|
Searsia (fish)
''Searsia koefoedi'', or Koefoed's searsid, is a species of tubeshoulder found in the oceans at depths of from . It is named after Norwegian marine biologist Einar Koefoed. Size This species grows to a length of SL. Habitat and distribution ''Searsia koefoedi'' can be found in a marine environment within a depth range of . They live in deep-water environments. They are native to the areas of Eastern Atlantic, Denmark Strait, the Gulf of Guinea Northwest Atlantic in subtropical waters, Indian and Pacific oceans within tropical waters. Etymology The fish is named in honor of Norwegian marine biologist Einar Koefoed Einar Laurentius Koefoed (1875–1963) was a Danish-born marine biologist who spent most of his professional career in Norway. Taxon named in his honor ''Searsia koefoedi'' (Koefoed's searsid) is named after Einar Koefoed. Also the genus ''Ei ... (1875–1963), who was responsible for the collected part of the type specimens in 1926 and who authored several pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Eide Parr
Albert Eide Parr (15 August 1900 – 16 July 1991) was an American marine biologist, zoologist and oceanographer. He was the director of the American Museum of Natural History from 1942 to 1959. ''Parrosaurus missouriensis'', a species of plant-eating dinosaur, is named after him. Biography Albert Eide Parr was born and grew up in Bergen, Norway. His father, Thomas Johannes Lauritz Parr, was a professor at Bergen Cathedral School. He became well acquainted with Jørgen Brunchorst, director at the Bergen Museum and developed an early interest in marine biology. He studied at the University of Oslo (1921–24) and became cand.mag. in 1925. He worked was an assistant in zoology at the Bergen Museum from 1924 to 1926. He and his wife traveled to the United States in 1926 where Parr is said to have first found work "sweeping floors" at the New York Aquarium in New York City. In 1927, he met American financier and philanthropist Harry Payne Bingham. They launched a series of m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tubeshoulder
The tubeshoulders are a family, Platytroctidae, of ray-finned fish belonging to the order Alepocephaliformes Alepocephaliformes is an order of marine deep-sea teleost fishes. It was previously classified as the suborder Alepocephaloidei of the order Argentiniformes. As an adaptation to a life in the deep-sea, there is no swim bladder, and the ossifica .... They are found throughout the world, except for the Mediterranean Sea. Tubeshoulders live at moderate depths of , and some have light-producing organs. They are generally small to medium fish, ranging from in length. Genera The family contains the following genera: References * Otocephala families {{Alepocephaliformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Einar Laurentius Koefoed
Einar Laurentius Koefoed (1875–1963) was a Danish-born marine biologist who spent most of his professional career in Norway. Taxon named in his honor ''Searsia koefoedi'' (Koefoed's searsid) is named after Einar Koefoed. Also the genus ''Einara ''Einara'' is a small genus of slickheads found in the deep waters of the oceans. They can grow to standard length The etymology of the genus name is uncertain but could refer Norwegian marine biologist Einar Koefoed. Species There are curre ...'' might be named after him. Taxon described by him *See :Taxa named by Einar Laurentius Koefoed References {{DEFAULTSORT:Koefoed, Einar Laurentius 1875 births 1963 deaths Fisheries scientists 20th-century Danish zoologists 20th-century Norwegian zoologists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
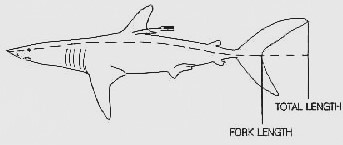
Fish Measurement
Fish measurement is the measuring of individual fish and various parts of their anatomies, for data used in many areas of ichthyology, including taxonomy and fishery biology. Overall length Standard length (SL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the posterior end of the last vertebra or to the posterior end of the midlateral portion of the hypural plate. This measurement excludes the length of the caudal (tail) fin. Total length (TL) is the length of a fish measured from the tip of the snout to the tip of the longer lobe of the caudal fin, usually measured with the lobes compressed along the midline. It is a straight-line measure, not measured over the curve of the body. Standard length measurements are used with Teleostei (most bony fish), while total length measurements are used with Myxini (hagfish), Petromyzontiformes ( lampreys) and usually Elasmobranchii (shark Sharks are a group of elasmobranch cartilaginous fish characterized by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Einar Koefoed
Einar Laurentius Koefoed (1875–1963) was a Danish-born marine biologist who spent most of his professional career in Norway. Taxon named in his honor ''Searsia koefoedi'' (Koefoed's searsid) is named after Einar Koefoed. Also the genus ''Einara'' might be named after him. Taxon described by him *See :Taxa named by Einar Laurentius Koefoed References {{DEFAULTSORT:Koefoed, Einar Laurentius 1875 births 1963 deaths Fisheries scientists 20th-century Danish zoologists 20th-century Norwegian zoologists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platytroctidae
The tubeshoulders are a family, Platytroctidae, of ray-finned fish Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fish or actinopterygians, is a class of bony fish that comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species. They are so called because of their lightly built fins made of webbings of sk ... belonging to the order Alepocephaliformes. They are found throughout the world, except for the Mediterranean Sea. Tubeshoulders live at moderate depths of , and some have light-producing organs. They are generally small to medium fish, ranging from in length. Genera The family contains the following genera: References * Otocephala families {{Alepocephaliformes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Of The Atlantic Ocean
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic animal, aquatic, Anamniotes, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fish fin, fins and craniate, a hard skull, but lacking limb (anatomy), limbs with digit (anatomy), digits. Fish can be grouped into the more basal (phylogenetics), basal jawless fish and the more common jawed fish, the latter including all extant taxon, living cartilaginous fish, cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as the extinct placoderms and acanthodians. In a break to the long tradition of grouping all fish into a single Class (biology), class (Pisces), modern phylogenetics views fish as a paraphyletic group. Most fish are ectotherm, cold-blooded, their body temperature varying with the surrounding water, though some large nekton, active swimmers like white shark and tuna can hold a higher core temperature. Many fish can communication in aquatic animals#Acoustic, communicate acoustically with each other, such as during courtship displays. The stud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Of The Indian Ocean
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fins and a hard skull, but lacking limbs with digits. Fish can be grouped into the more basal jawless fish and the more common jawed fish, the latter including all living cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as the extinct placoderms and acanthodians. In a break to the long tradition of grouping all fish into a single class (Pisces), modern phylogenetics views fish as a paraphyletic group. Most fish are cold-blooded, their body temperature varying with the surrounding water, though some large active swimmers like white shark and tuna can hold a higher core temperature. Many fish can communicate acoustically with each other, such as during courtship displays. The study of fish is known as ichthyology. The earliest fish appeared during the Cambrian as small filter feeders; they continued to evolve through the Paleozoic, diversifying into many forms. The earliest fish w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fish Described In 1937
A fish (: fish or fishes) is an aquatic, anamniotic, gill-bearing vertebrate animal with swimming fins and a hard skull, but lacking limbs with digits. Fish can be grouped into the more basal jawless fish and the more common jawed fish, the latter including all living cartilaginous and bony fish, as well as the extinct placoderms and acanthodians. In a break to the long tradition of grouping all fish into a single class (Pisces), modern phylogenetics views fish as a paraphyletic group. Most fish are cold-blooded, their body temperature varying with the surrounding water, though some large active swimmers like white shark and tuna can hold a higher core temperature. Many fish can communicate acoustically with each other, such as during courtship displays. The study of fish is known as ichthyology. The earliest fish appeared during the Cambrian as small filter feeders; they continued to evolve through the Paleozoic, diversifying into many forms. The earliest fish wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |