|
Sealedenvelope.com
Sealedenvelope.com is British collaboration that provides support services for clinical trials. They provide services such as randomization, allocation concealment, code-break procedure, code-break services, and case report management through a web-based design. They also perform certain calculations such as power (statistics), power calculations. References External links Official website Design of experiments Clinical trials {{Med-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allocation Concealment
In a randomized experiment, allocation concealment hides the sorting of trial participants into treatment groups so that this knowledge cannot be exploited. Adequate allocation concealment serves to prevent study participants from influencing treatment allocations for subjects. Studies with poor allocation concealment (or none at all) are prone to selection bias. Some standard methods of ensuring allocation concealment include sequentially numbered, opaque, sealed envelopes (SNOSE); sequentially numbered containers; pharmacy controlled randomization; and central randomization. CONSORT guidelines recommend that allocation concealment methods be included in a study's protocol, and that the allocation concealment methods be reported in detail in their publication; however, a 2005 study determined that most clinical trials have unclear allocation concealment in their protocols, in their publications, or both. A 2008 study of 146 meta-analyses concluded that the results of randomized cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Code-break Procedure
A code-break procedure is a set of rules which determine when planned unblinding should occur in a blinded experiment. FDA guidelines recommend that sponsors of blinded trials include a code-break procedure in their standard operating procedure. A code-break procedure should only allow a participant to be unblinded before the conclusion of a trial in the event of an emergency. Code-break usually refers to the unmasking of treatment allocation, but can refer to any form of unblinding. Traditionally, each patient's treatment allocation data was stored in a sealed envelopes, which was to be opened to break code. However, this system is prone to abuse. Reports of researchers opening envelopes prematurely or holding the envelopes up to lights to determine their contents has led some researchers to say that the use of sealed envelopes is no longer acceptable. , sealed envelopes were still in use in some clinical trials. Modern clinical trials usually store this information in computer file ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, drugs, dietary choices, dietary supplements, and medical devices) and known interventions that warrant further study and comparison. Clinical trials generate data on dosage, safety and efficacy. They are conducted only after they have received health authority/ethics committee approval in the country where approval of the therapy is sought. These authorities are responsible for vetting the risk/benefit ratio of the trial—their approval does not mean the therapy is 'safe' or effective, only that the trial may be conducted. Depending on product type and development stage, investigators initially enroll volunteers or patients into small pilot studies, and subsequently conduct progressively larger scale comparative studies. Clinical trials can vary i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Randomization
Randomization is the process of making something random. Randomization is not haphazard; instead, a random process is a sequence of random variables describing a process whose outcomes do not follow a deterministic pattern, but follow an evolution described by probability distributions. For example, a random sample of individuals from a population refers to a sample where every individual has a known probability of being sampled. This would be contrasted with nonprobability sampling where arbitrary individuals are selected. In various contexts, randomization may involve: * generating a random permutation of a sequence (such as when shuffling cards); * selecting a random sample of a population (important in statistical sampling); * allocating experimental units via random assignment to a treatment or control condition; * generating random numbers ( random number generation); or * transforming a data stream (such as when using a scrambler in telecommunications). Applications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
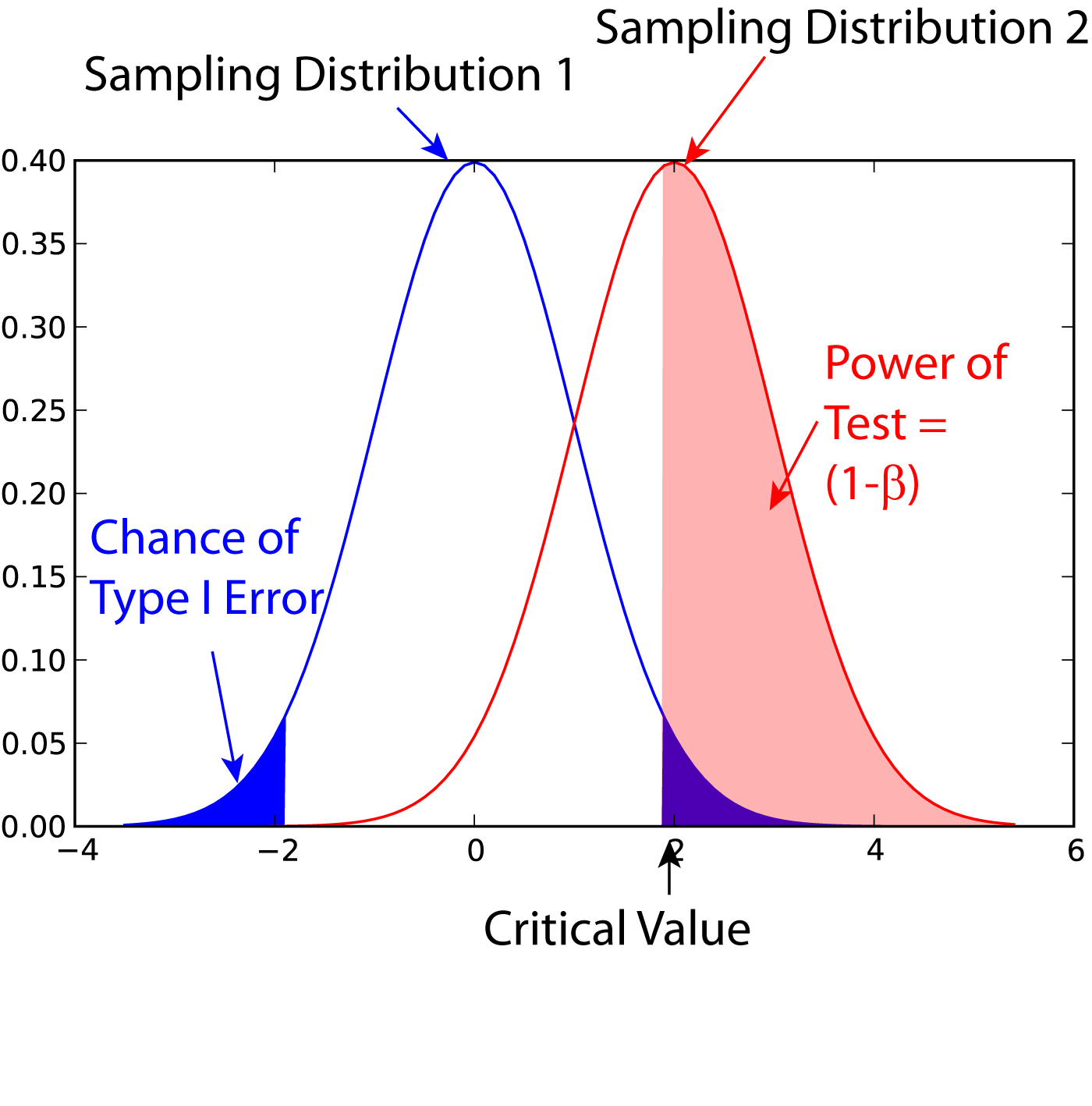
Power (statistics)
In statistics, the power of a binary hypothesis test is the probability that the test correctly rejects the null hypothesis (H_0) when a specific alternative hypothesis (H_1) is true. It is commonly denoted by 1-\beta, and represents the chances of a true positive detection conditional on the actual existence of an effect to detect. Statistical power ranges from 0 to 1, and as the power of a test increases, the probability \beta of making a type II error by wrongly failing to reject the null hypothesis decreases. Notation This article uses the following notation: * ''β'' = probability of a Type II error, known as a "false negative" * 1 − ''β'' = probability of a "true positive", i.e., correctly rejecting the null hypothesis. "1 − ''β''" is also known as the power of the test. * ''α'' = probability of a Type I error, known as a "false positive" * 1 − ''α'' = probability of a "true negative", i.e., correctly not rejecting the null hypothesis Description For a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Design Of Experiments
The design of experiments (DOE, DOX, or experimental design) is the design of any task that aims to describe and explain the variation of information under conditions that are hypothesized to reflect the variation. The term is generally associated with experiments in which the design introduces conditions that directly affect the variation, but may also refer to the design of quasi-experiments, in which natural conditions that influence the variation are selected for observation. In its simplest form, an experiment aims at predicting the outcome by introducing a change of the preconditions, which is represented by one or more independent variables, also referred to as "input variables" or "predictor variables." The change in one or more independent variables is generally hypothesized to result in a change in one or more dependent variables, also referred to as "output variables" or "response variables." The experimental design may also identify control variables that must ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)