|
Secondary Sex Characteristic
A secondary sex characteristic is a physical characteristic of an organism that is related to or derived from its sex, but not directly part of its reproductive system. In humans, these characteristics typically start to appear during puberty—and include enlarged breasts and widened hips of females, facial hair and Adam's apples on males, and pubic hair on both. In non-human animals, they can start to appear at sexual maturity—and include, for example, the manes of male lions, the bright facial and rump coloration of male mandrills, and horns in many goats and antelopes. Secondary sex characteristics are particularly evident in the sexually dimorphic phenotypic traits that distinguish the sexes of a species. In evolution, secondary sex characteristics are the product of sexual selection for traits that show fitness, giving an organism an advantage over its rivals in courtship and in aggressive interactions. Many characteristics are believed to have been establishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peacock
Peafowl is a common name for two bird species of the genus '' Pavo'' and one species of the closely related genus '' Afropavo'' within the tribe Pavonini of the family Phasianidae (the pheasants and their allies). Male peafowl are referred to as peacocks, and female peafowl are referred to as peahens. The two Asiatic species are the blue or Indian peafowl originally from the Indian subcontinent, and the green peafowl from Southeast Asia. The third peafowl species, the Congo peafowl, is native only to the Congo Basin. Male peafowl are known for their piercing calls and their extravagant plumage. The latter is especially prominent in the Asiatic species, which have an eye-spotted "tail" or "train" of covert feathers, which they display as part of a courtship ritual. The functions of the elaborate iridescent coloration and large "train" of peacocks have been the subject of extensive scientific debate. Charles Darwin suggested that they served to attract females, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
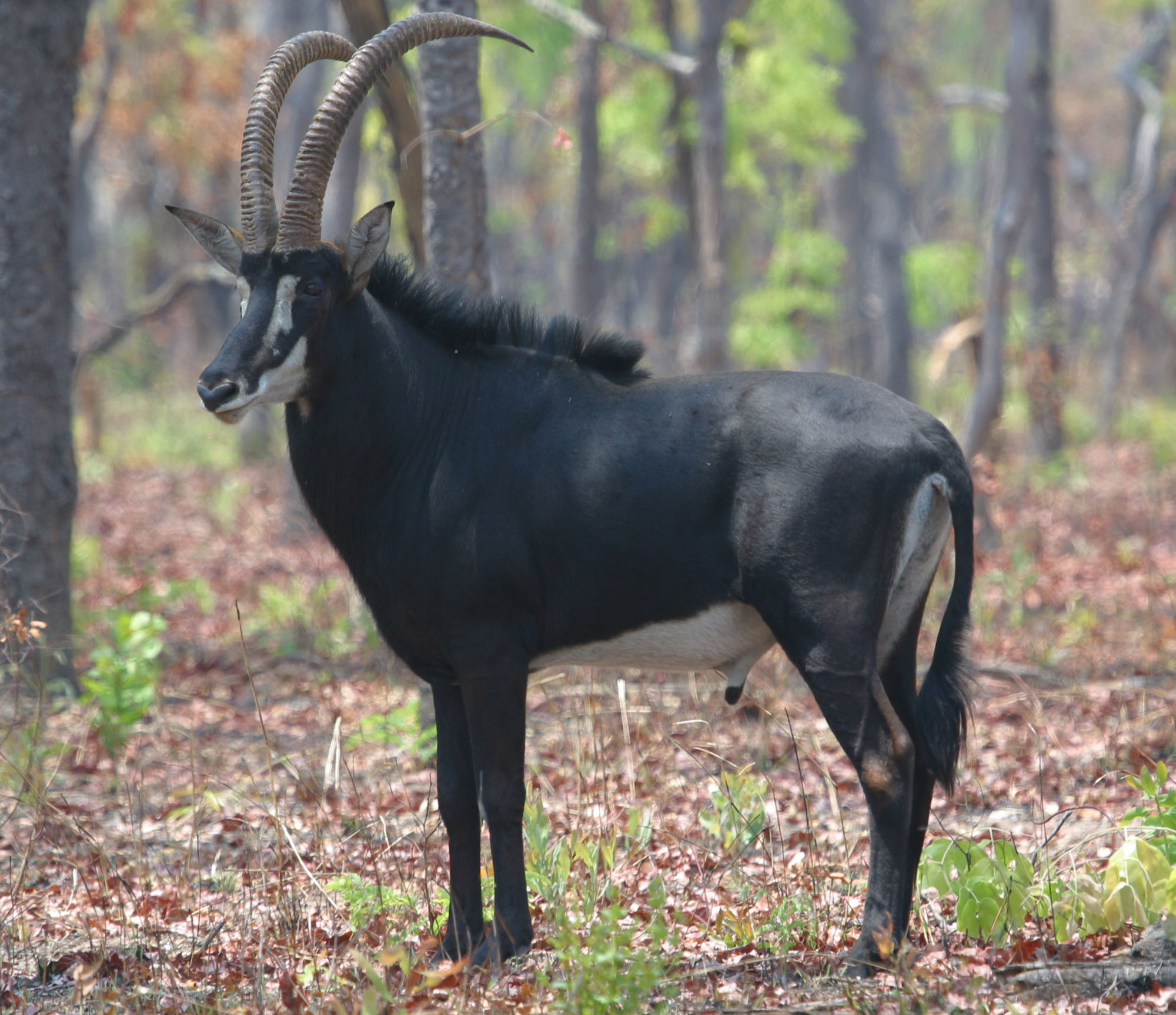
Antelope
The term antelope refers to numerous extant or recently extinct species of the ruminant artiodactyl family Bovidae that are indigenous to most of Africa, India, the Middle East, Central Asia, and a small area of Eastern Europe. Antelopes do not form a monophyletic group, as some antelopes are more closely related to other bovid groups, such as bovines, goats, and sheep, than to other antelopes. A stricter grouping, known as the true antelopes, includes only the genera '' Gazella'', '' Nanger'', '' Eudorcas'', and '' Antilope''. One North American mammal, the pronghorn or "pronghorn antelope", is colloquially referred to as the "American antelope", despite the fact that it belongs to a completely different family ( Antilocapridae) than the true Old-World antelopes; pronghorn are the sole extant member of an extinct prehistoric lineage that once included many unique species. Although antelope are sometimes referred to, and easily misidentified as, "deer" ( cervids), true ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Female
An organism's sex is female ( symbol: ♀) if it produces the ovum (egg cell), the type of gamete (sex cell) that fuses with the male gamete (sperm cell) during sexual reproduction. A female has larger gametes than a male. Females and males are results of the anisogamous reproduction system, wherein gametes are of different sizes (unlike isogamy where they are the same size). The exact mechanism of female gamete evolution remains unknown. In species that have males and females, sex-determination may be based on either sex chromosomes, or environmental conditions. Most female mammals, including female humans, have two X chromosomes. Characteristics of organisms with a female sex vary between different species, having different female reproductive systems, with some species showing characteristics secondary to the reproductive system, as with mammary glands in mammals. In humans, the word ''female'' can also be used to refer to gender in the social sense of gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Male
Male (Planet symbols, symbol: ♂) is the sex of an organism that produces the gamete (sex cell) known as sperm, which fuses with the larger female gamete, or Egg cell, ovum, in the process of fertilisation. A male organism cannot sexual reproduction, reproduce sexually without access to at least one ovum from a female, but some organisms can reproduce both sexually and Asexual reproduction, asexually. Most male mammals, including male humans, have a Y chromosome, which codes for the production of larger amounts of testosterone to develop male reproductive organs. In humans, the word ''male'' can also be used to refer to gender, in the social sense of gender role or gender identity. Overview The existence of separate sexes has evolved independently at different times and in different lineage (evolution), lineages, an example of convergent evolution. The repeated pattern is sexual reproduction in isogamy, isogamous species with two or more mating types with gametes of identic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Coloration
Animal coloration is the general appearance of an animal resulting from the reflection or emission of light from its surfaces. Some animals are brightly coloured, while others are hard to see. In some species, such as the peafowl, the male has strong patterns, conspicuous colours and is iridescent, while the female is far less visible. There are several separate reasons why animals have evolved colours. Camouflage enables an animal to remain hidden from view. Animals use colour to advertising in biology, advertise services such as cleaning symbiosis, cleaning to animals of other species; to signalling theory, signal their Sexual selection, sexual status to other members of the same species; and in mimicry, taking advantage of the aposematism, warning coloration of another species. Some animals use flashes of colour to divert attacks by deimatic behaviour, startling predators. Zebras may possibly use motion dazzle, confusing a predator's attack by moving a bold pattern rapidly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fisherian Runaway
Fisherian runaway or runaway selection is a sexual selection mechanism proposed by the mathematical biologist Ronald Fisher in the early 20th century, to account for the evolution of ostentatious male ornamentation by persistent, directional female choice. An example is the colourful and elaborate peacock plumage compared to the relatively subdued peahen plumage; the costly ornaments, notably the bird's extremely long tail, appear to be incompatible with natural selection. Fisherian runaway can be postulated to include sexually dimorphic phenotypic traits such as behavior expressed by a particular sex. Extreme and (seemingly) maladaptive sexual dimorphism represented a paradox for evolutionary biologists from Charles Darwin's time up to the modern synthesis. Darwin attempted to resolve the paradox by assuming heredity for both the preference and the ornament, and supposed an "aesthetic sense" in higher animals, leading to powerful selection of both characteristics in subseque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
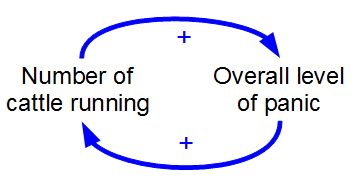
Positive Feedback
Positive feedback (exacerbating feedback, self-reinforcing feedback) is a process that occurs in a feedback loop where the outcome of a process reinforces the inciting process to build momentum. As such, these forces can exacerbate the effects of a small disturbance. That is, the effects of a perturbation on a system include an increase in the magnitude of the perturbation. That is, ''A produces more of B which in turn produces more of A''.Keesing, R.M. (1981). Cultural anthropology: A contemporary perspective (2nd ed.) p.149. Sydney: Holt, Rinehard & Winston, Inc. In contrast, a system in which the results of a change act to reduce or counteract it has negative feedback. Both concepts play an important role in science and engineering, including biology, chemistry, and cybernetics. Mathematically, positive feedback is defined as a positive loop gain around a closed loop of cause and effect. That is, positive feedback is Phase (waves), in phase with the input, in the sense that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Routledge
Routledge ( ) is a British multinational corporation, multinational publisher. It was founded in 1836 by George Routledge, and specialises in providing academic books, academic journals, journals and online resources in the fields of the humanities, behavioral science, behavioural science, education, law, and social science. The company publishes approximately 1,800 journals and 5,000 new books each year and their backlist encompasses over 140,000 titles. Routledge is claimed to be the largest global academic publisher within humanities and social sciences. In 1998, Routledge became a subdivision and Imprint (trade name), imprint of its former rival, Taylor & Francis, Taylor & Francis Group (T&F), as a result of a £90-million acquisition deal from Cinven, a venture capital group which had purchased it two years previously for £25 million. Following the merger of Informa and T&F in 2004, Routledge became a publishing unit and major imprint within the Informa "academic publishing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aggression
Aggression is behavior aimed at opposing or attacking something or someone. Though often done with the intent to cause harm, some might channel it into creative and practical outlets. It may occur either reactively or without provocation. In humans, aggression can be caused by various triggers. For example, built-up frustration due to blocked goals or perceived disrespect. Human aggression can be classified into direct and indirect aggression; while the former is characterized by physical or verbal behavior intended to cause harm to someone, the latter is characterized by behavior intended to harm the social relations of an individual or group. In definitions commonly used in the social sciences and behavioral sciences, aggression is an action or response by an individual that delivers something unpleasant to another person. Some definitions include that the individual must intend to harm another person. In an interdisciplinary perspective, aggression is regarded as "an ensem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courtship
Courtship is the period wherein some couples get to know each other prior to a possible marriage or committed romantic, ''de facto'' relationship. Courtship traditionally may begin after a betrothal and may conclude with the celebration of marriage. A courtship may be an informal and private matter between two people or may be a public affair, or a formal arrangement with family approval. Traditionally, in the case of a formal cisnormative heterosexual engagement, it is the role of a male to actively "court" or "woo" a female, thus encouraging her to understand him and her receptiveness to a marriage proposal. Courtship as a social practice is a relatively recent phenomenon, emerging only within the last few centuries. From the standpoint of anthropology and sociology, courtship is linked with other institutions such as marriage and the family which have changed rapidly, having been subject to the effects of advances in technology and medicine. In non-human animals, ''courts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fitness (biology)
Fitness (often denoted w or ω in population genetics models) is a quantitative representation of individual reproductive success. It is also equal to the average contribution to the gene pool of the next generation, made by the same individuals of the specified genotype or phenotype. Fitness can be defined either with respect to a genotype or to a phenotype in a given environment or time. The fitness of a genotype is manifested through its phenotype, which is also affected by the developmental environment. The fitness of a given phenotype can also be different in different selective environments. With asexual reproduction, it is sufficient to assign fitnesses to genotypes. With sexual reproduction, recombination scrambles alleles into different genotypes every generation; in this case, fitness values can be assigned to alleles by averaging over possible genetic backgrounds. Natural selection tends to make alleles with higher fitness more common over time, resulting in Darwini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Selection
Sexual selection is a mechanism of evolution in which members of one sex mate choice, choose mates of the other sex to mating, mate with (intersexual selection), and compete with members of the same sex for access to members of the opposite sex (intrasexual selection). These two forms of selection mean that some individuals have greater reproductive success than others within a population, for example because they are more Animal sexual behaviour, attractive or prefer more attractive partners to produce offspring. Successful males benefit from frequent mating and monopolizing access to one or more fertile females. Females can maximise the return on the energy they invest in reproduction by selecting and mating with the best males. The concept was first articulated by Charles Darwin who wrote of a "second agency" other than natural selection, in which competition between mate candidates could lead to speciation. The theory was given a mathematical basis by Ronald Fisher in the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |