|
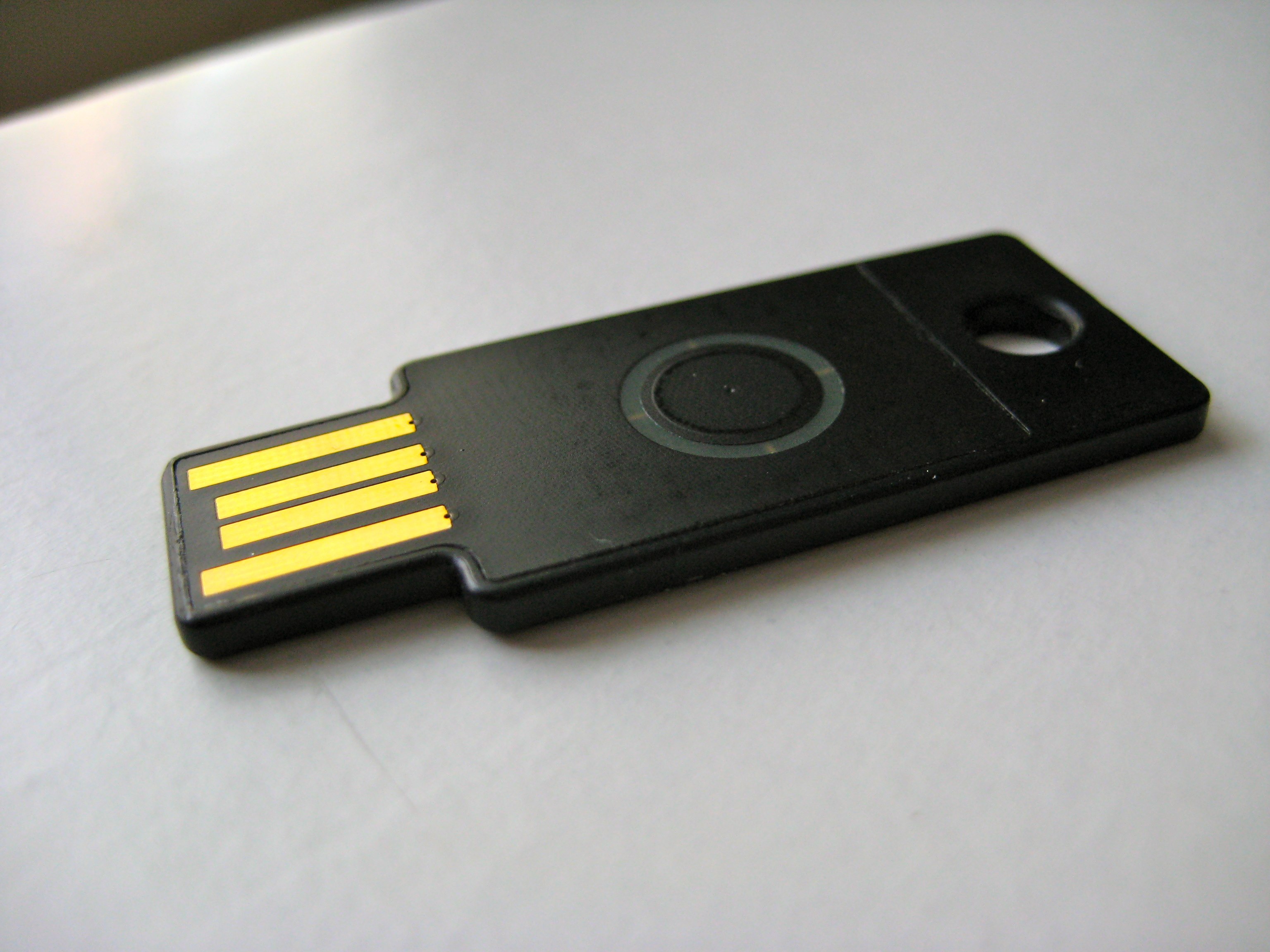
SecurID
RSA SecurID, formerly referred to as SecurID, is a mechanism developed by RSA for performing two-factor authentication for a user to a network resource. Description The RSA SecurID authentication mechanism consists of a " token"—either hardware (e.g. a key fob) or software (a soft token)—which is assigned to a computer user and which creates an authentication code at fixed intervals (usually 60 seconds) using a built-in clock and the card's factory-encoded almost random key (known as the "seed"). The seed is different for each token, and is loaded into the corresponding RSA SecurID server (RSA Authentication Manager, formerly ACE/Server) as the tokens are purchased. On-demand tokens are also available, which provide a tokencode via email or SMS delivery, eliminating the need to provision a token to the user. The token hardware is designed to be tamper-resistant to deter reverse engineering. When software implementations of the same algorithm ("software tokens") appe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SecureID Token New
RSA SecurID, formerly referred to as SecurID, is a mechanism developed by RSA Security, RSA for performing two-factor authentication for a user to a network resource. Description The RSA SecurID authentication mechanism consists of a "security token, token"—either hardware (e.g. a key fob) or software (a software token, soft token)—which is assigned to a computer user and which creates an authentication code at fixed intervals (usually 60 seconds) using a built-in clock and the card's factory-encoded almost random Key (cryptography), key (known as the "seed"). The seed is different for each token, and is loaded into the corresponding RSA SecurID server (RSA Authentication Manager, formerly ACE/Server) as the tokens are purchased. On-demand tokens are also available, which provide a tokencode via email or SMS delivery, eliminating the need to provision a token to the user. The token hardware is designed to be tamper resistance, tamper-resistant to deter reverse engineeri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RSA Security
RSA Security LLC, formerly RSA Security, Inc. and trade name RSA, is an American computer security, computer and network security company with a focus on encryption and decryption standards. RSA was named after the initials of its co-founders, Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir and Leonard Adleman, after whom the RSA (algorithm), RSA public key cryptography algorithm was also named. Among its products is the SecurID authentication token. The BSAFE cryptography libraries were also initially owned by RSA. RSA is known for incorporating backdoors developed by the National Security Agency, NSA in its products. It also organizes the annual RSA Conference, an information security conference. Founded as an independent company in 1982, RSA Security was acquired by EMC Corporation in 2006 for US$2.1 billion and operated as a division within EMC. When EMC was acquired by Dell Technologies in 2016, RSA became part of the Dell Technologies family of brands. On 10 March 2020, Dell Technologies announced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
One-time Password
A one-time password (OTP), also known as a one-time PIN, one-time passcode, one-time authorization code (OTAC) or dynamic password, is a password that is valid for only one login session or transaction, on a computer system or other digital device. OTPs avoid several shortcomings that are associated with traditional (static) password-based authentication; a number of implementations also incorporate two-factor authentication by ensuring that the one-time password requires access to ''something a person has'' (such as a small keyring fob device with the OTP calculator built into it, or a smartcard or specific cellphone) as well as ''something a person knows'' (such as a PIN). OTP generation algorithms typically make use of pseudorandomness or randomness to generate a shared key or seed, and cryptographic hash functions, which can be used to derive a value but are hard to reverse and therefore difficult for an attacker to obtain the data that was used for the hash. This is necessa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Engineering (security)
In the context of information security, social engineering is the use of psychological influence of people into performing actions or divulging Confidentiality, confidential information. This differs from psychological manipulation in that it doesn't need to be controlling, negative or a one-way transaction. Manipulation involves a zero-sum game where one party wins and the other loses while social engineering can be win-win for both parties. A type of confidence trick for the purpose of information gathering, fraud, or system access, it differs from a traditional "con" in the sense that it is often one of many steps in a more complex fraud scheme. It has also been defined as "any act that influences a person to take an action that may or may not be in their best interests." Research done in 2020 has indicated that social engineering will be one of the most prominent challenges of the upcoming decade. Having proficiency in social engineering will be increasingly important for orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Security Token
A security token is a peripheral device used to gain access to an electronically restricted resource. The token is used in addition to, or in place of, a password. Examples of security tokens include wireless key cards used to open locked doors, a banking token used as a digital authenticator for signing in to online banking, or signing transactions such as wire transfers. Security tokens can be used to store information such as passwords, cryptographic keys used to generate digital signatures, or biometric data (such as fingerprints). Some designs incorporate tamper resistant packaging, while others may include small keypads to allow entry of a PIN or a simple button to start a generation routine with some display capability to show a generated key number. Connected tokens utilize a variety of interfaces including USB, near-field communication (NFC), radio-frequency identification (RFID), or Bluetooth. Some tokens have audio capabilities designed for those who are visi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Key Fob
A keychain () (also keyring) is a small ring or chain of metal to which several keys, or fobs can be attached. The terms keyring and keychain are often used interchangeably to mean both the individual ring, or a combined unit of a ring and fob. The length of a keychain or fob may also allow an item to be used more easily than if connected directly to a keyring. Some keychains allow one or both ends to rotate, keeping the keychain from becoming twisted, while the item is being used. Use of keychains Advertising & Souvenirs Keychains are one of the most common souvenir and advertising items. In the 1950s and 1960s, with the improvement of plastic manufacturing techniques, promotional items including keychains became unique. Businesses could place their names and logos on promotional keychains that were three-dimensional for less cost than the standard metal keychains. Keychains are small and inexpensive enough to become promotional items for larger national companies t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smart Card
A smart card (SC), chip card, or integrated circuit card (ICC or IC card), is a card used to control access to a resource. It is typically a plastic credit card-sized card with an Embedded system, embedded integrated circuit (IC) chip. Many smart cards include a pattern of metal contacts to electrically connect to the internal chip. Others are Contactless smart card, contactless, and some are both. Smart cards can provide personal identification, authentication, data storage, and application processing. Applications include identification, financial, public transit, computer security, schools, and healthcare. Smart cards may provide strong security authentication for single sign-on (SSO) within organizations. Numerous nations have deployed smart cards throughout their populations. The universal integrated circuit card (UICC) for mobile phones, installed as pluggable SIM card or embedded eSIM, is also a type of smart card. , 10.5billion smart card IC chips are manufactured annually ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-factor Authentication
Multi-factor authentication (MFA; two-factor authentication, or 2FA) is an electronic authentication method in which a user is granted access to a website or Application software, application only after successfully presenting two or more distinct types of evidence (or Authentication#Authentication factors, factors) to an authentication mechanism. MFA protects personal data—which may include personal identification or financial assets—from being accessed by an unauthorized third party that may have been able to discover, for example, a single password. Usage of MFA has increased in recent years. Security issues which can cause the bypass of MFA are #Fatigue attack, fatigue attacks, phishing and SIM swap scam, SIM swapping. Accounts with MFA enabled are significantly less likely to be compromised. Authentication factors Authentication takes place when someone tries to log into a computer resource (such as a computer network, device, or application). The resource requires ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VASCO Data Security International, Inc
Vasco may refer to: People Given name Middle Ages * Vasco da Gama (c. 1460s–1524), Portuguese explorer * Vasco Núñez de Balboa (1475–1519), Spanish conquistador * Vasco Fernandes Coutinho, captain of Espírito Santo (1490–1561), Portuguese nobleman and first donatary of the Captaincy of Espírito Santo * Vasco Fernandes (artist) (1475–1540), Portuguese painter * Vasco de Quiroga (1470/78–1565), Spanish bishop and judge, first bishop of Michoacán, Mexico * Vasco Martins de Sousa (1320s–1387), Lord of Mortágua and Chancellor mor under King Peter I of Portugal Modern world * Vasco Cordeiro (born 1973), Portuguese politician * Vasco da Gama Fernandes (1908–1991), Portuguese politician, Chairman of the Portuguese Parliament * Vasco Fernandes (footballer) (born 1986), Portuguese footballer * Vasco Gonçalves, Portuguese army officer and Prime Minister of Portugal from 1974 to 1975 * Vasco Lopes (born 1999), Portuguese footballer * Vasco Oliveira (footballer, born 192 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freescale Semiconductor
Freescale Semiconductor, Inc. was an American semiconductor manufacturer. It was created by the divestiture of the Semiconductor Products Sector of Motorola in 2004. Freescale focused their integrated circuit products on the automotive, embedded and communications markets. It was bought by a private investor group in 2006, and subsequently merged with NXP Semiconductors in 2015. History Divestiture from Motorola and first IPO As of 2003, Motorola Semiconductor Products Sector earned US$5.0 billion in semiconductor sales in 2002 (out of US$27 billion sales for all of Motorola). Motorola announced that their semiconductor division would be divested on October 6, 2003 and would have a temporary name ''SPS Spinco''. Freescale completed its Initial public offering (IPO) on July 16, 2004, at a price of US$13. In its announcement, it estimated the stock price to be US$17.50- 19.50 but following a cooling of the market towards tech stocks, it lowered its price to US$13. Existing sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |