|
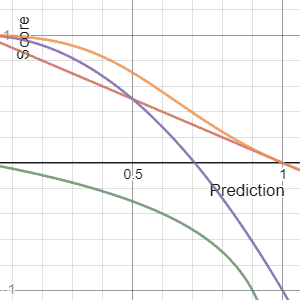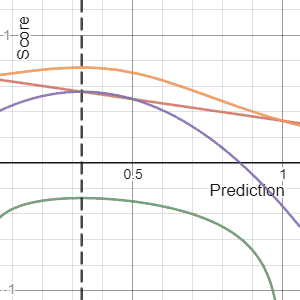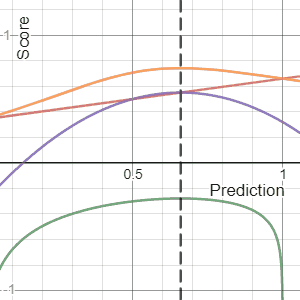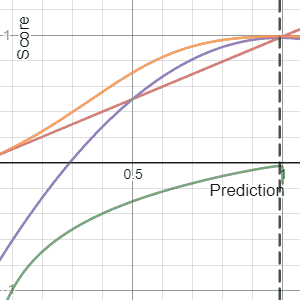
Scoring Rule
In decision theory, a scoring rule provides evaluation metrics for probabilistic forecasting, probabilistic predictions or forecasts. While "regular" loss functions (such as mean squared error) assign a goodness-of-fit score to a predicted value and an observed value, scoring rules assign such a score to a predicted probability distribution and an observed value. On the other hand, a scoring function provides a summary measure for the evaluation of point predictions, i.e. one predicts a property or Functional (mathematics), functional T(F), like the Expected value, expectation or the median. Scoring rules answer the question "how good is a predicted probability distribution compared to an observation?" Scoring rules that are (strictly) proper are proven to have the lowest expected score if the predicted distribution equals the underlying distribution of the target variable. Although this might differ for individual observations, this should result in a minimization of the expect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scoring Functions
SCORE may refer to: *SCORE (software), a music scorewriter program *SCORE (television), a weekend sports service of the defunct Financial News Network *SCORE! Educational Centers *SCORE International, an offroad racing organization *Sarawak Corridor of Renewable Energy, a regional development corridor in Malaysia *Singapore Corporation of Rehabilitative Enterprises, the former name of Yellow Ribbon Singapore, a statutory board under the Ministry of Home Affairs *Project SCORE, a communications satellite *Service Corps of Retired Executives, a mentorship program affiliated with the Small Business Administration See also *Score (other) *The Score (other) *Scores (other) {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Realization (probability)
In probability and statistics, a realization, observation, or observed value, of a random variable is the value that is actually observed (what actually happened). The random variable itself is the process dictating how the observation comes about. Statistical quantities computed from realizations without deploying a statistical model are often called "empirical", as in empirical distribution function or empirical probability. Conventionally, to avoid confusion, upper case letters denote random variables; the corresponding lower case letters denote their realizations. Formal definition In more formal probability theory, a random variable is a function ''X'' defined from a sample space Ω to a measurable space called the state space. If an element in Ω is mapped to an element in state space by ''X'', then that element in state space is a realization. Elements of the sample space can be thought of as all the different possibilities that ''could'' happen; while a re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glenn W
Glenn may refer to: Name or surname * Glenn (name) * John Glenn, U.S. astronaut Cultivars * Glenn (mango) * a 6-row barley variety Places In the United States: * Glenn, California * Glenn County, California * Glenn, Georgia, a settlement in Heard County * Glenn, Illinois * Glenn, Michigan * Glenn, Missouri * Glenn Highway in Alaska Organizations *Glenn Research Center, a NASA center in Cleveland, Ohio See also * New Glenn New Glenn is a heavy-lift launch vehicle developed and operated by the American company Blue Origin. The rocket is designed to have a Reusable launch vehicle, partially reusable, two-stage design with a diameter of . The first stage is powered ..., a heavy-lift orbital launch vehicle * * * Glen, a valley * Glen (other) {{disambiguation, geo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brier Score
The Brier score is a strictly proper scoring rule that measures the accuracy of probabilistic predictions. For unidimensional predictions, it is strictly equivalent to the mean squared error as applied to predicted probabilities. The Brier score is applicable to tasks in which predictions must assign probabilities to a set of mutually exclusive discrete outcomes or classes. The set of possible outcomes can be either binary or categorical in nature, and the probabilities assigned to this set of outcomes must sum to one (where each individual probability is in the range of 0 to 1). It was proposed by Glenn W. Brier in 1950. The Brier score can be thought of as a cost function. More precisely, across all items i\in in a set of ''N'' predictions, the Brier score measures the mean squared difference between: * The predicted probability assigned to the possible outcomes for item ''i'' * The actual outcome o_i Therefore, the ''lower'' the Brier score is for a set of predictions, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Theory
Information theory is the mathematical study of the quantification (science), quantification, Data storage, storage, and telecommunications, communication of information. The field was established and formalized by Claude Shannon in the 1940s, though early contributions were made in the 1920s through the works of Harry Nyquist and Ralph Hartley. It is at the intersection of electronic engineering, mathematics, statistics, computer science, Neuroscience, neurobiology, physics, and electrical engineering. A key measure in information theory is information entropy, entropy. Entropy quantifies the amount of uncertainty involved in the value of a random variable or the outcome of a random process. For example, identifying the outcome of a Fair coin, fair coin flip (which has two equally likely outcomes) provides less information (lower entropy, less uncertainty) than identifying the outcome from a roll of a dice, die (which has six equally likely outcomes). Some other important measu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayesian Inference
Bayesian inference ( or ) is a method of statistical inference in which Bayes' theorem is used to calculate a probability of a hypothesis, given prior evidence, and update it as more information becomes available. Fundamentally, Bayesian inference uses a prior distribution to estimate posterior probabilities. Bayesian inference is an important technique in statistics, and especially in mathematical statistics. Bayesian updating is particularly important in the dynamic analysis of a sequence of data. Bayesian inference has found application in a wide range of activities, including science, engineering, philosophy, medicine, sport, and law. In the philosophy of decision theory, Bayesian inference is closely related to subjective probability, often called "Bayesian probability". Introduction to Bayes' rule Formal explanation Bayesian inference derives the posterior probability as a consequence of two antecedents: a prior probability and a "likelihood function" derive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-information
In information theory, the information content, self-information, surprisal, or Shannon information is a basic quantity derived from the probability of a particular event occurring from a random variable. It can be thought of as an alternative way of expressing probability, much like odds or log-odds, but which has particular mathematical advantages in the setting of information theory. The Shannon information can be interpreted as quantifying the level of "surprise" of a particular outcome. As it is such a basic quantity, it also appears in several other settings, such as the length of a message needed to transmit the event given an optimal source coding of the random variable. The Shannon information is closely related to ''entropy'', which is the expected value of the self-information of a random variable, quantifying how surprising the random variable is "on average". This is the average amount of self-information an observer would expect to gain about a random variable wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability Vector
In mathematics and statistics, a probability vector or stochastic vector is a vector with non-negative entries that add up to one. The positions (indices) of a probability vector represent the possible outcomes of a discrete random variable, and the vector gives us the probability mass function of that random variable, which is the standard way of characterizing a discrete probability distribution.. Examples Here are some examples of probability vectors. The vectors can be either columns or rows. * x_0=\begin0.5 \\ 0.25 \\ 0.25 \end, * x_1=\begin 0 \\ 1 \\ 0 \end, * x_2=\begin 0.65 & 0.35 \end, * x_3=\begin 0.3 & 0.5 & 0.07 & 0.1 & 0.03 \end. Geometric interpretation Writing out the vector components of a vector p as :p=\begin p_1 \\ p_2 \\ \vdots \\ p_n \end\quad \text \quad p=\begin p_1 & p_2 & \cdots & p_n \end the vector components must sum to one: :\sum_^n p_i = 1 Each individual component must have a probability between zero and one: :0\le p_i \le 1 for all i. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Decision
A binary decision is a choice between two alternatives, for instance between taking some specific action or not taking it. Binary decisions are basic to many fields. Examples include: *Truth values in mathematical logic, and the corresponding Boolean data type in computer science, representing a value which may be chosen to be either true or false. * Conditional statements (if-then or if-then-else) in computer science, binary decisions about which piece of code to execute next. *Decision trees and binary decision diagrams, representations for sequences of binary decisions. * Binary choice, a statistical model for the outcome of a binary decision. Binary decision diagrams A binary decision diagram (BDD) is a way to visually represent a boolean function. One application of BDDs is in CAD software and digital circuit analysis where they are an efficient way to represent and manipulate boolean functions. The value of a boolean function can be determined by following a path in its B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Personal Probability
Bayesian probability ( or ) is an interpretation of the concept of probability, in which, instead of frequency or propensity of some phenomenon, probability is interpreted as reasonable expectation representing a state of knowledge or as quantification of a personal belief. The Bayesian interpretation of probability can be seen as an extension of propositional logic that enables reasoning with hypotheses; that is, with propositions whose truth or falsity is unknown. In the Bayesian view, a probability is assigned to a hypothesis, whereas under frequentist inference, a hypothesis is typically tested without being assigned a probability. Bayesian probability belongs to the category of evidential probabilities; to evaluate the probability of a hypothesis, the Bayesian probabilist specifies a prior probability. This, in turn, is then updated to a posterior probability in the light of new, relevant data (evidence). The Bayesian interpretation provides a standard set of procedures a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bonus
Bonus commonly means: * Bonus, a Commonwealth term for a distribution of profits to a with-profits insurance policy * Bonus payment, an extra payment received as a reward for doing one's job well or as an incentive Bonus may also refer to: Places * Bonus, Pennsylvania * Bonus, Texas * 10028 Bonus, a main belt asteroid People * Bonus (patrician) (6th-century–627), Byzantine statesman and general, active in the reign of Heraclius * Bonus (Sirmium), a Byzantine general, active in the reign of Justin II (r. 565–578) * Petrus Bonus, a physician Brands and enterprises * Bónus, an Icelandic supermarket * TeST TST-14 Bonus, a Czech glider * Bofors/Nexter Bonus, an artillery round Energy * Bonus Energy A/S, a Danish wind turbine manufacturer, later called Siemens Wind Power * Boiling Nuclear Superheater (BONUS), a decommissioned nuclear facility in Puerto Rico Games and sports * Bonus (basketball), a situation wherein one team accumulates a certain number of fouls * Bon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |