|
Scott Jay Kenyon
Scott Jay Kenyon (born 1956) is an American astrophysicist. His work has included advances in symbiotic and other types of interacting binary stars, the formation and evolution of stars, and the formation of planetary systems. Career Kenyon received a B.S. in physics from Arizona State University in 1978 and a Ph.D. in astronomy from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign in 1983. His doctoral dissertation is titled ''The Physical Structure of the Symbiotic Stars'' and was expanded into a book, ''The Symbiotic Stars''. After postdoctoral work at the Center for Astrophysics Harvard & Smithsonian, including a CfA Fellowship, he joined the scientific staff at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory. Kenyon is a Fellow of the AAAS, a Fellow of the American Physical Society, and is included in the Web of Knowledge index of highly cited researchers. Scientific work Kenyon has worked extensively on symbiotic binary stars. His book ''The Symbiotic Stars'' was the first to su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrophysics
Astrophysics is a science that employs the methods and principles of physics and chemistry in the study of astronomical objects and phenomena. As one of the founders of the discipline said, Astrophysics "seeks to ascertain the nature of the heavenly bodies, rather than their positions or motions in space–''what'' they are, rather than ''where'' they are." Among the subjects studied are the Sun, other stars, galaxies, extrasolar planets, the interstellar medium and the cosmic microwave background. Emissions from these objects are examined across all parts of the electromagnetic spectrum, and the properties examined include luminosity, density, temperature, and chemical composition. Because astrophysics is a very broad subject, ''astrophysicists'' apply concepts and methods from many disciplines of physics, including classical mechanics, electromagnetism, statistical mechanics, thermodynamics, quantum mechanics, relativity, nuclear and particle physics, and atomic a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Tauri Stars
T Tauri stars (TTS) are a class of variable stars that are less than about ten million years old. This class is named after the prototype, T Tauri, a young star in the Taurus star-forming region. They are found near molecular clouds and identified by their optical variability and strong chromospheric lines. T Tauri stars are pre-main-sequence stars in the process of contracting to the main sequence along the Hayashi track, a luminosity–temperature relationship obeyed by infant stars of less than 3 solar masses () in the pre-main-sequence phase of stellar evolution. It ends when a star of or larger develops a radiative zone, or when a smaller star commences nuclear fusion on the main sequence. History While T Tauri itself was discovered in 1852, the T Tauri class of stars were initially defined by Alfred Harrison Joy in 1945. Characteristics T Tauri stars comprise the youngest visible F, G, K and M spectral type stars (). Their surface temperatures are similar to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
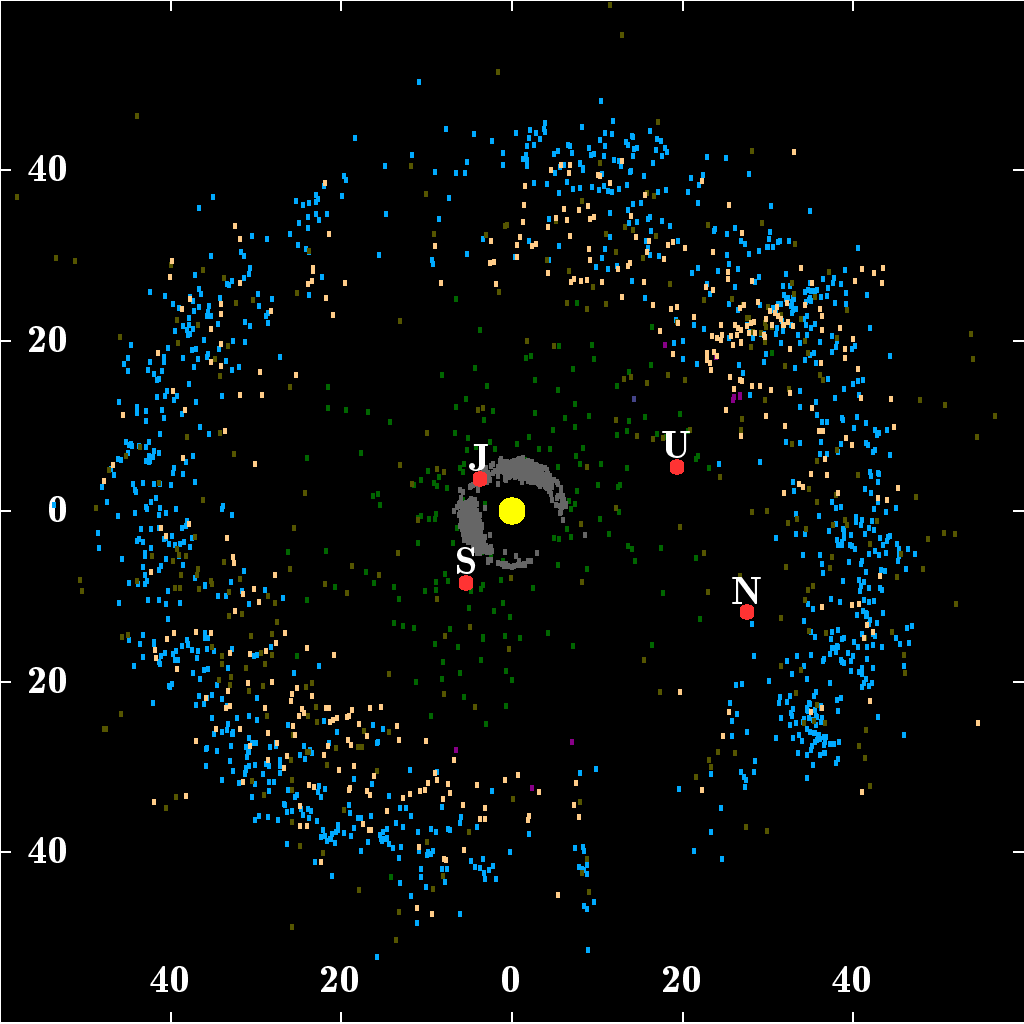
Outer Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar System" and "solar system" structures in theinaming guidelines document. The name is commonly rendered in lower case ('solar system'), as, for example, in the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' an''Merriam-Webster's 11th Collegiate Dictionary''. is the gravitationally bound system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it. It formed 4.6 billion years ago from the gravitational collapse of a giant interstellar molecular cloud. The vast majority (99.86%) of the system's mass is in the Sun, with most of the remaining mass contained in the planet Jupiter. The four inner system planets— Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars—are terrestrial planets, being composed primarily of rock and metal. The four giant planets of the outer system are subst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
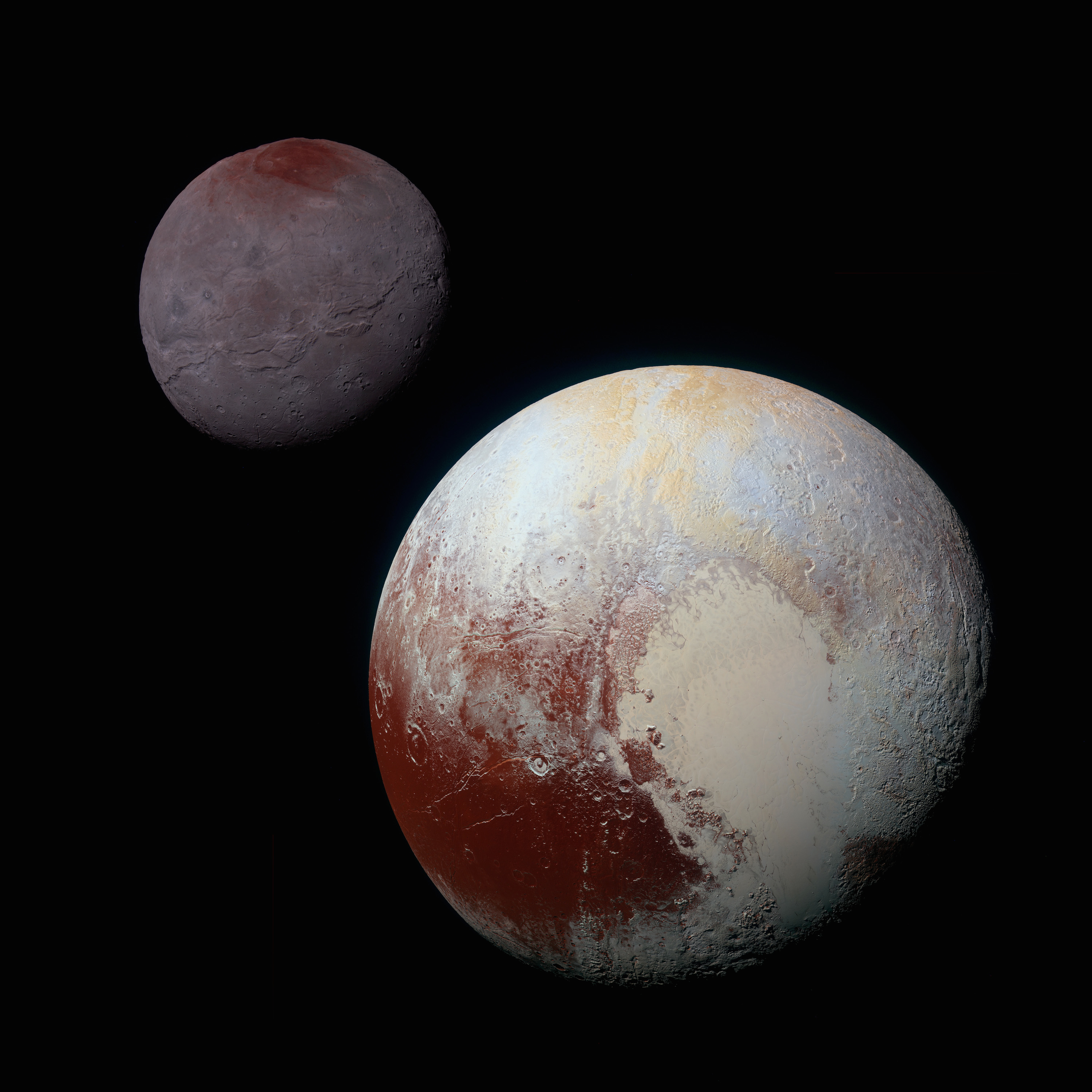
90377 Sedna
Sedna ( minor-planet designation 90377 Sedna) is a dwarf planet in the outer reaches of the Solar System that is in the innermost part of its orbit; it is 84 astronomical units (AU), or 1.26×1010 km, from the Sun, almost three times farther than Neptune. Spectroscopy has revealed that Sedna's surface composition is largely a mixture of water, methane, and nitrogen ices with tholins, similar to those of some other trans-Neptunian objects. Its surface is one of the reddest among Solar System objects. Sedna, within estimated uncertainties, is tied with as the largest planetoid not known to have a moon. Sedna's orbit is one of the largest in the Solar System other than those of long-period comets, with its aphelion (farthest distance from the Sun) estimated at 937 AU. This is 31 times Neptune's distance from the Sun, or 5.5 light-days, and well beyond the closest portion of the heliopause, which defines the boundary of interstellar space. As of 2022, the dwarf plane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dwarf Planet
A dwarf planet is a small planetary-mass object that is in direct orbit of the Sun, smaller than any of the eight classical planets but still a world in its own right. The prototypical dwarf planet is Pluto. The interest of dwarf planets to planetary geologists is that they may be geologically active bodies, an expectation that was borne out in 2015 by the '' Dawn'' mission to and the '' New Horizons'' mission to Pluto. Astronomers are in general agreement that at least the nine largest candidates are dwarf planets: Pluto, , , , , , , , and . Of these and the tenth-largest candidate , all but Sedna have either been visited by spacecraft (Pluto and Ceres) or have at least one known moon (Pluto, Eris, Haumea, Makemake, Gonggong, Quaoar, Orcus, and Salacia), which allows their masses and thus an estimate of their densities to be determined. Mass and density in turn can be fit into geophysical models in an attempt to determine the nature of these worlds. Some astronomers includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuiper Belt Objects
The Kuiper belt () is a circumstellar disc in the outer Solar System, extending from the orbit of Neptune at 30 astronomical units (AU) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun. It is similar to the asteroid belt, but is far larger—20 times as wide and 20–200 times as massive. Like the asteroid belt, it consists mainly of small bodies or remnants from when the Solar System formed. While many asteroids are composed primarily of rock and metal, most Kuiper belt objects are composed largely of frozen volatiles (termed "ices"), such as methane, ammonia, and water. The Kuiper belt is home to most of the objects that astronomers generally accept as dwarf planets: Orcus, Pluto, Haumea, Quaoar, and Makemake. Some of the Solar System's moons, such as Neptune's Triton and Saturn's Phoebe, may have originated in the region. The Kuiper belt was named after Dutch astronomer Gerard Kuiper, although he did not predict its existence. In 1992, minor planet (15760) Albion wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debris Disks
Debris (, ) is rubble, wreckage, ruins, litter and discarded garbage/refuse/trash, scattered remains of something destroyed, or, as in geology, large rock fragments left by a melting glacier, etc. Depending on context, ''debris'' can refer to a number of different things. The first apparent use of the French word in English is in a 1701 description of the army of Prince Rupert upon its retreat from a battle with the army of Oliver Cromwell, in England. Disaster In disaster scenarios, tornadoes leave behind large pieces of houses and mass destruction overall. This debris also flies around the tornado itself when it is in progress. The tornado's winds capture debris it kicks up in its wind orbit, and spins it inside its vortex. The tornado's wind radius is larger than the funnel itself. Tsunamis and hurricanes also bring large amounts of debris, such as Hurricane Katrina in 2005 and Hurricane Sandy in 2012. Earthquakes rock cities to rubble debris. Geological In geolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spitzer
Spitzer is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Andre Spitzer (1945–1972), Israeli fencing coach and victim of the Munich massacre * Bernard Spitzer (1924–2014), American real estate developer and philanthropist, father of Eliot Spitzer * Eliot Spitzer (born 1959), 54th Governor of New York (2007–2008) * Frank Spitzer (1926–1992), Austrian-born American mathematician, author of Spitzer's formula * Frédéric Spitzer, 19th century art dealer, after whom the Spitzer Cross is named * Leo Spitzer (1887–1960), Austrian linguist * Lyman Spitzer (1914–1997), American theoretical physicist and mountaineer * Moritz Spitzer, scholar who gave his name to the Spitzer Manuscript * Robert Spitzer (priest) (born 1952), American Jesuit priest and president of Gonzaga University (1998–2009) * Robert R. Spitzer (1922–2019), American agricultural researcher and president of the Milwaukee School of Engineering (1977–1991) * Robert Spitzer (political scientist) (bor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
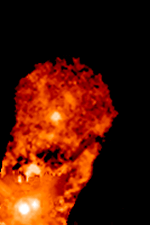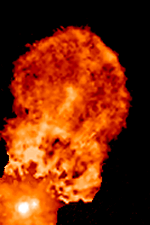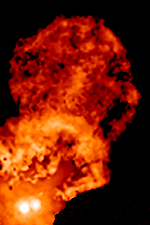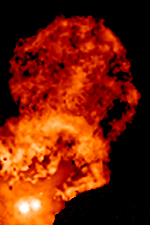
FU Orionis Stars
In stellar evolution, an FU Orionis star (also FU Orionis object, or ''FUor'') is a pre–main-sequence star which displays an extreme change in magnitude and spectral type. One example is the star V1057 Cyg, which became 6 magnitudes brighter and went from spectral type dKe to F-type supergiant during 1969-1970. These stars are named after their type-star, FU Orionis. The current model developed primarily by Lee Hartmann and Scott Jay Kenyon associates the FU Orionis flare with abrupt mass transfer from an accretion disc onto a young, low mass T Tauri star. Mass accretion rates for these objects are estimated to be around 10−4 solar masses per year. The rise time of these eruptions is typically on the order of 1 year, but can be much longer. The lifetime of this high-accretion, high-luminosity phase is on the order of decades. However, even with such a relatively short timespan, no FU Orionis object had been observed shutting off. By comparing the number of FUor outburs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
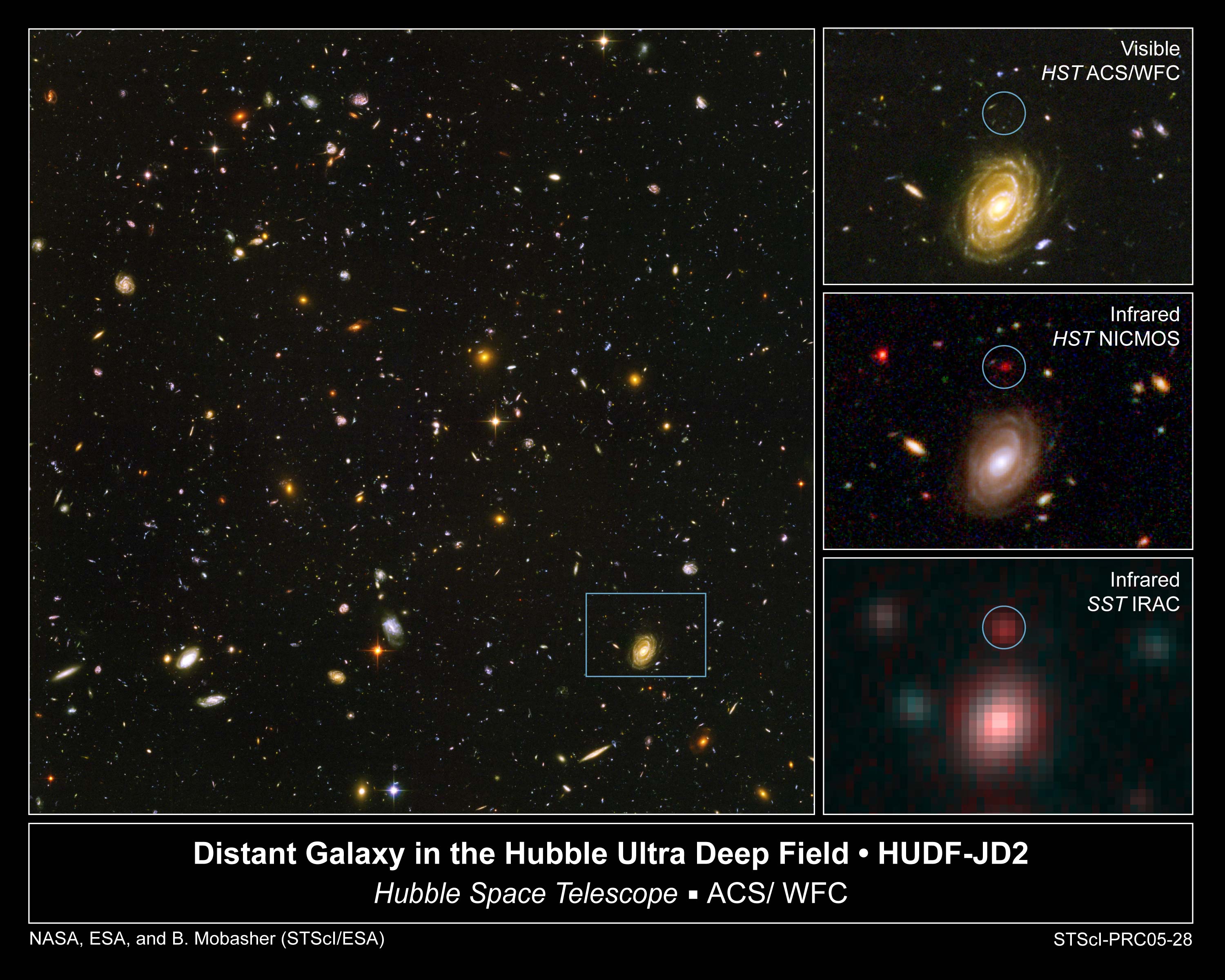
Spitzer Space Telescope
The Spitzer Space Telescope, formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), was an infrared space telescope launched in 2003. Operations ended on 30 January 2020. Spitzer was the third space telescope dedicated to infrared astronomy, following IRAS (1983) and ISO (1995–1998). It was the first spacecraft to use an Earth-trailing orbit, later used by the Kepler planet-finder. The planned mission period was to be 2.5 years with a pre-launch expectation that the mission could extend to five or slightly more years until the onboard liquid helium supply was exhausted. This occurred on 15 May 2009. Without liquid helium to cool the telescope to the very low temperatures needed to operate, most of the instruments were no longer usable. However, the two shortest-wavelength modules of the IRAC camera continued to operate with the same sensitivity as before the helium was exhausted, and continued to be used into early 2020 in the Spitzer Warm Mission. During the warm missio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Luminosity
The solar luminosity (), is a unit of radiant flux ( power emitted in the form of photons) conventionally used by astronomers to measure the luminosity of stars, galaxies and other celestial objects in terms of the output of the Sun. One nominal solar luminosity is defined by the International Astronomical Union to be . This does not include the solar neutrino luminosity, which would add , or , i.e. a total of (the mean energy of the solar photons is 26 MeV and that of the solar neutrinos 0.59 MeV, i.e. 2.27%; the Sun emits photons and as many neutrinos each second, of which per m2 reach the Earth each second). The Sun is a weakly variable star, and its actual luminosity therefore fluctuates. The major fluctuation is the eleven-year solar cycle (sunspot cycle) that causes a quasi-periodic variation of about ±0.1%. Other variations over the last 200–300 years are thought to be much smaller than this. Determination Solar luminosity is related to solar irradiance (the so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |