|
Scrambling (military)
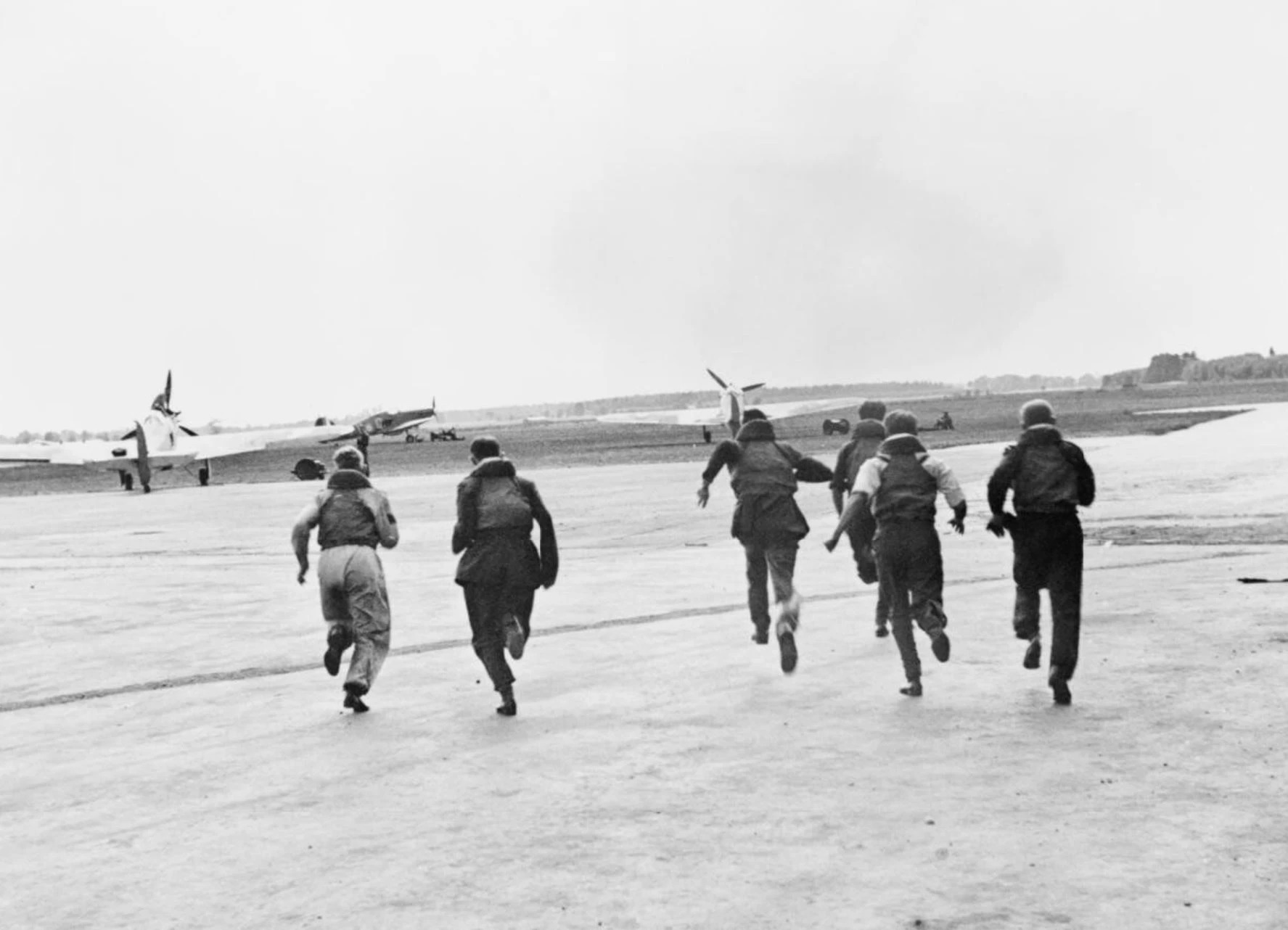
In military aviation, scrambling is the act of quickly mobilising military aircraft. Scrambling can be in reaction to an immediate threat, usually to intercept hostile aircraft. Battle of Britain The term was used during the Battle of Britain, when Royal Air Force pilots and their fighters were readied and available to fly. Detection and monitoring of enemy aircraft, e.g. by the Chain Home radar stations, would feed into the RAF Fighter Command's Dowding system for control and management of the defenses. Once a decision had been made to intercept the enemy formation a telephone call would be made to the chosen fighter squadron's airfield, and those air crews available would be scrambled. The scramble order was communicated to alert pilots waiting by their aircraft by the loud ringing of a bell. Every minute lost before takeoff would be advantageous to the enemy, as it could allow a pilot to gain extra height above the advancing plane formations. Information passed to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilot Seen Running To Fighter
An aircraft pilot or aviator is a person who controls the flight of an aircraft by operating its directional flight controls. Some other aircrew members, such as navigators or flight engineers, are also considered aviators because they are involved in operating the aircraft's navigation and engine systems. Other aircrew members, such as drone operators, flight attendants, mechanics and ground crew, are not classified as aviators. In recognition of the pilots' qualifications and responsibilities, most militaries and many airlines worldwide award aviator badges to their pilots. Definition The first recorded use of the term ''aviator'' (''aviateur'' in French) was in 1887, as a variation of ''aviation'', from the Latin ''avis'' (meaning ''bird''), coined in 1863 by in ''Aviation Ou Navigation Aérienne'' ("Aviation or Air Navigation"). The term ''aviatrix'' (''aviatrice'' in French), now archaic, was formerly used for a female pilot. The term ''aviator'' (''aviateur'' in F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airspace
Airspace is the portion of the atmosphere controlled by a country above its territory, including its territorial waters or, more generally, any specific three-dimensional portion of the atmosphere. It is not the same as outer space which is the expanse or space outside the Earth and aerospace which is the general term for Earth's atmosphere and the outer space within the planet's vicinity. Horizontal boundary By international law, a state "has complete and exclusive sovereignty over the airspace above its territory", which corresponds with the maritime definition of territorial waters as being 12 nautical miles (22.2 km) out from a nation's coastline. Airspace not within any country's territorial limit is considered international, analogous to the "high seas" in maritime law. However, a country may, by international agreement, assume responsibility for controlling parts of international airspace, such as those over the oceans. Such airspace in respect of which a countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Point Defense
Point defence (or point defense; see spelling differences) is the defence of a single object or a limited area, e.g. a ship, building or an airfield, now usually against air attacks and guided missiles. Point defence weapons have a smaller range in contrast to area-defence systems and are placed near or on the object to be protected. Point defence may include: * short-ranged interceptor aircraft * Close-in weapon systems on ship * land-based short-ranged anti-aircraft guns or surface-to-air missile systems * Active protection systems on tanks or other armoured fighting vehicles Coastal artillery to protect harbours is similar conceptually, but is generally not classified as point defence. Similarly, passive systems—electronic countermeasures, decoys, chaff, flares, barrage balloons—are not considered point defence. Examples Aircraft * Bachem Ba 349 ''Natter'' – vertical take-off rocket powered crewed interceptor (prototypes only) * Convair XF-92 – Later used as test ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
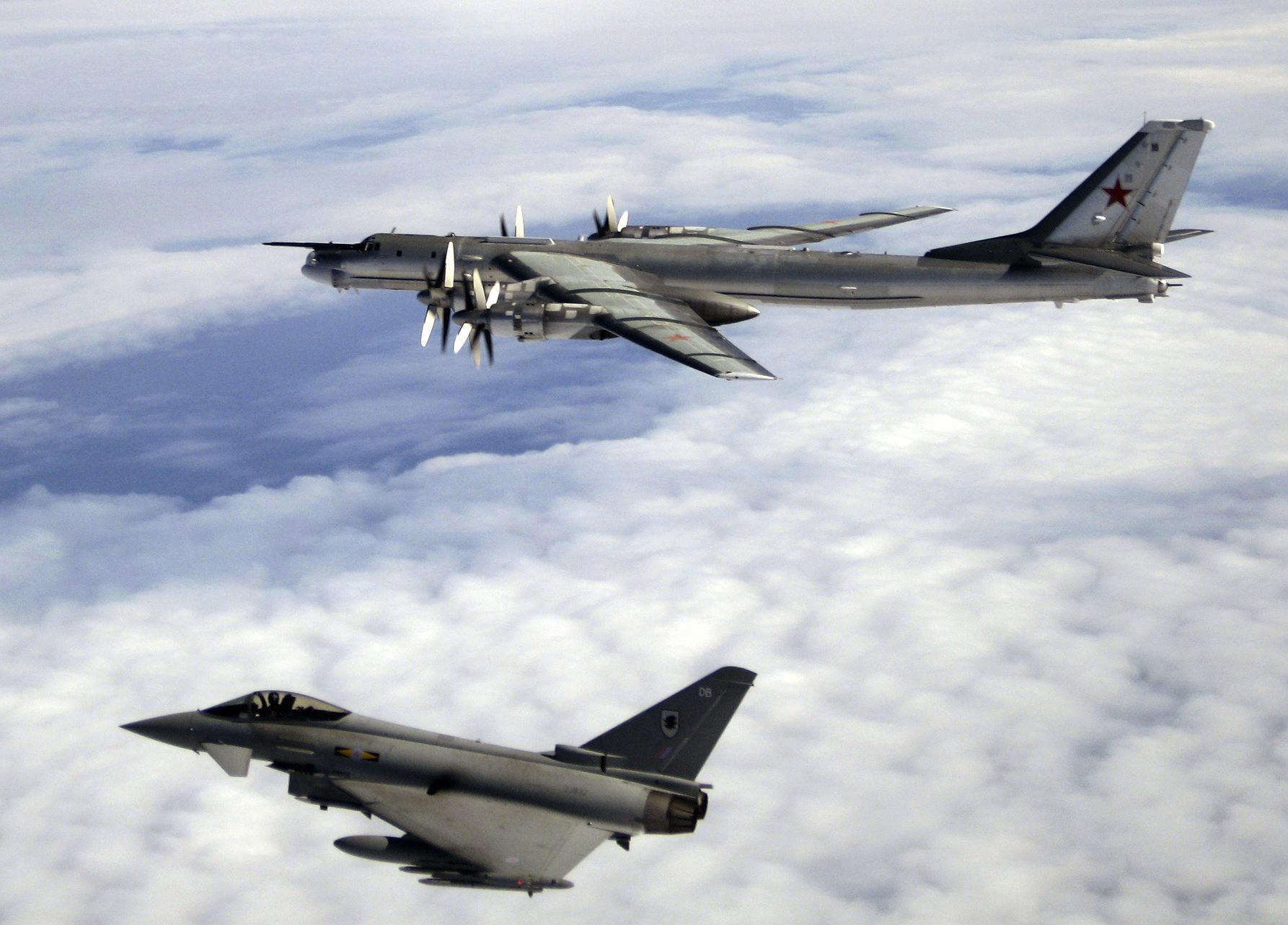
Operational Readiness Platform
Quick Reaction Alert (QRA) is state of readiness and ''modus operandi'' of air defence maintained at all hours of the day by NATO air forces. The United States usually refers to Quick Reaction Alert as 'Airspace Control Alert'. Some non-NATO countries maintain a QRA, either full-time or part-time. Operation QRA in the United Kingdom There are two QRA stations in the United Kingdom, one at RAF Coningsby in the east of England, and the other at RAF Lossiemouth in Scotland. Pilots and engineers on QRA duty are at immediate readiness twenty-four hours a day. They are fully dressed in the Crew Ready Room, which are next to the hangars, a hardened aircraft shelter known informally as ''Q-sheds'', which houses the interceptor aircraft, since 2007 the Eurofighter Typhoon. Pilots are on QRA duty around once or twice a month, each a twenty-four-hour shift. Engineers are on QRA duty three or four times a year, each for a twenty-four-hour a day shift, for seven days at a time. Two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary Of RAF Code Names
Code words used by the Royal Air Force during the Second World War: *Angels – height in thousands of feet. * Balbo – a large formation of aircraft.Rawlings, John D.R., ''Fighter Squadrons of the RAF and their Aircraft'', London: Macdonald and Jane's Publishers Ltd. *Bandit – identified enemy aircraft. *Bogey – unidentified (possibly unfriendly) aircraft. *Buster – radio-telephony code phrase for 'maximum throttle' or full power climb. *Cab rank – an airborne patrol of fighter-bombers near a combat zone which could be called upon to attack specific targets as necessary. *Channel Stop – air operations intended to stop enemy shipping passing through the Straits of Dover. *Circus – daytime bomber attacks with fighter escorts against short range targets, to occupy enemy fighters and keep them in the area concerned. *Diver – radio-telephony code word for a sighted V-1 flying bomb. *Fighter night – introduced in November 1940, night patrols above a specified height wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground-controlled Interception
Ground-controlled interception (GCI) is an air defence tactic whereby one or more radar stations or other observational stations are linked to a command communications centre which guides interceptor aircraft to an airborne target. This tactic was pioneered during World War I by the London Air Defence Area organization, which became the Royal Air Force's Dowding system in World War II, the first national-scale system. The ''Luftwaffe'' introduced similar systems during the war, but most other combatants did not suffer the same threat of air attack and did not develop complex systems like these until the Cold War era. Today the term GCI refers to the style of battle direction, but during WWII it also referred to the radars themselves. Specifically, the term was used to describe a new generation of radars that spun on their vertical axis in order to provide a complete 360 degree view of the sky around the station. Previous systems, notably Chain Home (CH), could only be directed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimum Interval Takeoff
A minimum interval takeoff (MITO) is a technique of the United States Air Force for scrambling all available bomber and Aerial refueling, tanker aircraft at twelve- and fifteen-second intervals, respectively. Before takeoff, the aircraft perform an Elephant walk (aeronautics), elephant walk to the runway. It is designed to maximize the number of aircraft launched in the least amount of time possible before the base suffers a nuclear strike, which would obliterate all remaining aircraft. Although the practice is aimed to efficiently send aircraft off as quickly as possible, it does not come without risks. Sending aircraft into the wake turbulence of another aircraft at such close intervals could cause unpredictable aerodynamic behavior and loss of aircraft control. More than once, aircraft have crashed on takeoff after encountering such wake turbulence. Description The minimum interval takeoff was designed by the U.S. Air Force to get its bomber fleet in the air within fifteen min ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Combat Readiness
Combat readiness is a condition of the armed forces and their constituent units and formations, warships, aircraft, weapon systems or other military technology and equipment to perform during combat military operations, or functions consistent with the purpose for which they are organized or designed, or the managing of resources and personnel training in preparation for combat. Different armed forces maintain different levels of readiness for the troops to engage in combat, varying from minutes to months; economic considerations are a major factor in explaining the variation.Jordan, pp. 2–3 See also *Alert crew *Alert state *COGCON *DEFCON *Mobilization *Scrambling (military) *List of established military terms This is a list of established military terms which have been in use for at least 50 years. Since technology and doctrine have changed over time, not all of them are in current use, or they may have been superseded by more modern terms. However, th ... Reference ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Established Military Terms
This is a list of established military terms which have been in use for at least 50 years. Since technology and doctrine have changed over time, not all of them are in current use, or they may have been superseded by more modern terms. However, they are still in current use in articles about previous military periods. Some of them like ''camouflet'' have been adapted to describe modern versions of old techniques. Administrative (all arms) * Access control * Base of operation * Cantonment: a temporary or semi-permanent military quarters; in South Asia, the term cantonment also describes permanent military stations. * Chief of defence * Cloak and Dagger * Combat information center * Command (military formation) * Command center * Command and control * Commander-in-chief * Command hierarchy * Defense diplomacy * Defence minister * Directive control * Force multiplication * Headquarters unit * Military facility * Military genius - Clausewitz's attempt to identify cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index Of Aviation Articles
Aviation is the design, development, production, operation, and use of aircraft, especially heavier-than-air aircraft. Articles related to aviation include: A Aviation accidents and incidents – Above Mean Sea Level (AMSL) – ADF – Accessory drive – Advance airfield – Advanced air mobility – Advanced technology engine – Adverse yaw – Aerial ramming – Aerial reconnaissance – Aerobatics – Aerodrome – Aerodrome mapping database (AMDB) – Aerodynamics – Aerofoil – Aerodrome beacon – Aeronautical Information Manual (AIM) – Aeronautical chart – Aeronautical Message Handling System – Aeronautical phraseology – Aeronautics – Aeronaval – Aerospace – Aerospace engineering – Afterburner – Agile Combat Employment (ACE) – Aileron – Air charter – Air defense identification zone (ADIZ) – Air freight terminal – Air traffic flow management – Air-augmented rocket – Airband – Airbase (AFB) – Airborne colli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quick Reaction Alert
Quick Reaction Alert (QRA) is state of Combat readiness, readiness and ''modus operandi'' of Anti-aircraft warfare, air defence maintained at all hours of the day by NATO air forces. The United States usually refers to Quick Reaction Alert as 'Airspace Control Alert'. Some non-NATO countries maintain a QRA, either full-time or part-time. Operation QRA in the United Kingdom There are two QRA stations in the United Kingdom, one at RAF Coningsby in the east of England, and the other at RAF Lossiemouth in Scotland. Pilots and engineers on QRA duty are at immediate readiness twenty-four hours a day. They are Flight suit, fully dressed in the Crew Ready Room, which are next to the hangars, a hardened aircraft shelter known informally as ''Q-sheds'', which houses the interceptor aircraft, since 2007 the Eurofighter Typhoon. Fighter pilot, Pilots are on QRA duty around once or twice a month, each a twenty-four-hour shift. Engineers are on QRA duty three or four times a year, each for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bomber
A bomber is a military combat aircraft that utilizes air-to-ground weaponry to drop bombs, launch aerial torpedo, torpedoes, or deploy air-launched cruise missiles. There are two major classifications of bomber: strategic and tactical. Strategic bombing is done by heavy bombers primarily designed for long-range bombing missions against strategic targets to diminish the enemy's ability to wage war by limiting access to resources through crippling infrastructure, reducing industrial output, or inflicting massive civilian casualties to an extent deemed to force surrender. Tactical bombing is aimed at countering enemy military activity and in supporting offensive operations, and is typically assigned to smaller aircraft operating at shorter ranges, typically near the troops on the ground or against enemy shipping. Bombs were first dropped from an aircraft during the Italo-Turkish War, with the first major deployments coming in the World War I, First World War and World War II, Seco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |