|
Sean Nee
Sean Nee (born 3 July 1959) is an evolutionary biologist and theoretical ecologist. He has been a lecturer at Oxford University and Professor at the University of Edinburgh. He has published scientific research papers with ecologist Robert May, theoretical biologist John Maynard Smith and epidemiologist Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population, and application of this knowledge to prevent diseases. It is a cornerstone ... and novelist Sunetra Gupta. Selected publications * * * * * References {{DEFAULTSORT:Nee, Sean 1959 births Living people Academics of the University of Oxford Academics of the University of Edinburgh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary Biology
Evolutionary biology is the subfield of biology that studies the evolutionary processes such as natural selection, common descent, and speciation that produced the diversity of life on Earth. In the 1930s, the discipline of evolutionary biology emerged through what Julian Huxley called the Modern synthesis (20th century), modern synthesis of understanding, from previously unrelated fields of biological research, such as genetics and ecology, systematics, and paleontology. The investigational range of current research has widened to encompass the genetic architecture of adaptation, molecular evolution, and the different forces that contribute to evolution, such as sexual selection, genetic drift, and biogeography. The newer field of evolutionary developmental biology ("evo-devo") investigates how embryogenesis is controlled, thus yielding a wider synthesis that integrates developmental biology with the fields of study covered by the earlier evolutionary synthesis. Subfields ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
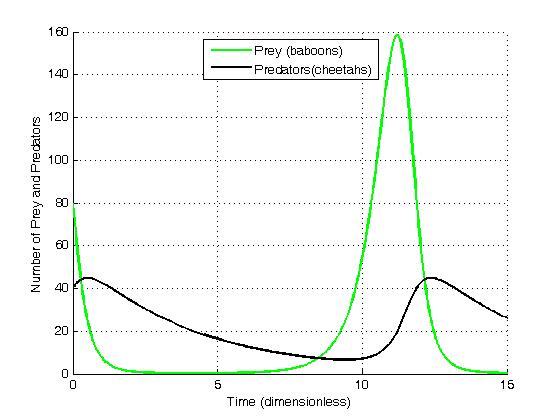
Theoretical Ecology
Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecosystem, ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computer simulation, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world. The field is broad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary Biologist
Evolutionary biology is the subfield of biology that studies the evolutionary processes such as natural selection, common descent, and speciation that produced the diversity of life on Earth. In the 1930s, the discipline of evolutionary biology emerged through what Julian Huxley called the modern synthesis of understanding, from previously unrelated fields of biological research, such as genetics and ecology, systematics, and paleontology. The investigational range of current research has widened to encompass the genetic architecture of adaptation, molecular evolution, and the different forces that contribute to evolution, such as sexual selection, genetic drift, and biogeography. The newer field of evolutionary developmental biology ("evo-devo") investigates how embryogenesis is controlled, thus yielding a wider synthesis that integrates developmental biology with the fields of study covered by the earlier evolutionary synthesis. Subfields Evolution is the central un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theoretical Ecologist
Theoretical ecology is the scientific discipline devoted to the study of ecological systems using theoretical methods such as simple conceptual models, mathematical models, computational simulations, and advanced data analysis. Effective models improve understanding of the natural world by revealing how the dynamics of species populations are often based on fundamental biological conditions and processes. Further, the field aims to unify a diverse range of empirical observations by assuming that common, mechanistic processes generate observable phenomena across species and ecological environments. Based on biologically realistic assumptions, theoretical ecologists are able to uncover novel, non-intuitive insights about natural processes. Theoretical results are often verified by empirical and observational studies, revealing the power of theoretical methods in both predicting and understanding the noisy, diverse biological world. The field is broad and includes foundations in ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University
The University of Oxford is a collegiate research university in Oxford, England. There is evidence of teaching as early as 1096, making it the oldest university in the English-speaking world and the second-oldest continuously operating university globally. It expanded rapidly from 1167, when Henry II prohibited English students from attending the University of Paris. When disputes erupted between students and the Oxford townspeople, some Oxford academics fled northeast to Cambridge, where they established the University of Cambridge in 1209. The two English ancient universities share many common features and are jointly referred to as ''Oxbridge''. The University of Oxford comprises 43 constituent colleges, consisting of 36 semi-autonomous colleges, four permanent private halls and three societies (colleges that are departments of the university, without their own royal charter). and a range of academic departments that are organised into four divisions. Each college ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Edinburgh
The University of Edinburgh (, ; abbreviated as ''Edin.'' in Post-nominal letters, post-nominals) is a Public university, public research university based in Edinburgh, Scotland. Founded by the City of Edinburgh Council, town council under the authority of a royal charter from King James VI and I, James VI in 1582 and officially opened in 1583, it is one of Scotland's Ancient universities of Scotland, four ancient universities and the List of oldest universities in continuous operation, sixth-oldest university in continuous operation in the English-speaking world. The university played a crucial role in Edinburgh becoming a leading intellectual centre during the Scottish Enlightenment and contributed to the city being nicknamed the "Etymology of Edinburgh#Athens of the North, Athens of the North". The three main global university rankings (Academic Ranking of World Universities, ARWU, Times Higher Education World University Rankings, THE, and QS World University Rankings, QS) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert May, Baron May Of Oxford
Robert McCredie May, Baron May of Oxford (8 January 1936 – 28 April 2020) was an Australian scientist who was Chief Scientific Adviser to the UK Government, President of the Royal Society, and a professor at the University of Sydney and Princeton University. He held joint professorships at the University of Oxford and Imperial College London. He was also a crossbench member of the House of Lords from 2001 until his retirement in 2017. May was a Fellow of Merton College, Oxford, and an appointed member of the council of the British Science Association. He was also a member of the advisory council for the Campaign for Science and Engineering. Early life and education May was born in Sydney on 8 January 1936, to lawyer Henry Wilkinson May and Kathleen Mitchell (née McCredie), who divorced when he was seven years old. His father was of prosperous middle-class Northern Irish origin, and his mother was the daughter of a Scottish engineer. May was educated at Sydney Boys High Sch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Maynard Smith
John Maynard Smith (6 January 1920 – 19 April 2004) was a British mathematical and theoretical biology, theoretical and mathematical evolutionary biologist and geneticist. Originally an aeronautical engineer during the Second World War, he took a second degree in genetics under the biologist J. B. S. Haldane. Maynard Smith was instrumental in the application of game theory to evolution with George R. Price, and theorised on other problems such as the evolution of sex and signalling theory. Biography Early years John Maynard Smith was born in London, the son of the surgeon Sidney Maynard Smith, but following his father's death in 1928, the family moved to Exmoor, where he became interested in natural history. Quite unhappy with the lack of formal science education at Eton College, Maynard Smith took it upon himself to develop an interest in Darwinism, Darwinian evolutionary theory and mathematics, after having read the work of old Etonian J. B. S. Haldane, whose books were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and Risk factor (epidemiology), determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population, and application of this knowledge to prevent diseases. It is a cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evidence-based practice by identifying Risk factor (epidemiology), risk factors for disease and targets for preventive healthcare. Epidemiologists help with study design, collection, and statistical analysis of data, amend interpretation and dissemination of results (including peer review and occasional systematic review). Epidemiology has helped develop methodology used in clinical research, public health studies, and, to a lesser extent, basic research in the biological sciences. Major areas of epidemiological study include disease causation, transmission (medicine), transmission, outbreak investigation, disease surveillance, environmental epidemiology, forensic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunetra Gupta
Sunetra Gupta (born 15 March 1965) is an Indian-born British infectious disease epidemiologist and a professor of theoretical epidemiology at the Department of Zoology, University of Oxford. She has performed research on the transmission dynamics of various infectious diseases, including malaria, influenza and COVID-19, and has received the Scientific Medal of the Zoological Society of London and the Rosalind Franklin Award of the Royal Society. She is a member of the scientific advisory board of Collateral Global, an organisation which examines the global impact of COVID-19 restrictions. Gupta is also a novelist and a recipient of the Sahitya Akademi Award. Early life and education Gupta was born in Kolkata, India, to Dhruba and Minati Gupta. She trained in biology, and was awarded a bachelor's degree from Princeton University. In 1992 she obtained her PhD from Imperial College London for a thesis on the transmission dynamics of infectious diseases. Career and research Positi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1959 Births
Events January * January 1 – Cuba: Fulgencio Batista flees Havana when the forces of Fidel Castro advance. * January 2 – Soviet lunar probe Luna 1 is the first human-made object to attain escape velocity from Earth. It reaches the vicinity of Earth's Moon, where it was intended to crash-land, but instead becomes the first spacecraft to go into heliocentric orbit. * January 3 ** Alaska is admitted as the 49th U.S. state. ** The southernmost island of the Maldives archipelago, Addu Atoll, declares its independence from the Kingdom of the Maldives, initiating the United Suvadive Republic. * January 4 ** In Cuba, rebel troops led by Che Guevara and Camilo Cienfuegos enter the city of Havana. ** Léopoldville riots: At least 49 people are killed during clashes between the police and participants of a meeting of the ABAKO Party in Kinshasa, Léopoldville in the Belgian Congo. * January 6 – The International Maritime Organization is inaugurated. * January 7 – The United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living People
Purpose: Because living persons may suffer personal harm from inappropriate information, we should watch their articles carefully. By adding an article to this category, it marks them with a notice about sources whenever someone tries to edit them, to remind them of WP:BLP (biographies of living persons) policy that these articles must maintain a neutral point of view, maintain factual accuracy, and be properly sourced. Recent changes to these articles are listed on Special:RecentChangesLinked/Living people. Organization: This category should not be sub-categorized. Entries are generally sorted by family name In many societies, a surname, family name, or last name is the mostly hereditary portion of one's personal name that indicates one's family. It is typically combined with a given name to form the full name of a person, although several give .... Maintenance: Individuals of advanced age (over 90), for whom there has been no new documentation in the last ten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |