one of the 19 railway zones in India. It is headquartered at Hajipur and comprises Sonpur, Samastipur, Danapur, Pt. Deen Dayal Upadhyaya, and Dhanbad divisions. History First set up on 8 September 1996 with headquarters at Hajipur, Bihar, East Central Railway became operational on 1 October 2002 by carving out areas from Eastern and North Eastern Railway zones currently consists of the divisions viz. Dhanbad, Danapur, Mughalsarai of Eastern Railway and Sonpur and Samastipur of North Eastern Railway. The last 13 years of its existence has been full of challenges and every obstacle was dealt in a dedicated manner despite constraints of work force and infrastructure. ECR, has a vast network of 5402.693 track kilometers and 3707.988 route kilometers encompassing the states of Bihar, Jharkhand, Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh. Out of the route, have been electrified. ECR has been lifeline for the people in its expanse an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Railway Zone
The Northern Railway (NR) is one of the 19 Railway zones of India and the northernmost zone of the Indian Railways. It is headquartered at Baroda House in New Delhi. History Officially notified as a new railway zone on 14 April 1952, its origin goes back to 3 March 1859. On 14 April 1952, the Northern Railway zone was created by merging Jodhpur Railway, Bikaner Railway, Eastern Punjab Railway and three divisions of the East Indian Railway north-west of Mughalsarai ( Uttar Pradesh). On 3 March 1859, Allahabad–Kanpur, the first passenger railway line in North India was opened, which falls under Northern Railway zone. In 1864, a broad-gauge track from Calcutta to Delhi was laid. In 1864, the railway line between Old Delhi and Meerut City railway station was constructed. Meerut Cantt railway station was established by British India government around 1865 after the sepoy mutiny of 1857. In 1866, through trains started running on the East Indian Railway Com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |