|
Scuol, Switzerland
Scuol () is a municipality in the Engiadina Bassa/Val Müstair Region in the Swiss canton of Grisons. The official language in Scuol is Romansh. On 1 January 2015 the former municipalities of Ardez, Guarda, Tarasp, Ftan and Sent merged into Scuol. Name The official name has undergone several changes in the 20th century: * Until 1943, the official name of the municipality was ''Schuls''. * In 1943, it was changed to ''Bad Scuol/Schuls''. * In 1970 ''Schuls'' was dropped as an official name, leaving only ''Bad Scuol''. * In 1999 ''Bad'' was dropped, leaving today's name, ''Scuol.'' History Scuol is first mentioned in 1095 as ''Schulles''. At the end of the 11th and in the 12th century, the lords of Tarasp owned extensive estates in Scuol. In 1095/1096 their family founded a Marian monastery in Scuol and endowed it richly. In 1150 the monastery was moved to Marienberg in the Vinschgau valley. In 1178 Pope Alexander III confirmed all of the monastery's possessions in Scuol, inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inn District, Switzerland
Inn District () is a former administrative district in the canton of Graubünden, Switzerland. It had an area of and had a population of 9,476 in 2015. It was replaced with the Engiadina Bassa/Val Müstair Region on 1 January 2017 as part of a reorganization of the Canton. It consisted of four '' Kreise'' (sub-districts) and seven municipalities A municipality is usually a single administrative division having municipal corporation, corporate status and powers of self-government or jurisdiction as granted by national and regional laws to which it is subordinate. The term ''municipality' ...: Mergers and name changes *In 2009 Fuldera, Lü, Müstair, Santa Maria Val Müstair, Tschierv and Valchava merged to form the municipality of Val Müstair.Amtli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neo-Renaissance
Renaissance Revival architecture (sometimes referred to as "Neo-Renaissance") is a group of 19th-century Revivalism (architecture), architectural revival styles which were neither Greek Revival architecture, Greek Revival nor Gothic Revival architecture, Gothic Revival but which instead drew inspiration from a wide range of classicizing Italian modes. Under the broad designation Renaissance architecture 19th-century architects and critics went beyond the architectural style which began in Florence and Central Italy in the early 15th century as an expression of Renaissance humanism; they also included styles that can be identified as Mannerism, Mannerist or Baroque. Self-applied style designations were rife in the mid- and later 19th century: "Neo-Renaissance" might be applied by contemporaries to structures that others called "Italianate", or when many French Baroque features are present (Second Empire (architecture), Second Empire). The divergent forms of Renaissance architect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Lift
A surface lift is a type of cable transport for mountain sports in which skiers, snowboarders, or mountain bikers remain on the ground as they are pulled uphill. While they were once prevalent, they have been overtaken in popularity by higher-capacity and higher-comfort aerial lifts, such as chairlifts and gondola lifts. Today, surface lifts are most often found on beginner slopes, small ski areas, and peripheral slopes. They are also often used to access glacier ski slopes because their supports can be anchored in glacier ice due to the lower forces and realigned due to glacier movement. Surface lifts have some disadvantages compared to aerial lifts: they require more passenger skill and may be difficult for some beginners (especially snowboarders, whose boards point at an angle different than the direction of travel) and children; sometimes they lack a suitable route back to the piste; the snow surface must be continuous; they can get in the way of skiable terrain; they are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
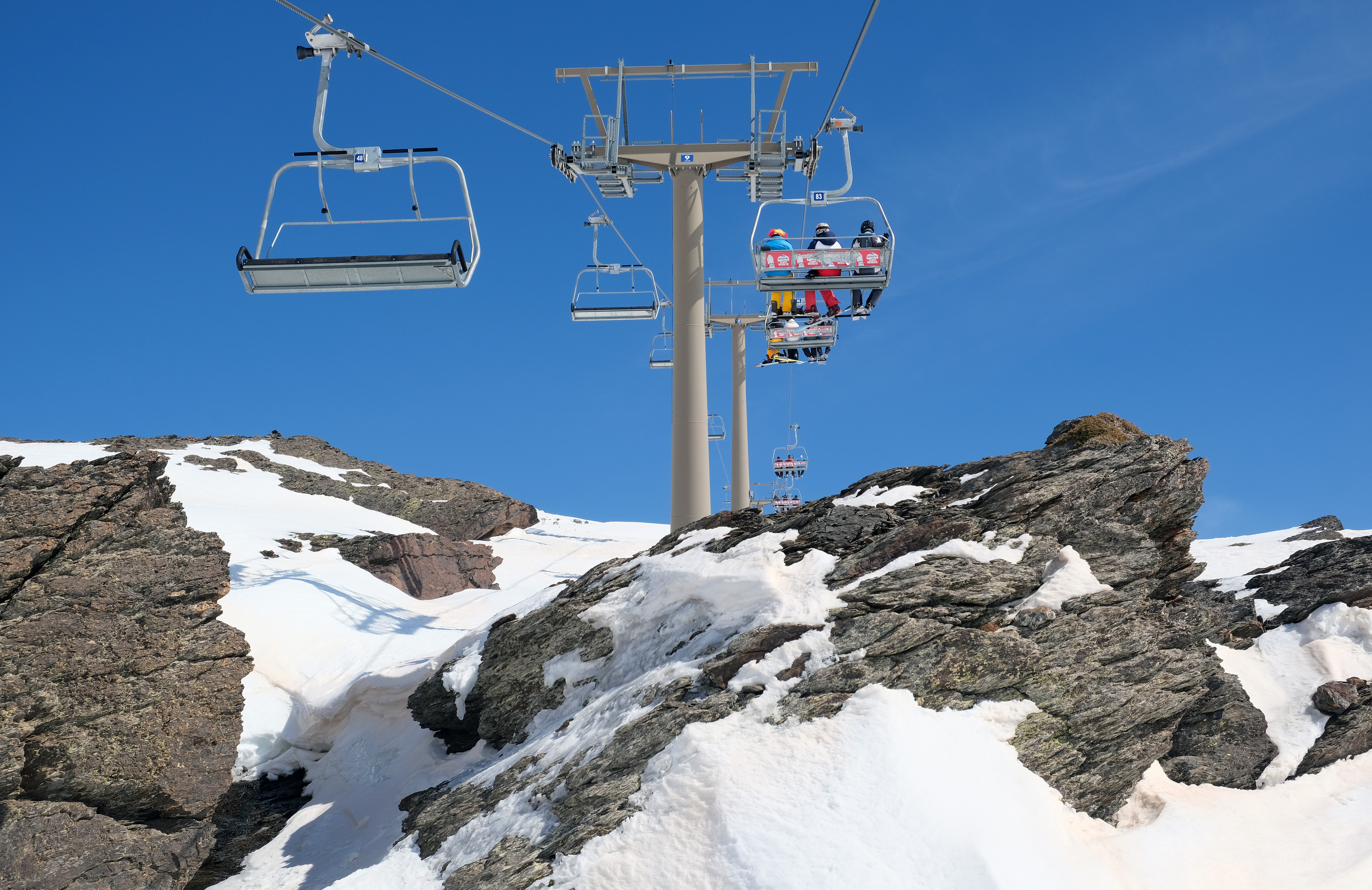
Chairlift
An elevated passenger ropeway, or chairlift, is a type of aerial lift, which consists of a continuously circulating steel wire rope loop strung between two end terminals and usually over intermediate towers. They are the primary on-hill transport at most ski areas (in such cases referred to as 'ski lifts'), but are also found at amusement parks and various tourist attractions. Depending on carrier size and loading efficiency, a passenger ropeway can move up to 4,000 people per hour, and the fastest lifts achieve operating speeds of up to or . The two-person double chair, which for many years was the workhorse of the ski industry, can move roughly 1,200 people per hour at rope speeds of up to . The four person detachable chairlift ("high-speed quad") can transport 2,400 people per hour with an average rope speed of . Some bi- and tri-cable elevated ropeways and reversible tramways achieve much greater operating speeds. Design and function A chairlift consists of numerous c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gondola Lift
A gondola lift is a means of cable transport and type of aerial lift which is supported and propelled by cables from above. It consists of a loop of steel wire rope that is strung between two stations, sometimes over intermediate supporting towers. The cable is driven by a bullwheel in a terminal, which is typically connected to an engine or electric motor. It is often considered a ''continuous system'' since it features a haul rope which continuously moves and circulates around two terminal stations. In contrast, an aerial tramway operates solely with fixed grips and simply shuttles back and forth between two end terminals. The capacity, cost, and functionality of a gondola lift will differ dramatically depending on the combination of cables used for support and haulage and the type of grip (detachable or fixed). Because of the proliferation of such systems in the Alps, the and are also used in English-language texts. The systems may also be referred to as cable car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waldhaus Vulpera 1907
is a privately-owned brewery in Weilheim in the German state of Baden-Württemberg Baden-Württemberg ( ; ), commonly shortened to BW or BaWü, is a states of Germany, German state () in Southwest Germany, east of the Rhine, which forms the southern part of Germany's western border with France. With more than 11.07 million i .... History Waldhaus Brewery was opened in 1833. In 1894 Johann Schmid acquired it and it has been owned by the Schmid family since that time. References {{Commons category, Privatbrauerei Waldhaus External linksOfficial Website 1833 establishments in the German Confederation Beer brands of Germany Breweries in Germany Breweries in Baden-Württemberg Companies based in Baden-Württemberg German companies established in 1833 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhaetian Railway
The Rhaetian Railway (; ; ), abbreviated RhB, is a Swiss transport company that owns the largest network of all private railway operators in Switzerland. Headquartered in Chur, the RhB operates all the railway lines of the Cantons of Switzerland, Swiss canton of canton of Grisons, Grisons, except for the line from Sargans to the cantonal capital, Chur, which are operated by Swiss Federal Railways (SBB CFF FFS), as well as the line from Disentis/Mustér to the Oberalp Pass and further on to Andermatt, Canton of Uri, Uri, which is operated by Matterhorn Gotthard Bahn (MGB). Inaugurated in 1888 and expanded from 1896 onwards in various sections, the RhB network is located almost entirely within Grisons, with one station across the Italy–Switzerland border, Italian border at Tirano (Rhaetian Railway station), Tirano. The Rhaetian Railway serves a number of major tourist destinations, such as St. Moritz and Davos. One of the RhB lines, the Bernina Railway, crosses the Berni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bever–Scuol-Tarasp Railway
The Bever–Scuol-Tarasp railway—also called the Engadinerbahn (Engadine Railway), Engadinerlinie (Engadine Line), Unterengadinerbahn (Lower Engadine Railway) or Unterengadinerlinie (Lower Engadine Line)—is a Swiss Metre-gauge railway, metre-gauge railway, which is operated by the Rhaetian Railway (''Rhätischen Bahn''; RhB) and connects the Lower Engadine with the Albula Railway. The Samedan–Pontresina railway is often also considered part of the line. Both lines are closely linked with each other. The Bever–Scuol-Tarasp railway is part of the RhB mainline network, so the kilometrage (chainage) has its zero point in Landquart railway station, Landquart. History After the construction of the Albula Railway the canton of Grisons and the federal military authorities, among others, were very interested in a railway line through the Engadine. Originally this line was intended only as a branch line, but due to its high popularity it was given a higher priority. The line was fin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protestantism
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that emphasizes Justification (theology), justification of sinners Sola fide, through faith alone, the teaching that Salvation in Christianity, salvation comes by unmerited Grace in Christianity, divine grace, the priesthood of all believers, and the Bible as the sole infallible source of authority for Christian faith and practice. The five solae, five ''solae'' summarize the basic theological beliefs of mainstream Protestantism. Protestants follow the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began in the 16th century with the goal of reforming the Catholic Church from perceived Criticism of the Catholic Church, errors, abuses, and discrepancies. The Reformation began in the Holy Roman Empire in 1517, when Martin Luther published his ''Ninety-five Theses'' as a reaction against abuses in the sale of indulgences by the Catholic Church, which purported to offer the remission of the Purgatory, temporal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
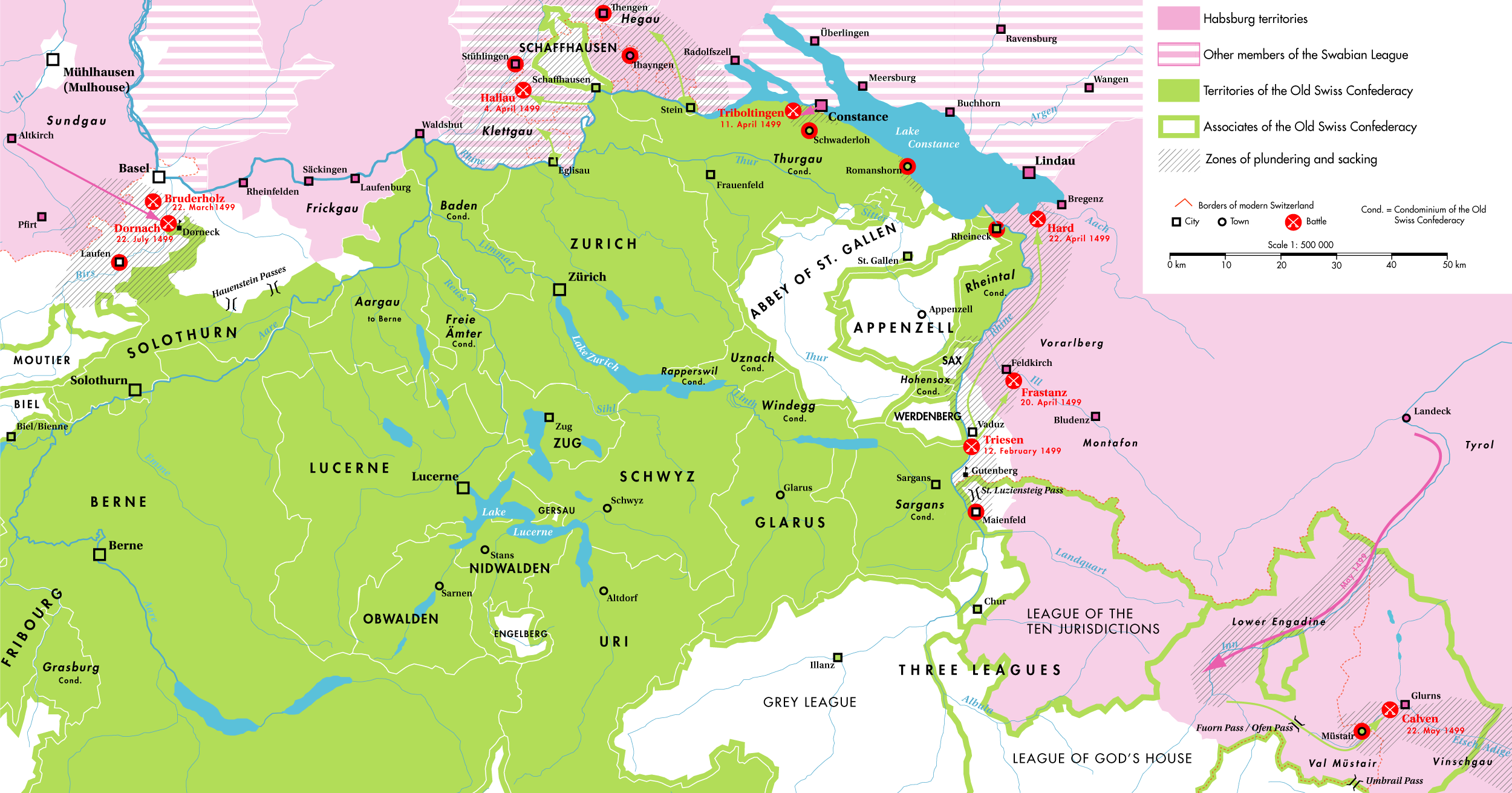
Swabian War
The Swabian War of 1499 ( (spelling depending on dialect), called or ("Swiss War") in Germany and ("War of the Engadin" in Austria) was the last major armed conflict between the Old Swiss Confederacy and the House of Habsburg. What had begun as a local conflict over the control of the Val Müstair and the Umbrail Pass in the Grisons soon got out of hand when both parties called upon their allies for help; the Habsburgs demanding the support of the Swabian League, while the Federation of the Three Leagues of the Grisons turning to the Swiss '' Eidgenossenschaft''. Hostilities quickly spread from the Grisons through the Rhine valley to Lake Constance and even to the Sundgau in southern Alsace, the westernmost part of the Habsburg region of Further Austria.The main references used are Morard in general and Riezler for the detailed chronology in the section on the course of the war. Many battles were fought from January to July 1499, and in all but a few minor skirmishes, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |