|
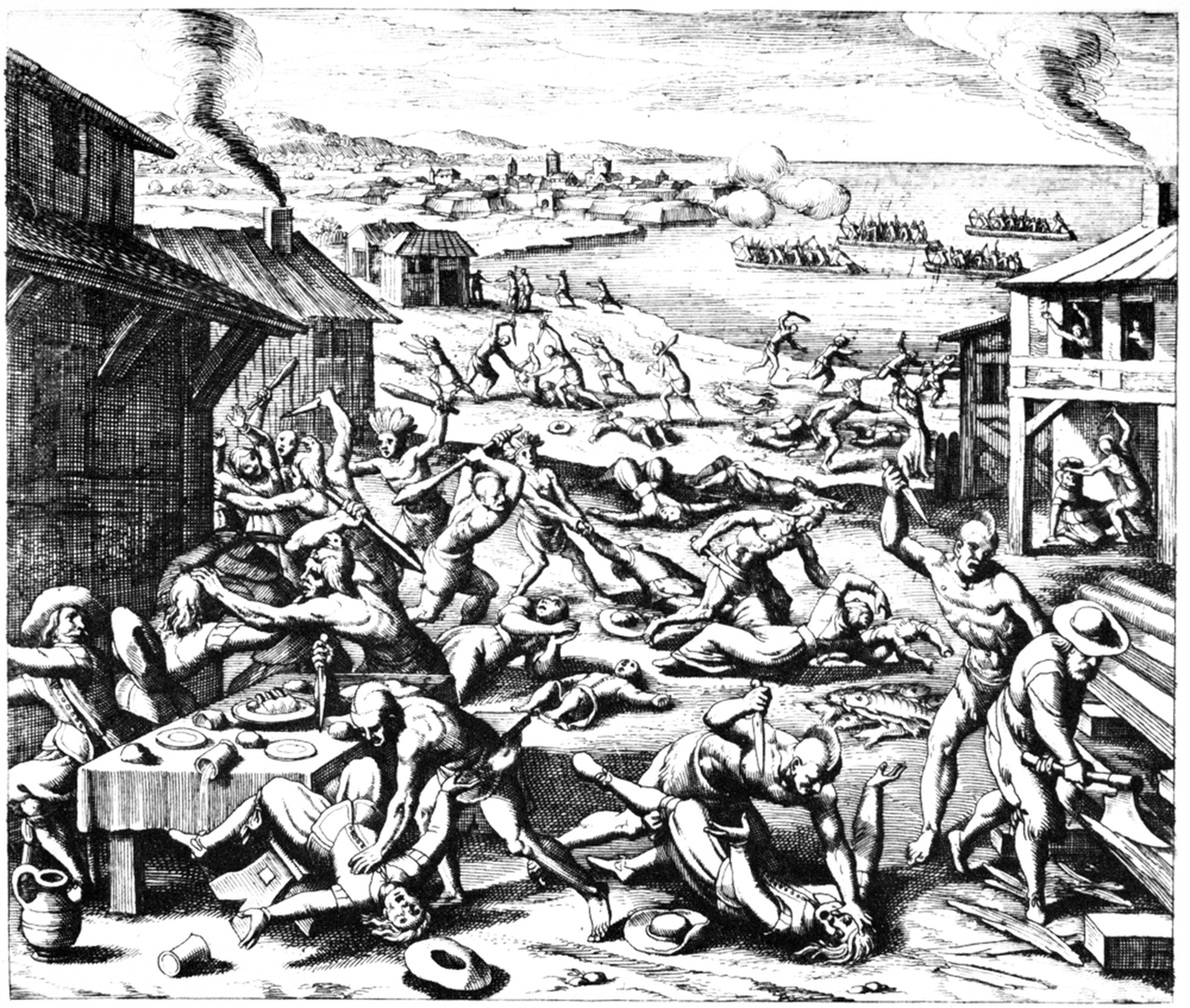
Second Anglo-Powhatan War
The AngloPowhatan Wars were three wars fought between settlers of the Colony of Virginia and the Powhatan People of Tsenacommacah in the early 17th century. The first war started in 1609 and ended in a peace settlement in 1614. The second war lasted from 1622 to 1632. The third war lasted from 1644 until 1646 and ended when Opechancanough was captured and killed. That war resulted in a defined boundary between the Native Americans and colonial lands that could only be crossed for official business with a special pass. This situation lasted until 1677 and the Treaty of Middle Plantation which established Indian reservations following Bacon's Rebellion. Early conflict The settlement at Jamestown, Virginia, was established in May 1607 within the territory of the Powhatan, who were led by Chief Wahunsunacawh, known to the colonists as Chief Powhatan. The area was quite swampy and ill-suited to farming, and Powhatan wanted Captain John Smith and the colonists to forsake the swamp a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Indian Wars
The American Indian Wars, also known as the American Frontier Wars, and the Indian Wars, was a conflict initially fought by European colonization of the Americas, European colonial empires, the United States, and briefly the Confederate States of America and Republic of Texas against various Tribe (Native American), American Indian tribes in North America. These conflicts occurred from the time of the earliest colonial settlements in the 17th century until the end of the 19th century. The various wars resulted from a wide variety of factors, the most common being the desire of settlers and governments for Indian tribes' lands. The European powers and their colonies enlisted allied Indian tribes to help them conduct warfare against each other's colonial settlements. After the American Revolution, many conflicts were local to specific states or regions and frequently involved disputes over land use; some entailed cycles of violent reprisal. As American pioneer, American settlers s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jamestown Island
Jamestown Island is a island in the James River in Virginia, part of James City County, Virginia, James City County. It is located off Glasshouse Point, to which it is connected via a causeway to the Colonial Parkway. Much of the island is wetland, including both swamp and marsh. History Prior to English settlement, the nearby area was home to the Paspahegh people, or Virginia Algonquians. In May 1607, the island (then a peninsula) became site of Jamestown, Virginia, James Fort, the first permanent English settlement in the Americas. The chief of the Powatan at that time, also named Powhatan (Native American leader), Powhatan, was father of Pocahontas. After Powhatan's death in 1618, hostilities with colonists escalated under his brother, Opechancanough. His large-scale attacks in 1622 and 1644 met strong reprisals by the English, resulting in the near elimination of both the settlement and the tribe. After Bacon's rebellion in 1677, Jamestown lasted until 1699, when it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starving Time
The Starving Time at Jamestown in the Colony of Virginia was a period of starvation during the winter of 1609–1610. There were about 500 Jamestown residents at the beginning of the winter; by spring only 61 people remained alive. The colonists, the first group of whom had originally arrived on May 13, 1607, had never planned to grow all of their own food. Their plans depended upon trade with the local Powhatan to supply them with food between the arrivals of periodic supply ships from England. Lack of access to water and a severe drought crippled the agricultural production of the colonists. The water that the colonists drank was brackish and potable for only half of the year. A fleet from England, damaged by a hurricane, arrived months behind schedule with new colonists but without adequate food supplies. On June 7, 1610, the survivors boarded ships, abandoned the colony site, and sailed downstream to the Chesapeake Bay. There, another supply convoy with new supplies, headed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Ratcliffe (governor)
John Ratcliffe (born John Sicklemore; 1549 – December 1609) was an early Jamestown colonist, governor, and sea captain. Ratcliffe became the second president of the colony of Jamestown. He was tortured to death by the Pamunkey (indigenous Native Americans) in the winter of 1609–1610. Biography John Sicklemore was born in Lancashire. In early life, he changed his name to Ratcliffe as an alias. He served as a seaman before going to Virginia, and he may be the Captain Ratcliffe taken prisoner with Sir Henry Cary, 1st Viscount Falkland and Captain Piggot, at Mülheim, in 1605. Virginia colony Ratcliffe commanded ''Discovery'' and became a councillor of the Jamestown Colony. ''Discovery'' was the smallest of all three ships; it had a crew of only 21 men. He became president of the colony upon the deposition of Edward Maria Wingfield on 10 September 1607. Ratcliffe fell out of favour with many colonists after enlisting men to build a governor's house. Many colonists also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Point Comfort
Old Point Comfort is a point of land located in the Independent city (United States), independent city of Hampton, Virginia. Previously known as Point Comfort, it lies at the extreme tip of the Virginia Peninsula at the mouth of Hampton Roads in the United States. It was renamed Old Point Comfort to differentiate it from New Point Comfort up the Chesapeake Bay. A First Africans in Virginia, group of enslaved Africans (first fleet) was brought to Colony of Virginia, colonial Virginia at this point in 1619. Today the location is home to Continental Park and Fort Monroe National Monument. History 17th and 18th centuries For more than 400 years, Point Comfort served as a maritime navigational landmark and military stronghold. According to a combination of old records and legend, the name derived from an incident when the Jamestown settlers first arrived. Captain Christopher Newport's flagship, ''Susan Constant'', anchored nearby on 28 April 1607. Members of the crew "rowed to a po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Algernon
Fort Algernon (also spelled Fort Algernourne) was established in the fall of 1609 at the mouth of Hampton Roads at Point Comfort in the Virginia Colony by Captain John Ratcliffe. A strategic point for guarding the shipping channel leading from the Chesapeake Bay, it would be the site for a series of military forts for the next few centuries, culminating with Fort Monroe built in the 1830s. The area is now known as Old Point Comfort. Long part of Elizabeth City County, the site is now located in the independent city of Hampton, Virginia. After Captain John Smith, President of the Council at Jamestown was deposed in September 1609 and soon returned to England, Captain James Davis, who arrived with one of the ships of the Third Supply, assumed command of the newly built fort in October. It is likely that his pinnace, ''Virginia'', the first ship built in the English colonies (at the Virginia Company of Plymouth's failed Popham Colony in present-day Maine), was anchored nearby. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richmond, Virginia
Richmond ( ) is the List of capitals in the United States, capital city of the Commonwealth (U.S. state), U.S. commonwealth of Virginia. Incorporated in 1742, Richmond has been an independent city (United States), independent city since 1871. The city's population in the 2020 United States census was 226,610, up from 204,214 in 2010, making it Virginia's List of cities and counties in Virginia#Largest cities, fourth-most populous city. The Greater Richmond Region, Richmond metropolitan area, with over 1.3 million residents, is the Commonwealth's Virginia statistical areas, third-most populous. Richmond is located at the Atlantic Seaboard fall line, James River's fall line, west of Williamsburg, Virginia, Williamsburg, east of Charlottesville, Virginia, Charlottesville, east of Lynchburg, Virginia, Lynchburg and south of Washington, D.C. Surrounded by Henrico County, Virginia, Henrico and Chesterfield County, Virginia, Chesterfield counties, Richmond is at the intersection o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
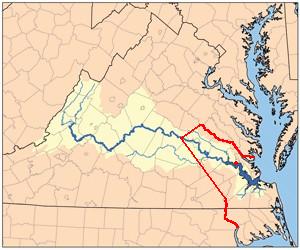
James River
The James River is a river in Virginia that begins in the Appalachian Mountains and flows from the confluence of the Cowpasture and Jackson Rivers in Botetourt County U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map , accessed April 1, 2011 to the Chesapeake Bay. The river length extends to if the Jackson River (Virginia), Jackson River, the longer of its two headwaters, is included. It is the longest river in Virginia. Jamestown, Virginia, Jamestown and Williamsburg, Virginia, Williamsburg, Virginia's first colonial capitals, and Richmond, Virginia, Richmond, Virginia's current capital, lie on the James River. History The Native American tribes in Virginia, Native Americans who populated the area east of the Atlantic Seaboard Fall Line, Fall Line in the late 16th and early 17th centuries called the James River the Powhatan River, named for the Powhatan, Powhatans who occupied the area. The Jamestown, Virginia, Jamestown colo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis West
Francis West ( – ) was a Deputy Governor of the Colony of Virginia. Early and family life Born in Salisbury, Wiltshire on 28 October 1586, West was one of four sons of Thomas West, 2nd Baron De La Warr (1556–1602) of Wherwell Abbey in Hampshire and his wife, Anne Knollys who made their fortunes in the Virginia colony. His elder brother, Thomas West, 3rd Baron De La Warr (1577–1618), served as a governor of the Virginia Company of London from 1610–1611. His younger brother, John West (1590-ca 1659), served as Acting Governor of Virginia from 1635–1637. A fourth brother, Nathaniel West, died in Virginia in August 1623, aged 30. Career Francis West was one of the distinguished passengers on Captain Christopher Newport's third voyage to Jamestown, Virginia, aboard the ''Mary and Margaret'', which arrived in the summer of 1608. Newport returned to London with a load of iron ore sold to the East India Company. Francis West was selected to the Governor's Council in 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kecoughtan
In the seventeenth century, Kecoughtan was the name of the settlement now known as Hampton, Virginia. In the early twentieth century, it was also the name of a town nearby in Elizabeth City County. It was annexed into the City of Newport News in 1927. Colonial and Native American Kecoughtan Kecoughtan in Virginia was originally named Kikotan (also spelled Kiccowtan, Kikowtan), the name of the Algonquian Native Americans living there when colonists led by Captain John Smith arrived in the Hampton Roads area in 1607. According to William Strachey, Chief Powhatan had slain the ''weroance'' at Kecoughtan in 1597, appointing his own young son Pochins as successor there, while resettling some of the tribe at the Piankatank River. Powhatan annihilated the inhabitants at Piankatank in 1608. The Kecoughtan village was where Captain John Smith and his group of settlers received their first welcome in 1607. The tribe remained generally friendly to them until the summer of 1609, when pres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nansemond
The Nansemond are the Indigenous people of the Nansemond River, a 20-mile-long tributary of the James River in Virginia. Nansemond people lived in settlements on both sides of the Nansemond River where they fished (with the name "Nansemond" meaning "fishing point" in Algonquian), harvested oysters, hunted, and farmed in fertile soil. Today, Nansemond people belong to the federally recognized Nansemond Indian Nation. Gradually pushed off their lands in the colonial and following periods, the Nansemond struggled to maintain their culture. They reorganized in the late 20th century and gained state recognition from Virginia in 1985. They gained federal recognition in 2018 after Congress passed a bill. Many members of the tribe still live on former ancestral lands in Suffolk, Chesapeake, and surrounding cities. Language The Nansemond language is believed to have been Algonquian, similar to that of many other Atlantic coastal tribes. But only six words have been preserved, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Martin (Jamestown)
Capt. John Martin () was a Councillor of the Jamestown Colony in 1607. He was the proprietor of Martin's Brandon Plantation on the south bank of the James River. Located in modern-day Prince George County, Virginia and known as Lower Brandon Plantation, in the 21st century, his plantation is both a National Historic Landmark and one of America's oldest continuous farming operations. Early life Martin was the third son of goldsmith and Sir Richard Martin (d. 1617) and Dorcas Eccleston (d. 1599). Sir Richard later held office as Master of the Mint and Lord Mayor of London. (He is not the same as the Mr. Richard Martin (1570–1618) who was the recorder of London, counsel for the Virginia Company and organiser of The Society of Martin's Hundred, whose subsidiary "particular plantation" development –19 was known as Martin's Hundred). Brothers Richard and Nathaniel Martin also worked at the Royal Mint with their father, the former as master and the latter as a clerk. Sir Richar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |