|
Scott County, Tennessee
Scott County is a county located in the U.S. state of Tennessee. As of the 2020 census, its population was 22,039, down from 22,228 at the 2010 census. Its county seat is Huntsville and the largest town is Oneida. Scott County is known for having seceded from Tennessee in protest of the state's decision to join the Confederacy during the Civil War, and subsequently forming '' The Free and Independent State of Scott.'' History Scott County was formed in 1849 from portions of Anderson, Campbell, Fentress and Morgan counties. It is named for U.S. Army General Winfield Scott, a hero of the Mexican War.Margaret D. BinnickerScott County ''Tennessee Encyclopedia of History and Culture'', accessed April 17, 2011 State of Scott During the Civil War, the county was a Southern Unionist bastion, voting against secession from the Union in Tennessee's June 1861 referendum by a higher percentage (521 to 19, or 96%) than in any other Tennessee county. This sentiment was encoura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winfield Scott
Winfield Scott (June 13, 1786May 29, 1866) was an American military commander and political candidate. He served as Commanding General of the United States Army from 1841 to 1861, and was a veteran of the War of 1812, American Indian Wars, Mexican–American War, and the early stages of the American Civil War. Scott was the Whig Party's presidential nominee in the 1852 election but was defeated by Democrat Franklin Pierce. He was known as Old Fuss and Feathers for his insistence on proper military etiquette and the Grand Old Man of the Army for his many years of service. Scott was born near Petersburg, Virginia, in 1786. After training as a lawyer and brief militia service, he joined the army in 1808 as a captain of the light artillery. In the War of 1812, Scott served on the Canadian front, taking part in the Battle of Queenston Heights and the Battle of Fort George, and was promoted to brigadier general in early 1814. He served with distinction in the Battle of Chippawa bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secession
Secession is the formal withdrawal of a group from a Polity, political entity. The process begins once a group proclaims an act of secession (such as a declaration of independence). A secession attempt might be violent or peaceful, but the goal is the creation of a new state or entity independent of the group or territory from which it seceded. Threats of secession can be a strategy for achieving more limited goals.Allen Buchanan"Secession" Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, 2007. There is some academic debate about this definition, and in particular how it relates to separatism. Secession theory There is no consensus on the definition of political secession despite many political theories on the subject. According to the 2017 book ''Secession and Security,'' by political scientist Ahsan I. Butt, Ahsan Butt, states respond violently to secessionist movements if the potential state poses a greater threat than the would-be secessionist movement. States perceive a future war with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big South Fork Of The Cumberland River
The Big South Fork of the Cumberland River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed June 8, 2011 river in the U.S. states of Tennessee and Kentucky. It is a major drainage feature of the Cumberland Plateau, a major tributary of the Cumberland River system, and the major feature of the Big South Fork National River and Recreation Area. Physical geography The Big South Fork begins at the confluence of the New River and the Clear Fork in Scott County, Tennessee, and flows northwest, northeast, and north until ending at Lake Cumberland in McCreary County, Kentucky, near the town of Burnside. It is the third largest tributary of the Cumberland River, and is free flowing for a distance of approximately before being affected by the headwaters of the lake. The terrain furthest upstream near the confluence is the most rugged, with reliefs of as much as . This area is characterized by dendritic draining pattern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New River (Tennessee)
The New River is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed June 8, 2011 tributary of the Big South Fork of the Cumberland River in the U.S. state of Tennessee. Via the Big South Fork and the Cumberland and Ohio rivers, it is part of the Mississippi River watershed. The New River rises on Frozen Head, a notable mountain of Morgan County, Tennessee. Named for its frequent winter appearance, Frozen Head is the focal point of Frozen Head State Park and Natural Area. Draining an area of Pennsylvanian Period rock that has been subjected to extensive strip mining for coal, the upper reaches of the stream have at times been subject to heavy pollution. The stream initially trends northeast. The upper portion of the course is paralleled by State Route 116. It soon crosses into a remote area of Anderson County, and then into Campbell County. At this juncture, State Route 116 turns to the southeast to follow the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clear Fork (Big South Fork Cumberland River)
The Clear Fork (also known as the Clear Fork River or Clear Fork Creek) is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed June 8, 2011 stream draining part of the Cumberland Plateau of Tennessee, United States. It is a tributary of the Big South Fork of the Cumberland River. By that river, the Cumberland River, and the Ohio River, it is part of the Mississippi River watershed. The Clear Fork rises on the Cumberland Plateau in southern Fentress County, Tennessee. It is composed of two major components, the North Prong and the South Prong, and numerous smaller tributaries. The North Prong drains an area adjacent to and east of U.S. Highway 127. The South Prong is slightly further east; it and its tributaries form an important portion of the border between Fentress County and Morgan County. The former English settlement of Rugby, Tennessee, promoted in the late 19th century as a settlement for the "second sons" of En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumberland Plateau
The Cumberland Plateau is the southern part of the Appalachian Plateau in the Appalachian Mountains of the United States. It includes much of eastern Kentucky and Tennessee, and portions of northern Alabama and northwest Georgia. The terms " Allegheny Plateau" and the "Cumberland Plateau" both refer to the dissected plateau lands lying west of the main Appalachian Mountains. The terms stem from historical usage rather than geological difference, so there is no strict dividing line between the two. Two major rivers share the names of the plateaus, with the Allegheny River rising in the Allegheny Plateau and the Cumberland River rising in the Cumberland Plateau in Harlan County, Kentucky. Geography The Cumberland Plateau is a deeply dissected plateau, with topographic relief commonly of about , and frequent sandstone outcroppings and bluffs. At Kentucky's Pottsville Escarpment, which is the transition from the Cumberland Plateau to the Bluegrass in the north and the Penny ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1872 United States Presidential Election
United States presidential election, Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 5, 1872. Incumbent President of the United States, President Ulysses S. Grant, the Republican Party (United States), Republican nominee, easily defeated Democratic Party (United States), Democratic-endorsed Liberal Republican Party (United States), Liberal Republican nominee Horace Greeley. Grant was unanimously re-nominated at the 1872 Republican National Convention, but his intra-party opponents organized the Liberal Republican Party and held their own convention. The 1872 Liberal Republican convention nominated Greeley, a New York newspaper publisher, and wrote a platform calling for U.S. Civil Service Reform, civil service reform and an end to Reconstruction Era, Reconstruction. Democratic Party (United States), Democratic Party leaders believed that their only hope of defeating Grant was to unite around Greeley, and the 1872 Democratic National Convention nominated the Libe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1868 United States Presidential Election
Presidential elections were held in the United States on November 3, 1868. In the first election of the Reconstruction Era, Republican nominee Ulysses S. Grant defeated Horatio Seymour of the Democratic Party. It was the first presidential election to take place after the conclusion of the American Civil War and the abolition of slavery. It was the first election in which African Americans could vote in the reconstructed Southern states, in accordance with the First Reconstruction Act. Incumbent president Andrew Johnson had succeeded to the presidency in 1865 following the assassination of Abraham Lincoln, a Republican. Johnson, a War Democrat from Tennessee, had served as Lincoln's running mate in 1864 on the National Union ticket, which was designed to attract Republicans and War Democrats. Upon accession to office, Johnson clashed with the Republican Congress over Reconstruction policies and was impeached and nearly removed from office. Johnson received some support for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulysses S
Ulysses is the Latin Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ... name for Odysseus, a legendary Greek hero recognized for his intelligence and cunning. He is famous for his long, adventurous journey home to Ithaca after the Trojan War, as narrated in Homer's Odyssey. Ulysses may also refer to: People * Ulysses (given name), including a list of people with this name Places * 5254 Ulysses, an asteroid Places in the United States * Ulysses, Kansas * Ulysses, Kentucky * Ulysses, Nebraska * Ulysses Township, Butler County, Nebraska * Ulysses, New York * Ulysses, Pennsylvania * Ulysses Township, Pennsylvania Animals * Ulysses butterfly (''Papilio ulysses'') a butterfly endemic to Australasia * Ulysses (horse) (born 2013), a thoroughbred racehorse Arts and enter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
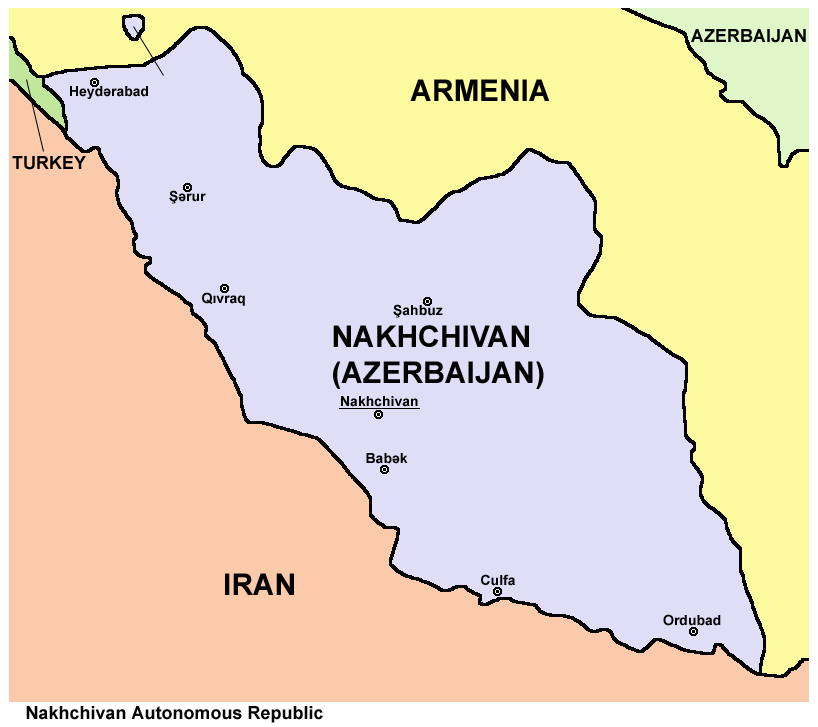
Enclave
An enclave is a territory that is entirely surrounded by the territory of only one other state or entity. An enclave can be an independent territory or part of a larger one. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is sometimes used improperly to denote a territory that is only partly surrounded by another state. Enclaves that are not part of a larger territory are not exclaves, for example Lesotho (enclaved by South Africa), and San Marino and Vatican City (both enclaved by Italy) are enclaved sovereign states. An exclave is a portion of a state or district geographically separated from the main part, by some surrounding alien territory. Many exclaves are also enclaves, but an exclave surrounded by the territory of more than one state is not an enclave. The Azerbaijani exclave of Nakhchivan is an example of an exclave that is not an enclave, as it borders Armenia, Iran, and Turkey. Semi-enclaves and semi-exclaves are areas that, except for possessing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |