|
Secretory Leukocyte Protease Inhibitor
Antileukoproteinase, also known as secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor (SLPI), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''SLPI'' gene. SLPI is a highly cationic single-chain protein with eight intramolecular disulfide bonds. It is found in large quantities in bronchial, cervical, and nasal mucosa, saliva, and seminal fluids. SLPI inhibits human leukocyte elastase, human cathepsin G, human trypsin, neutrophil elastase, and mast cell chymase. X-ray crystallography has shown that SLPI has two homologous domains of 53 and 54 amino acids, one of which exhibits anti-protease activity (C-terminal domain). The other domain (N-terminal domain) is not known to have any function. Function This gene encodes a secreted inhibitor which protects epithelial tissues from serine proteases. It is found in various secretions including seminal plasma, cervical mucus, and bronchial secretions, and has affinity for trypsin, leukocyte elastase, and cathepsin G. Its inhibitory effect contrib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parotid Duct
The parotid duct or Stensen duct is a salivary duct. It is the route that saliva takes from the major salivary gland, the parotid gland, into the mouth. Structure The parotid duct is formed when several interlobular ducts, the largest ducts inside the parotid gland, join. It emerges from the parotid gland. It runs forward along the lateral side of the masseter muscle for around 7 cm. In this course, the duct is surrounded by the buccal fat pad. It takes a steep turn at the border of the masseter muscle and passes through the buccinator muscle, opening into the vestibule of the mouth, the region of the mouth between the cheek and the gums, at the parotid papilla, which lies opposite to the second maxillary (upper) molar tooth. The parotid papillae can be palpated as small raised tissue area ( papillae) on both sides of the mouth and protects the opening of the parotid duct. The buccinator acts as a valve that prevents air forcing into the duct, which would cause pneumoparotiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PLSCR4
Phospholipid scramblase 4, also known as Ca2+-dependent phospholipid scramblase 4, is a protein that is encoded in humans by the ''PLSCR4'' gene. See also * Scramblase Scramblase is a protein responsible for the translocation of phospholipids between the two monolayers of a lipid bilayer of a cell membrane. In humans, phospholipid scramblases (PLSCRs) constitute a family of five homologous proteins tha ... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * {{gene-3-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PLSCR1
Phospholipid scramblase 1 (PL scramblase 1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PLSCR1'' gene. Interactions PLSCR1 has been shown to Protein-protein interaction, interact with: * CPSF6, * Epidermal growth factor receptor, * NEU4, * SHC1, * SLPI, and * TFG (gene), TFG. See also *Scramblase References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-3-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
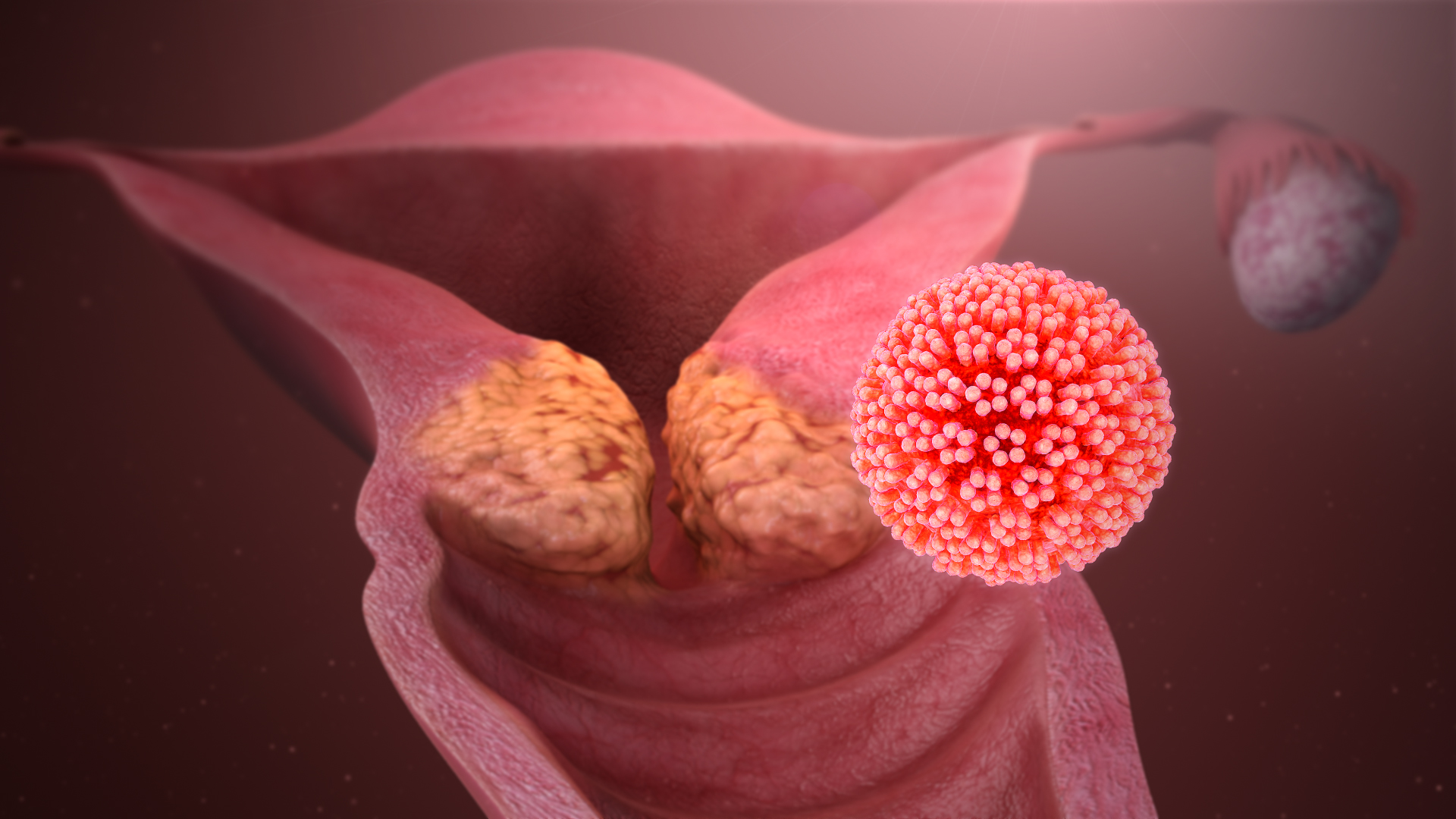
Human Papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the ''Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and results in either warts or precancerous lesions. All warts are caused by HPV. These lesions, depending on the site affected, increase the risk of cancer of the cervical cancer, cervix, vulva cancer, vulva, vaginal cancer, vagina, penis cancer, penis, anal cancer, anus, oropharyngeal cancer, mouth, tonsils, or throat. Nearly all cervical cancer is due to HPV, and two strains – HPV16 and HPV18 – account for 70% of all cases. HPV16 is responsible for almost 90% of HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancers. Between 60% and 90% of the other cancers listed above are also linked to HPV. HPV6 and HPV11 are common causes of genital warts and laryngeal papillomatosis. An HPV infection is caused by the ''human papillomavirus'', a DNA virus from the papi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living Cell (biology), cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898, more than 16,000 of the millions of List of virus species, virus species have been described in detail. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent viral particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) genetic material, i.e., long ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is an Inflammation, inflammatory condition of the lung primarily affecting the small air sacs known as Pulmonary alveolus, alveoli. Symptoms typically include some combination of Cough#Classification, productive or dry cough, chest pain, fever, and Shortness of breath, difficulty breathing. The severity of the condition is variable. Pneumonia is usually caused by infection with viruses or bacteria, and less commonly by other microorganisms. Identifying the responsible pathogen can be difficult. Diagnosis is often based on symptoms and physical examination. Chest X-rays, blood tests, and Microbiological culture, culture of the sputum may help confirm the diagnosis. The disease may be classified by where it was acquired, such as community- or hospital-acquired or healthcare-associated pneumonia. Risk factors for pneumonia include cystic fibrosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), sickle cell disease, asthma, diabetes, heart failure, a history of smoking, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asthma
Asthma is a common long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. A sudden worsening of asthma symptoms sometimes called an 'asthma attack' or an 'asthma exacerbation' can occur when allergens, pollen, dust, or other particles, are inhaled into the lungs, causing the bronchioles to constrict and produce mucus, which then restricts oxygen flow to the alveoli. These may occur a few times a day or a few times per week. Depending on the person, asthma symptoms may become worse at night or with exercise. Asthma is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Environmental factors include exposure to air pollution and allergens. Other potential triggers include medications such as aspirin and beta blockers. Diag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha 1-antitrypsin
Alpha-1 antitrypsin or α1-antitrypsin (A1AT, α1AT, A1A, or AAT) is a protein belonging to the serpin superfamily. It is encoded in humans by the ''SERPINA1'' gene. A protease inhibitor, it is also known as alpha1–proteinase inhibitor (A1PI) or alpha1-antiproteinase (A1AP) because it inhibits various proteases (not just trypsin). As a type of enzyme inhibitor, it protects tissues from enzymes of inflammatory cells, especially neutrophil elastase. When the blood contains inadequate or defective A1AT (as in alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency), neutrophil elastase can excessively break down elastin, leading to the loss of elasticity in the lungs. This results in respiratory issues, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, in adults. Normally, A1AT is produced in the liver and enters the systemic circulation. However, defective A1AT may accumulate in the liver, potentially causing cirrhosis in both adults and children. A1AT not only binds to neutrophil elastase from in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
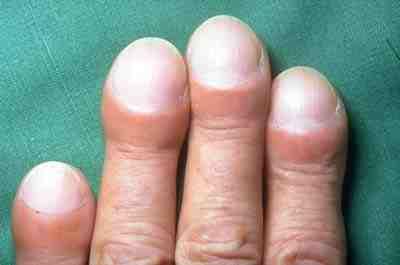
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) synonymous with cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis is a rare, progressive illness of the respiratory system, characterized by the thickening and stiffening of lung tissue, associated with the formation of scar tissue. It is a type of chronic pulmonary fibrosis characterized by a progressive and irreversible decline in lung function. The tissue in the lungs becomes thick and stiff, which affects the tissue that surrounds the air sacs in the lungs. Symptoms typically include gradual onset of dypsnea, shortness of breath and a dry cough. Other changes may include feeling tired, and nail clubbing, clubbing abnormally large and dome shaped finger and toenails. Complications may include pulmonary hypertension, heart failure, pneumonia or pulmonary embolism. The cause is unknown, hence the term Idiopathic disease, idiopathic. Risk factors include cigarette smoking, gastroesophageal reflux disease, certain viral infections, and genetic predisposition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder inherited in an autosomal recessive manner that impairs the normal clearance of Sputum, mucus from the lungs, which facilitates the colonization and infection of the lungs by bacteria, notably ''Staphylococcus aureus''. CF is a rare genetic disorder that affects mostly the lungs, but also the pancreas, liver, kidneys, and intestine. The hallmark feature of CF is the accumulation of thick mucus in different organs. Long-term issues include Shortness of breath, difficulty breathing and coughing up mucus as a result of frequent pneumonia, lung infections. Other signs and symptoms may include Sinusitis, sinus infections, failure to thrive, poor growth, Steatorrhea, fatty stool, Nail clubbing, clubbing of the fingers and toes, and infertility in most males. Different people may have different degrees of symptoms. Cystic fibrosis is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. It is caused by the presence of mutations in both copies (alleles) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |