|
Second Battle Of Ulrichen
The Second Battle of Ulrichen was fought in 1419 between the Old Swiss Confederacy led by Bern and rebels from Valais near Ulrichen (now part of Obergoms) in the district of Goms in the canton of Valais in Switzerland. Negotiations after the battle led to the end of the Raron affair and self-determination for Valais. Background During the late 14th century and early 15th century the residents of Valais were seeking independence from the Duke of Savoy. Around the same time the local noble Raron family had grown into one of the most powerful families in Valais. In 1413/14 the Emperor Sigismund had granted authority over the region to Prince-Bishop Wilhelm II of Raron and his uncle Witschard of Raron. Fearing a loss of their rights and privileges a rebellious movement had sprung up in the valley. When the baron supported a Savoy invasion of the Ossola south of Valais the leaders of the movement became increasingly concerned. In 1415 open rebellion broke out in the valley. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canton Of Valais
Valais ( , ; ), more formally, the Canton of Valais or Wallis, is one of the cantons of Switzerland, 26 cantons forming the Switzerland, Swiss Confederation. It is composed of thirteen districts and its capital and largest city is Sion, Switzerland, Sion. Valais is situated in the southwestern part of the country. It borders the cantons of Canton of Vaud, Vaud and Canton of Bern, Bern to the north, the cantons of Canton of Uri, Uri and Ticino to the east, as well as Italy to the south and France to the west. It is one of the three large southern Alps, Alpine cantons, along with Ticino and Grisons. It is a bilingual canton, French and German being its two official languages. Traditionally, the canton is divided into Lower, Central, and Upper Valais, the latter region constituting the German-speaking minority. Valais is essentially coextensive with the valley of the Rhône from its headwaters to Lake Geneva, separating the Pennine Alps from the Bernese Alps, the two largest mount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unterwalden
Unterwalden, translated from the Latin ''inter silvas'' ("between the forests"), is the old name of a forest-canton of the Old Swiss Confederacy in central Switzerland, south of Lake Lucerne, consisting of two valleys or '' Talschaften'', now two separate Swiss cantons (or two half-cantons), Obwalden and Nidwalden. The name ''Unterwalden'' is first recorded in 1304, as the translation of Latin ''inter silvas'', which together with ''in intramontanis'' was the name for monastery possessions in the area. In 1291, Rudolf I of Germany purchased the estates at Stans, Alpnach and Giswil. From 1304, the local bailiffs used their own seal. In 1309, Henry VII confirmed the imperial immediacy of the territory of Unterwalden as part of the imperial bailiwick of ''Waldstätte'' (but not as a political entity in its own right). The Federal Charter, internally dated 1291, is thought to originate at this time. In the text, Unterwalden figures as ''communitas hominum Intramontanorum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Battle Of Ulrichen
The First Battle of Ulrichen in 1211 was a decisive defeat of Bernese troops under Duke Berthold V of Zähringen by the army of the Canton of Valais under the Bishop of Sion Landrich von Mont. The battle took place near Ulrichen which is now part of Obergoms. Many details about the battle are uncertain or questioned by historians. History Twenty years before the battle, in 1191, Berchtold V had established the city of Bern to expand his power into the lands of the County of Savoy. By 1211 he had quarreled with Thomas of Savoy and determined to use the new city as a base to expand into the Canton of Valais. Assembling an army of about 13,000 men he marched over the Grimsel pass. As they descended from the pass they burnt Oberwald and Obergesteln villages. The Valaisian army assembled under the command of the Bishop of Sion Landrich von Mont near Ulrichen. Very little is recorded about the battle, but Berchtold's army suffered heavy casualties and the survivors retreated bac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Battles Of The Old Swiss Confederacy
A list is a set of discrete items of information collected and set forth in some format for utility, entertainment, or other purposes. A list may be memorialized in any number of ways, including existing only in the mind of the list-maker, but lists are frequently written down on paper, or maintained electronically. Lists are "most frequently a tool", and "one does not ''read'' but only ''uses'' a list: one looks up the relevant information in it, but usually does not need to deal with it as a whole".Lucie Doležalová,The Potential and Limitations of Studying Lists, in Lucie Doležalová, ed., ''The Charm of a List: From the Sumerians to Computerised Data Processing'' (2009). Purpose It has been observed that, with a few exceptions, "the scholarship on lists remains fragmented". David Wallechinsky, a co-author of ''The Book of Lists'', described the attraction of lists as being "because we live in an era of overstimulation, especially in terms of information, and lists help us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholic Diocese Of Sion
The Diocese of Sion (, , ) is a Latin Church, Latin Catholic ecclesiastical territory in the canton of Valais, Switzerland. It is the oldest bishopric in the country and one of the oldest north of the Alps. The history of the Bishops of Sion, of the Abbey of St. Maurice, and of Valais as a whole are inextricably intertwined. History Early history The see was established at Octodurum, now called Martigny, Switzerland, Martigny, the capital of the Roman province of Alpes Poeninae. The first authentically historical bishop was Saint Theodore/Theodolus (died in 391), who was present at the Council of Aquileia, 381, Council of Aquileia in 381. He founded the Agaunum, Abbey of Saint-Maurice, with a small church in honor of Saint Maurice, martyred there c. 300, when he united the local hermits in a common life, thus beginning the Abbey of Saint-Maurice, the oldest north of the Alps. Theodore rebuilt the church at Sion, which had been destroyed by Emperor Maximinus II, Maximinus at the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florin
The Florentine florin was a gold coin (in Italian ''Fiorino d'oro'') struck from 1252 to 1533 with no significant change in its design or metal content standard during that time. It had 54 grains () of nominally pure or 'fine' gold with a purchasing power difficult to estimate (and variable) but ranging according to social grouping and perspective from approximately 140 to 1,000 modern US dollars. The name of the coin comes from the ''Giglio bottonato'' ( it), the floral emblem of the city, which is represented at the head of the coin. History The ''fiorino d'oro'' (gold florin) was minted in the Republic of Florence after the sack of Constantinople by the Fourth Crusade disrupted the minting of fine gold coins in the Byzantine Empire. It came to be accepted across Europe like the Byzantine Solidus had been. The territorial usage of the ''lira'' and the florin often overlapped; where the lira was used for smaller transactions (wages, food purchases), the florin was for la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canton Of Neuchâtel
The Republic and Canton of Neuchâtel (; ; ; ) is a mostly French-speaking canton in western Switzerland. In 2007, its population was 169,782, of whom 39,654 (or 23.4%) were foreigners. The capital is Neuchâtel. History County of Neuchâtel Neuchâtel has a unique history as the only part of present-day Switzerland to enter the Confederation as a principality (on 19 May 1815). Its first recorded ruler, Rudolph III of Burgundy, mentioned Neuchâtel in his will in 1032. The dynasty of Ulrich count of Fenis (Hasenburg) took over the town and its territories in 1034. The dynasty prospered and, by 1373, all the lands now part of the canton belonged to the count. In 1405, the cities of Bern and Neuchâtel entered a union. The lands of Neuchâtel had passed to the Zähringen lords of Freiburg in the late 14th century as inheritance from the childless Elisabeth, Countess of Neuchâtel, to her nephews, and then in 1458 to margraves of Sausenburg who belonged to the House of Bad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canton Of Solothurn
The canton of Solothurn or canton of Soleure (; ; ; ) is a Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Switzerland. It is located in the northwest of Switzerland. The capital is Solothurn. History The village of ''Salodurum'' was founded in the time of the Roman emperor Tiberius (1st century CE). The territory of the canton comprises land acquired by the former town, mainly in the Middle Ages. For that reason the canton is irregular in shape and includes two exclaves along the French border, separated from the rest of the canton by Basel-Landschaft. In 1481, the canton became a member of the military alliance of the former Swiss confederation. At the end of the Reformation, Solothurn maintained its Catholic religion. Between 1798 and 1803 the canton was part of the Helvetic Republic. In 1803 Solothurn was one of the 19 Swiss cantons that were reconstituted by Napoleon (''Act of Mediation, Mediation''). In 1830, the population rebelled against the aristocratic regime and the canton became d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
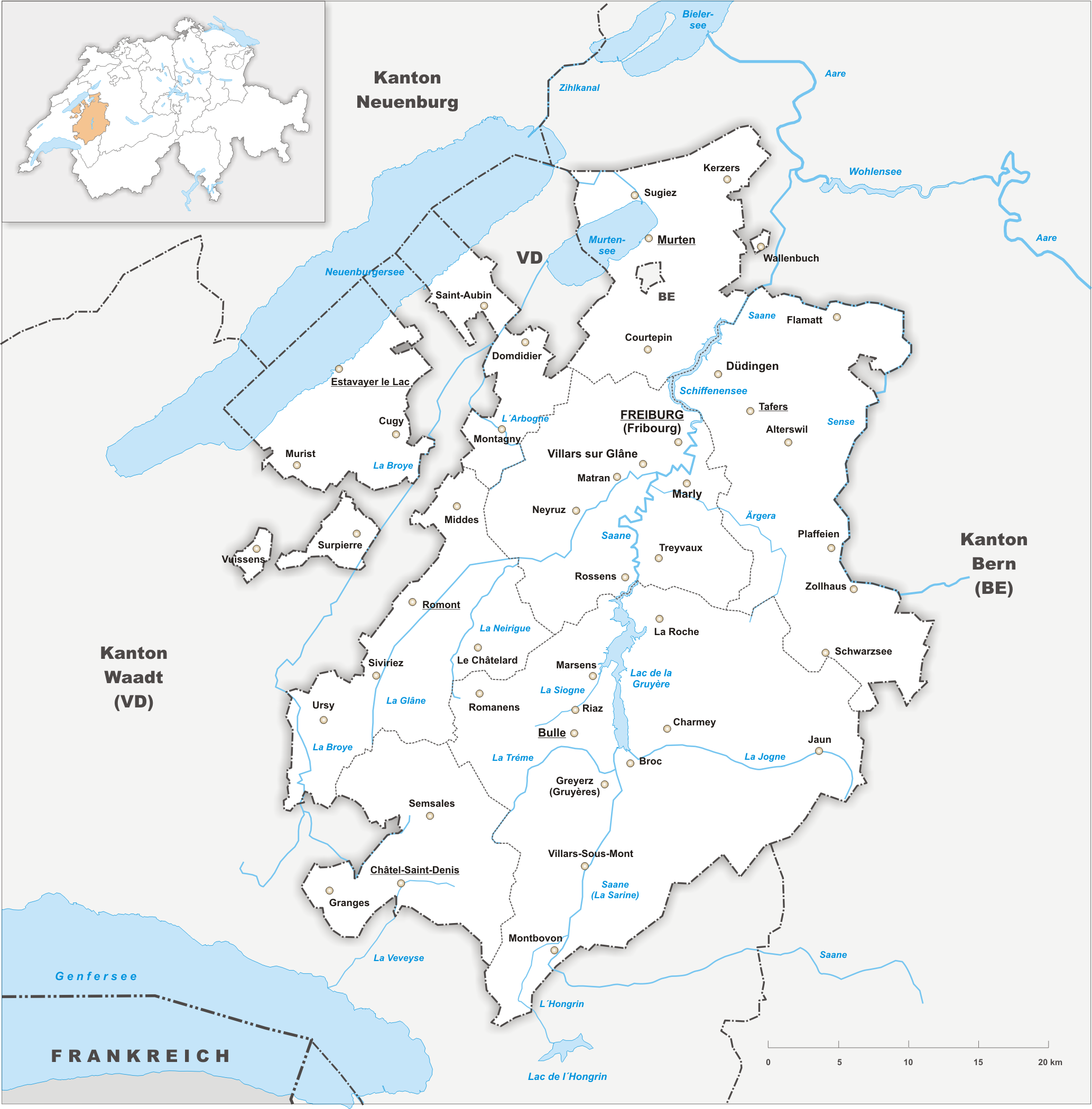
Canton Of Fribourg
The canton of Fribourg, also canton of Freiburg, is located in western Switzerland. The canton is bilingual, with French spoken by more than two thirds of the citizens and German by a little more than a quarter. Both are official languages in the canton. The canton takes its name from its capital city of Fribourg. History On the shores of Lake Neuchâtel and Lake Morat significant traces of prehistoric settlements have been unearthed. The canton of Fribourg joined the Swiss Confederation in 1481. The area is made up of lands acquired by the capital Fribourg. The present extent was reached in 1803 when Murten (Morat) was acquired. The canton of Fribourg joined the separatist league of Catholic cantons in 1846 ( Sonderbund). The following year, its troops surrendered to the federal army. Geography The canton is bounded to the west by Lake Neuchâtel, to the west and the south by the canton of Vaud, and to the east by the canton of Bern. The canton includes two enclaves with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grimsel Pass
The Grimsel Pass (; ; ) is a mountain pass in Switzerland, crossing the Bernese Alps at an elevation of . The pass connects the Haslital, the upper valley of the river Aare, with the upper valley of the Rhône. In so doing, and as the Aare is a tributary of the Rhine, the pass crosses the continental divide between the North Sea and the Mediterranean Sea. A paved road follows the pass, running from Gletsch to Meiringen. The road is normally closed between October and May, due to the high snowfall on the pass. As it is the only direct road pass between the cantons of Canton of Bern, Bern and Valais across the Bernese Alps, attempts are made to keep the road open as long as possible with snow ploughs. A PostBus Switzerland service uses the pass several times a day, connecting Meiringen and Oberwald. The Grimsel Pass road is part of the Aare Route, which is Swiss National Bike Routes, national cycle route 8 of Switzerland. It has been used on several occasions by the Tour de Suisse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sion, Switzerland
Sion (, ; former ; ) is a Switzerland, Swiss List of towns in Switzerland, town, a municipality, and the capital of the Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Valais and of the district of Sion (district), Sion. it had a population of (known as ''Sédunois(es)''). On 17 January 1968, the former municipality of Bramois merged into the municipality of Sion.Nomenklaturen – Amtliches Gemeindeverzeichnis der Schweiz accessed 9 February 2013 On 1 January 2013, the former municipality of Salins, Switzerland, Salins merged into the municipality of Sion, and on 1 January 2017, Les Agettes did the same. Landmarks in Sion include the Basilique de Valère and the Château de Tourbillon. Sion has an Sion Airport, airfield for civilian and Military o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanetsch Pass
Sanetsch Pass (French: ''Col du Sanetsch'' or ''Col de Sénin'') (el. 2242 m) is a high List of mountain passes in Switzerland, mountain pass in Switzerland across the western Bernese Alps, connecting Gsteig in the canton of Bern and Sion, Switzerland, Sion in the canton of Valais. Although a road leads to the pass from Sion and goes further to the Lac de Sanetsch, it can not be completely traversed by car. In the summer season the pass is accessible by PostBus Switzerland, PostBus and can also be traversed by cable car. The highest point of the road is at 2,252 metres. The pass itself is located in Valais 4 km south of the border with Bern. It separates the massif of the Diablerets on the west from the massif of the Wildhorn on the east. The Sanetschhorn and the Arpelistock overlook the pass on the west and east side respectively. The Col du Sanetsch is a popular destination because of the view over the Pennine Alps and the nearby Tsanfleuron Glacier. See also * List of hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |