|
Second Preimage
In cryptography, a preimage attack on cryptographic hash functions tries to find a message that has a specific hash value. A cryptographic hash function should resist attacks on its preimage (set of possible inputs). In the context of attack, there are two types of preimage resistance: * ''preimage resistance'': for essentially all pre-specified outputs, it is computationally infeasible to find any input that hashes to that output; i.e., given , it is difficult to find an such that . * ''second-preimage resistance'': for a specified input, it is computationally infeasible to find another input which produces the same output; i.e., given , it is difficult to find a second input such that . These can be compared with a collision resistance, in which it is computationally infeasible to find any two distinct inputs , that hash to the same output; i.e., such that . Collision resistance implies second-preimage resistance. Second-preimage resistance implies preimage resistance only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptography
Cryptography, or cryptology (from "hidden, secret"; and ''graphein'', "to write", or ''-logy, -logia'', "study", respectively), is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of Adversary (cryptography), adversarial behavior. More generally, cryptography is about constructing and analyzing Communication protocol, protocols that prevent third parties or the public from reading private messages. Modern cryptography exists at the intersection of the disciplines of mathematics, computer science, information security, electrical engineering, digital signal processing, physics, and others. Core concepts related to information security (confidentiality, data confidentiality, data integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation) are also central to cryptography. Practical applications of cryptography include electronic commerce, Smart card#EMV, chip-based payment cards, digital currencies, password, computer passwords, and military communications. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Password
A password, sometimes called a passcode, is secret data, typically a string of characters, usually used to confirm a user's identity. Traditionally, passwords were expected to be memorized, but the large number of password-protected services that a typical individual accesses can make memorization of unique passwords for each service impractical. Using the terminology of the NIST Digital Identity Guidelines, the secret is held by a party called the ''claimant'' while the party verifying the identity of the claimant is called the ''verifier''. When the claimant successfully demonstrates knowledge of the password to the verifier through an established authentication protocol, the verifier is able to infer the claimant's identity. In general, a password is an arbitrary String (computer science), string of character (computing), characters including letters, digits, or other symbols. If the permissible characters are constrained to be numeric, the corresponding secret is sometimes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainbow Table
A rainbow table is a precomputed table for caching the outputs of a cryptographic hash function, usually for cracking password hashes. Passwords are typically stored not in plain text form, but as hash values. If such a database of hashed passwords falls into the hands of attackers, they can use a precomputed rainbow table to recover the plaintext passwords. A common defense against this attack is to compute the hashes using a key derivation function that adds a "salt" to each password before hashing it, with different passwords receiving different salts, which are stored in plain text along with the hash. Rainbow tables are a practical example of a space–time tradeoff: they use less computer processing time and more storage than a brute-force attack which calculates a hash on every attempt, but more processing time and less storage than a simple table that stores the hash of every possible password. Rainbow tables were invented by Philippe Oechslin as an application of an ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puzzle Friendliness
In cryptography, puzzle friendliness is a property of cryptographic hash functions. Not all cryptographic hash functions have this property. SHA-256 is a cryptographic hash function that has this property. Informally, a hash function is puzzle friendly if no solution exists, which is better than just making random guesses and the only way to find a solution is the brute force method. Although the property is very general, it is of particular importance to proof-of-work, such as in Bitcoin mining. Definition Here is the formal technical definition of the puzzle friendliness property. * A hash function ''H'' is said to be ''puzzle friendly'' if for every possible ''n''-bit output value ''y'', if ''k'' is chosen with a distribution with high min-entropy, then it is infeasible to find ''x'' such that ''H''( ''k'' , , ''x'' ) = ''y'' (where the symbol ", , " denotes concatenation) in time significantly less than 2''n''. In the above definition, the distribution has high min-entropy me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hash Function Security Summary
This article summarizes publicly known attacks against cryptographic hash functions. Note that not all entries may be up to date. For a summary of other hash function parameters, see comparison of cryptographic hash functions. Table color key Common hash functions Collision resistance Chosen prefix collision attack Preimage resistance Length extension *Vulnerable: MD5, SHA1, SHA256, SHA512 *Not vulnerable: SHA384, SHA-3, BLAKE2 Less-common hash functions Collision resistance Preimage resistance Attacks on hashed passwords Hashes described here are designed for fast computation and have roughly similar speeds. Because most users typically choose short passwords formed in predictable ways, passwords can often be recovered from their hashed value if a fast hash is used. Searches on the order of 100 billion tests per second are possible with high-end graphics processors. Special hashes called key derivation functions have been created to slow brute for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryptographic Hash Function
A cryptographic hash function (CHF) is a hash algorithm (a map (mathematics), map of an arbitrary binary string to a binary string with a fixed size of n bits) that has special properties desirable for a cryptography, cryptographic application: * the probability of a particular n-bit output result (hash value) for a random input string ("message") is 2^ (as for any good hash), so the hash value can be used as a representative of the message; * finding an input string that matches a given hash value (a ''pre-image'') is infeasible, ''assuming all input strings are equally likely.'' The ''resistance'' to such search is quantified as security strength: a cryptographic hash with n bits of hash value is expected to have a ''preimage resistance'' strength of n bits, unless the space of possible input values is significantly smaller than 2^ (a practical example can be found in ); * a ''second preimage'' resistance strength, with the same expectations, refers to a similar problem of f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birthday Attack
A birthday attack is a bruteforce collision attack that exploits the mathematics behind the birthday problem in probability theory. This attack can be used to abuse communication between two or more parties. The attack depends on the higher likelihood of collisions found between random attack attempts and a fixed degree of permutations ( pigeonholes). Let H be the number of possible values of a hash function, with H=2^l. With a birthday attack, it is possible to find a collision of a hash function with 50% chance in \sqrt = 2^, where l is the bit length of the hash output, and with 2^ being the classical preimage resistance security with the same probability. There is a general (though disputed) result that quantum computers can perform birthday attacks, thus breaking collision resistance, in \sqrt = 2^. Although there are some digital signature vulnerabilities associated with the birthday attack, it cannot be used to break an encryption scheme any faster than a brute-for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt (cryptography)
In cryptography, a salt is random data fed as an additional input to a one-way function that hashes data Data ( , ) are a collection of discrete or continuous values that convey information, describing the quantity, quality, fact, statistics, other basic units of meaning, or simply sequences of symbols that may be further interpreted for ..., a password or passphrase. Salting helps defend against attacks that use precomputed tables (e.g. rainbow tables), by vastly growing the size of table needed for a successful attack. It also helps protect passwords that occur multiple times in a database, as a new salt is used for each password instance. Additionally, salting does not place any burden on users. Typically, a unique salt is randomly generated for each password. The salt and the password (or its version after key stretching) are concatenated and fed to a cryptographic hash function, and the output hash value is then stored with the salt in a database. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Password Cracking
In cryptanalysis and computer security, password cracking is the process of guessing passwords protecting a computer system. A common approach (brute-force attack) is to repeatedly try guesses for the password and to check them against an available cryptographic hash of the password. Another type of approach is password spraying, which is often automated and occurs slowly over time in order to remain undetected, using a list of common passwords. The purpose of password cracking might be to help a user recover a forgotten password (due to the fact that installing an entirely new password would involve System Administration privileges), to gain unauthorized access to a system, or to act as a preventive measure whereby system administrators check for easily crackable passwords. On a file-by-file basis, password cracking is utilized to gain access to digital evidence to which a judge has allowed access, when a particular file's permissions restricted. Time needed for password searche ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
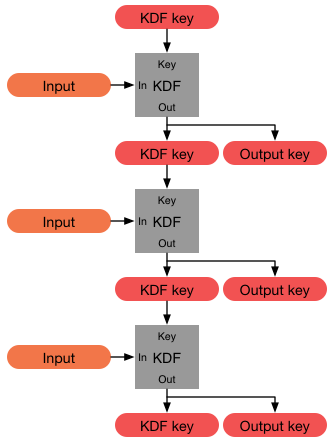
Key Derivation Function
In cryptography, a key derivation function (KDF) is a cryptographic algorithm that derives one or more secret keys from a secret value such as a master key, a password, or a passphrase using a pseudorandom function (which typically uses a cryptographic hash function or block cipher). KDFs can be used to stretch keys into longer keys or to obtain keys of a required format, such as converting a group element that is the result of a Diffie–Hellman key exchange into a symmetric key for use with AES. Keyed cryptographic hash functions are popular examples of pseudorandom functions used for key derivation. History The first deliberately slow (key stretching) password-based key derivation function was called "crypt" (or "crypt(3)" after its man page), and was invented by Robert Morris in 1978. It would encrypt a constant (zero), using the first 8 characters of the user's password as the key, by performing 25 iterations of a modified DES encryption algorithm (in which a 12-b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ars Technica
''Ars Technica'' is a website covering news and opinions in technology, science, politics, and society, created by Ken Fisher and Jon Stokes in 1998. It publishes news, reviews, and guides on issues such as computer hardware and software, science, technology policy, and video games. ''Ars Technica'' was privately owned until May 2008, when it was sold to Condé Nast Digital, the online division of Condé Nast Publications. Condé Nast purchased the site, along with two others, for $25 million and added it to the company's ''Wired'' Digital group, which also includes '' Wired'' and, formerly, Reddit. The staff mostly works from home and has offices in Boston, Chicago, London, New York City, and San Francisco. The operations of ''Ars Technica'' are funded primarily by advertising, and it has offered a paid subscription service since 2001. History Ken Fisher, who serves as the website's current editor-in-chief, and Jon Stokes created ''Ars Technica'' in 1998. Its purpose was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Collision Attack
In cryptography, a collision attack on a cryptographic hash tries to find two inputs producing the same hash value, i.e. a hash collision. This is in contrast to a preimage attack where a specific target hash value is specified. There are roughly two types of collision attacks: ;Classical collision attack: Find two different messages ''m''1 and ''m''2 such that ''hash''(''m''1) = ''hash''(''m''2). More generally: ;Chosen-prefix collision attack: Given two different prefixes ''p''1 and ''p''2, find two suffixes ''s''1 and ''s''2 such that ''hash''(''p''1 ∥ ''s''1) = ''hash''(''p''2 ∥ ''s''2), where ∥ denotes the concatenation operation. Classical collision attack Much like symmetric-key ciphers are vulnerable to brute force attacks, every cryptographic hash function is inherently vulnerable to collisions using a birthday attack. Due to the birthday problem, these attacks are much faster than a brute force would be. A hash of ''n'' bits can be broken in 2''n''/2 time steps (e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |