|
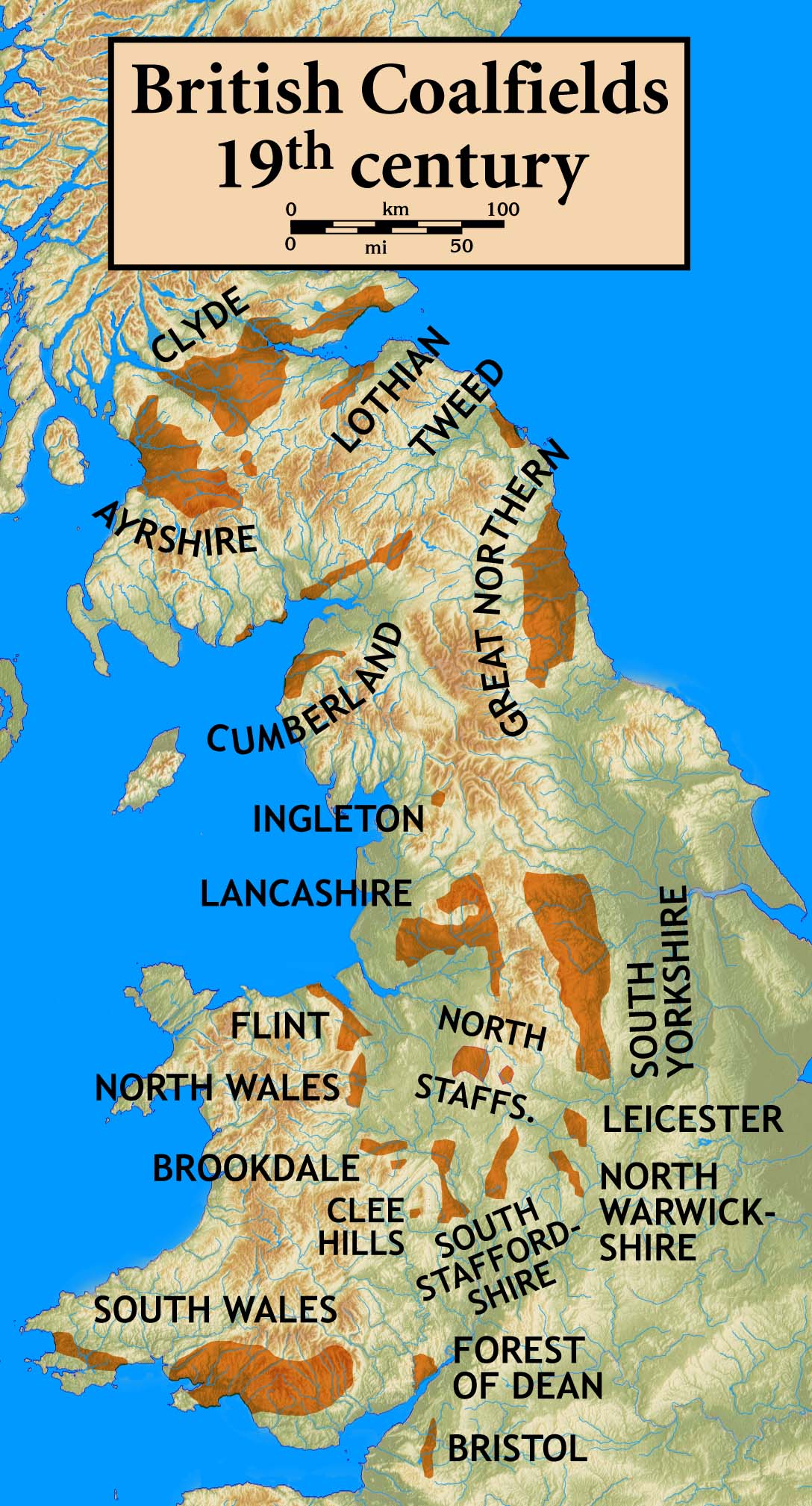
Scottish Coal Measures Group
The Scottish Coal Measures Group is a lithostratigraphic unit referring to the coal-bearing succession of rock strata which occur in Scotland during the Westphalian regional stage of the Carboniferous Period. It is the Scottish portion of the informal Coal Measures Group, which also includes the South Wales and Pennine coal measures. The Scottish coal measures are well-exposed across the Midland Valley. The group is also found within small grabens in the vicinity of Sanquhar and Thornhill. Stratigraphy From youngest to oldest, the Scottish Coal Measures Group comprises the: * Scottish Upper Coal Measures Formation ( Bolsovian / Westphalian C) * Scottish Middle Coal Measures Formation ( Duckmantian / Westphalian B) * Scottish Lower Coal Measures Formation ( Langsettian / Westphalian A) Paleobiota The Scottish coal measures represent a lush coal swamp ecosystem populated by large amphibious tetrapods (amphibians, in the broad sense). Amphibians known from the group i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group (stratigraphy)
In geology, a group is a lithostratigraphic unit consisting of a series of related formations that have been classified together to form a group. Formations are the fundamental unit of stratigraphy. Groups may sometimes be combined into supergroups. Groups are useful for showing relationships between formations, and they are also useful for small-scale mapping or for studying the stratigraphy of large regions. Geologists exploring a new area have sometimes defined groups when they believe the strata within the groups can be divided into formations during subsequent investigations of the area. It is possible for only some of the strata making up a group to be divided into formations. An example of a group is the Glen Canyon Group, which includes (in ascending order) the Wingate Sandstone, the Moenave Formation, the Kayenta Formation, and the Navajo Sandstone. Each of the formations can be distinguished from its neighbor by its lithology, but all were deposited in the sam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westphalian (stage)
The Westphalian is a stage in the regional stratigraphy of northwest Europe with an age between roughly 313 and 304 Ma (million years ago). It is a subdivision of the Carboniferous system or period and the regional Silesian series. The Westphalian is named for the region of Westphalia (German: ''Westfalen'') in western Germany where strata of this age occur. The Coal Measures of England and Wales are also largely of Westphalian age though they also extend into the succeeding Stephanian. The Westphalian age is preceded by the Namurian stage/age (which corresponds to the Millstone Grit Series of Great Britain) and succeeded by the Stephanian stage/age (which corresponds to the uppermost part of the Coal Measures of Great Britain). In the official geologic timescale of the ICS, the Westphalian is placed within the Pennsylvanian epoch (318-299 Ma).F M Gradstein, J G Ogg, A G Smith et al 2004, ‘A Geologic Time Scale 2004’. The (regionally defined) Westphalian stage corres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embolomeri
Embolomeri is an order of tetrapods or stem-tetrapods, possibly members of Reptiliomorpha. Embolomeres first evolved in the Early Carboniferous (Mississippian) Period and were the largest and most successful predatory tetrapods of the Late Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) Period. They were specialized semiaquatic predators with long bodies for eel-like undulatory swimming. Embolomeres are characterized by their vertebral centra, which are formed by two cylindrical segments, the pleurocentrum at the rear and intercentrum at the front. These segments are equal in size. Most other tetrapods have pleurocentra and intercentra which are drastically different in size and shape. Embolomeres were among the earliest large carnivorous tetrapods, with members such as the crocodilian-like '' Proterogyrinus'' appearing in the Visean stage of the Carboniferous. They declined in diversity during the Permian period, though at least one representative ('' Archeria)'' was common in the Early Permia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limb (anatomy), limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant taxon, extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (pelycosaurs, extinct therapsids and all extant mammals). Tetrapods evolved from a clade of primitive semiaquatic animals known as the Tetrapodomorpha which, in turn, evolved from ancient lobe-finned fish (sarcopterygians) around 390 million years ago in the Middle Devonian, Middle Devonian period; their forms were transitional between lobe-finned fishes and true four-limbed tetrapods. Limbed vertebrates (tetrapods in the broad sense of the word) are first known from Middle Devonian trackways, and body fossils became common near the end of the Late Devonian but these were all aquatic. The first crown group, crown-tetrapods (last common ancestors of extant tetrapods capable of terrestrial locomotion) appeared by the very early Mississippian ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coal Swamp
Coal forests were the vast swathes of wetlands that covered much of the Earth's tropical land areas during the late Carboniferous (Pennsylvanian) and Permian times.Cleal, C. J. & Thomas, B. A. (2005). "Palaeozoic tropical rainforests and their effect on global climates: is the past the key to the present?" ''Geobiology'', ''3'', p. 13-31. As vegetable matter from these forests decayed, enormous deposits of peat accumulated, which later changed into coal. Much of the carbon in the peat deposits produced by coal forests came from photosynthetic splitting of existing carbon dioxide, which released the accompanying split-off oxygen into the atmosphere. This process may have greatly increased the oxygen level, possibly as high as about 35%, making the air more easily breathable by animals with inefficient respiratory systems, as indicated by the size of ''Meganeura'' compared to modern dragonflies. Coal forests covered tropical Euramerica (Europe, eastern North America, northwestern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thornhill, Dumfries And Galloway
Thornhill ( gd, Bàrr na Driseig Archived frothe original on 5 March 2014) is a village in the Mid Nithsdale area of Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland, south of Sanquhar and north of Dumfries on the main A76 road. Thornhill sits in the Nithsdale valley with the Carsphairn and Scaur range to the west and the Lowther hills to the east. It was initially a small village, planned and built in 1717 on the Queensberry Estate on the road linking Dumfries to Glasgow. The Earl of Queensberry initially named the village ' New Dalgarnock' however the name did not achieve popular approval. The village is primarily comprised a grid pattern with the main street of Drumlanrig Street (the A76), East and West Morton Streets, New Street, Townhead Street and Gill Road (the A702). The village is near Drumlanrig Castle, a 17th-century turreted mansion once the ancient Douglas stronghold, now home to the Duke of Buccleuch and Queensberry. The grounds contain Tibbers Castle which was founded in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanquhar
Sanquhar ( sco, Sanchar, gd, Seanchair) is a village on the River Nith in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland, north of Thornhill and west of Moffat. It is a former Royal Burgh. It is notable for its tiny post office, established in 1712 and considered the oldest working post office in the world. It was also where the Covenanters, who opposed episcopalisation of the church, signed the ''Sanquhar Declaration'' renouncing their allegiance to the King, an event commemorated by a monument in the main street. The church of St Brides contains a memorial to James Crichton, a 16th-century polymath. The ruins of Sanquhar Castle stand nearby. Nithsdale Wanderers, the local football team, were formed in 1897. In 1924–25, they won the Scottish Division Three. History The name "Sanquhar" comes from the Scottish Gaelic language ''An t-Seanchair'', meaning "old fort". A 15th-century castle ruin overlooks the town, but the name predates even this ancient fort. The antiquary, William Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graben
In geology, a graben () is a depressed block of the crust of a planet or moon, bordered by parallel normal faults. Etymology ''Graben'' is a loan word from German, meaning 'ditch' or 'trench'. The word was first used in the geologic context by Eduard Suess in 1883. The plural form is either ''graben'' or ''grabens''. Formation A graben is a valley with a distinct escarpment on each side caused by the displacement of a block of land downward. Graben often occur side by side with horsts. Horst and graben structures indicate tensional forces and crustal stretching. Graben are produced from parallel normal faults, where the displacement of the hanging wall is downward, while that of the footwall is upward. The faults typically dip toward the center of the graben from both sides. Horsts are parallel blocks that remain between graben; the bounding faults of a horst typically dip away from the center line of the horst. Single or multiple graben can produce a rift valley. Ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coal Measures
In lithostratigraphy, the coal measures are the coal-bearing part of the Upper Carboniferous System. In the United Kingdom, the Coal Measures Group consists of the Upper Coal Measures Formation, the Middle Coal Measures Formation and the Lower Coal Measures Formation. The group records the deposition of fluvio-deltaic sediments which consists mainly of clastic rocks ( claystones, shales, siltstones, sandstones, conglomerates) interstratified with the beds of coal. In most places, the coal measures are underlain by coarser clastic sequences known as Millstone Grit, of Namurian age. The top of the coal measures may be marked by an unconformity, the overlying rocks being Permian or later in age. In some parts of Britain, however, the coal measures grade up into mainly coal-barren red beds of late Westphalian and possibly Stephanian age. Within the Pennine Basin these barren measures are now referred to as the Warwickshire Group, from the district where they achieve their thic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennine Coal Measures Group
The Pennine Coal Measures Group is a lithostratigraphical term referring to the coal-bearing succession of rock strata which occur in the United Kingdom within the Westphalian Stage of the Carboniferous Period. In formal use, the term replaces the Coal Measures Group as applied to the succession of coal-bearing strata within the Pennine Basin which includes all of the coalfields of northern England and the English Midlands. It includes the largely concealed Canonbie Coalfield of southern Scotland and the coalfields of northeast Wales and the minor Anglesey coalfield. The sequence consists in the main of mudstones and siltstones together with numerous sandstones, the more significant ones of which are individually named. Some are laterally extensive, others are more restricted in their range. There are numerous coal seams, again with some being more laterally continuous than others. Those which were economically valuable were named though any individual seam may have attra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Wales Coal Measures Group
The South Wales Coal Measures Group is a lithostratigraphical term referring to the coal-bearing succession of rock strata which occur in South Wales within the Westphalian Stage of the Carboniferous Period. The Group name is also applied to rocks of similar age across southern England from the Bristol Coalfield east to the concealed Oxfordshire, Berkshire and Kent Coalfields. In formal use, the term replaces the earlier Coal Measures Group The Group comprises the: :* South Wales Upper Coal Measures Formation :* South Wales Middle Coal Measures Formation :* South Wales Lower Coal Measures Formation The term 'Productive Coal Measures' was formerly used for this succession. Note that, other than a 0-30m thick sequence immediately above the ''Cambriense'' Marine Band, the South Wales rock sequence which had formerly been assigned to the 'Upper Coal Measures' (which was also referred to as the 'Pennant Measures') is no longer considered to be a part of the Coal Measures and is now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |