|
Scolomys Melanops
''Scolomys melanops'', also known as the short-nosed scolomys, South American spiny mouse, Ecuadorian spiny mouse, or gray spiny mouse, is a species of rodent in the genus '' Scolomys'' of family Cricetidae. It is a forest mouse and was thought to be endemic to Ecuador but it is now known to have a wider distribution, being also present in part of Peru. Description The South American spiny mouse has a total length of between including a tail of . It has a short, broad head, a small body and a nearly naked tail. The dorsal pelage is short and dense and consists of a mixture of slender hairs with reddish or blackish tips and stouter spines of the same length that are darker at the tip, giving a grizzled appearance. The fur on the ventral surface has similar hairs and spines but they are a uniform grey colour. Morphologically this species is very similar to the closely related Ucayali spiny mouse (''Scolomys ucayalensis''). The differences are mostly in the skull characteristics an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harold Elmer Anthony
Harold may refer to: People * Harold (given name), including a list of persons and fictional characters with the name * Harold (surname), surname in the English language * András Arató, known in meme culture as "Hide the Pain Harold" Arts and entertainment * ''Harold'' (film), a 2008 comedy film * ''Harold'', an 1876 poem by Alfred, Lord Tennyson * ''Harold, the Last of the Saxons'', an 1848 book by Edward Bulwer-Lytton, 1st Baron Lytton * '' Harold or the Norman Conquest'', an opera by Frederic Cowen * ''Harold'', an 1885 opera by Eduard Nápravník * Harold, a character from the cartoon ''The Grim Adventures of Billy & Mandy'' * Harold & Kumar, a US movie; Harold/Harry is the main actor in the show. Places ;In the United States * Alpine, Los Angeles County, California, an erstwhile settlement that was also known as Harold * Harold, Florida, an unincorporated community * Harold, Kentucky, an unincorporated community * Harold, Missouri, an unincorporated community ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodent
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the Order (biology), order Rodentia ( ), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and Mandible, lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are native to all major land masses except for Antarctica, and several oceanic islands, though they have subsequently been introduced to most of these land masses by human activity. Rodents are extremely diverse in their ecology and lifestyles and can be found in almost every terrestrial habitat, including human-made environments. Species can be arboreal, fossorial (burrowing), saltatorial/ricochetal (leaping on their hind legs), or semiaquatic. However, all rodents share several morphological features, including having only a single upper and lower pair of ever-growing incisors. Well-known rodents include Mouse, mice, rats, squirrels, prairie dogs, porcupines, beavers, Cavia, guinea pigs, and hamsters. Once included wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scolomys
''Scolomys'' is a genus of rodent in the tribe Oryzomyini of the family Cricetidae. Some evidence suggests that it is related to ''Zygodontomys''. It is characterized, among other traits, by spiny fur. It contains two species, '' S. melanops'' and '' S. ucayalensis''. Taxonomy The genus ''Scolomys'' was first described by the American zoologist H. E. Anthony in 1920, to accommodate six specimens collected by the British-born American zoologist George Henry Hamilton Tate on the eastern slopes of the Andes in Ecuador. These specimens belonged to a single species ''Scolomys melanops'', and for a long time the genus was considered to be monotypic. However, following survey work in the upper Amazon basin many decades later, a further species '' S. ucayalensis'' was described from northern Peru by Pacheco in 1991, followed by a third, ''S. juruaense'' from western Brazil by Patton and da Silva in 1994. In 2004, Gomez-Laverde and co-workers reviewed the systematics of the genus and its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cricetidae
The Cricetidae are a family of rodents in the large and complex superfamily Muroidea. It includes true hamsters, voles, lemmings, muskrats, and New World rats and mice. At over 870 species, it is either the largest or second-largest family of mammals, and has members throughout the Americas, Europe and Asia. Characteristics The cricetids are small mammals, ranging from just in length and in weight in the New World pygmy mouse up to and in the muskrat. The length of their tails varies greatly in relation to their bodies, and they may be either furred or sparsely haired. The fur of most species is brownish in colour, often with a white underbelly, but many other patterns exist, especially in the cricetine and arvicoline subfamilies. Like the Old World mice, cricetids are adapted to a wide range of habitats, from the high Arctic to tropical rainforests and hot deserts. Some are arboreal, with long balancing tails and other adaptations for climbing, while others ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found elsewhere. For example, the Cape sugarbird is found exclusively in southwestern South Africa and is therefore said to be ''endemic'' to that particular part of the world. An endemic species can also be referred to as an ''endemism'' or, in scientific literature, as an ''endemite''. Similarly, many species found in the Western ghats of India are examples of endemism. Endemism is an important concept in conservation biology for measuring biodiversity in a particular place and evaluating the risk of extinction for species. Endemism is also of interest in evolutionary biology, because it provides clues about how changes in the environment cause species to undergo range shifts (potentially expanding their range into a larger area or bec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecuador
Ecuador, officially the Republic of Ecuador, is a country in northwestern South America, bordered by Colombia on the north, Peru on the east and south, and the Pacific Ocean on the west. It also includes the Galápagos Province which contains the Galapagos Islands in the Pacific, about west of the mainland. The country's Capital city, capital is Quito and its largest city is Guayaquil. The land that comprises modern-day Ecuador was once home to several groups of Indigenous peoples in Ecuador, indigenous peoples that were gradually incorporated into the Inca Empire during the 15th century. The territory was Spanish colonization of the Americas, colonized by the Spanish Empire during the 16th century, achieving independence in 1820 as part of Gran Colombia, from which it emerged as a sovereign state in 1830. The legacy of both empires is reflected in Ecuador's ethnically diverse population, with most of its million people being mestizos, followed by large minorities of Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scolomys Ucayalensis
''Scolomys ucayalensis'', also known as the long-nosed scolomysMusser and Carleton, 2005 or Ucayali spiny mouse is a nocturnal rodent species from South America. It is part of the genus ''Scolomys'' within the tribe Oryzomyini. It is found in Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador and Peru in various different habitats in the Amazon rainforest. Description ''Scolomys ucayalensis'' has a head-and-body length of between and a tail around 83% of this. The head is small but broad with a pointed snout and small rounded ears. The fur is a mixture of fine hairs and thicker, flattened spines. The dorsal surface is some shade of reddish-brown to reddish-black, sometimes grizzled or streaked with black, and the underparts are grey. The tail is nearly naked, and the hind feet are small but broad. The hypothenar pad (next to the outer digit on the sole of the foot) is either absent or reduced in size on the hind feet, and this contrasts with the otherwise similar '' Scolomys melanops '' which has well-de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
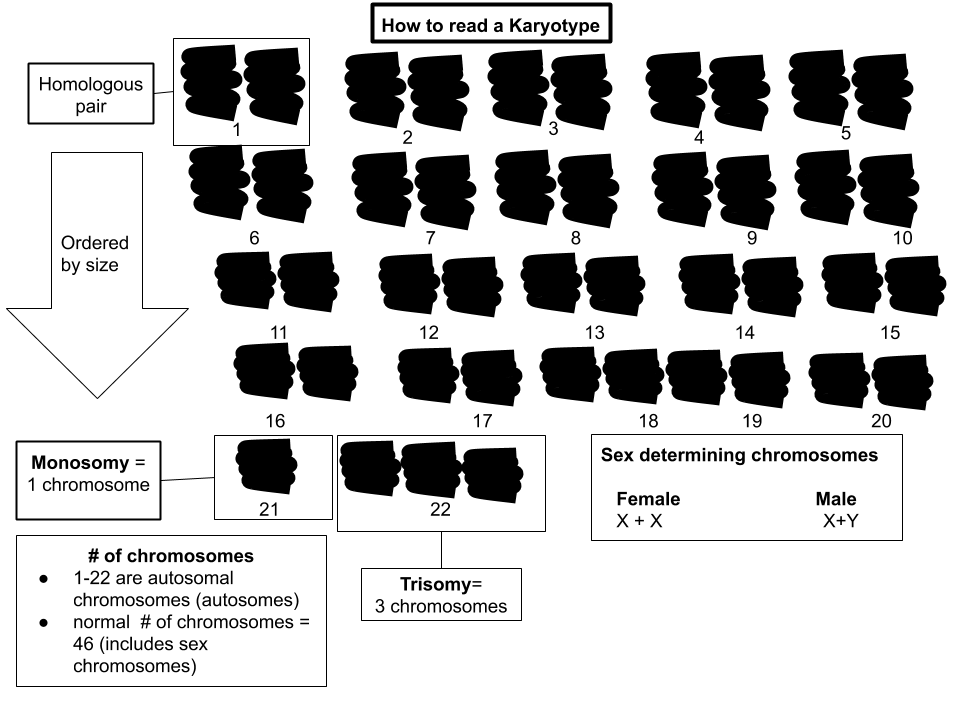
Karyotype
A karyotype is the general appearance of the complete set of chromosomes in the cells of a species or in an individual organism, mainly including their sizes, numbers, and shapes. Karyotyping is the process by which a karyotype is discerned by determining the chromosome complement of an individual, including the number of chromosomes and any abnormalities. A karyogram or idiogram is a graphical depiction of a karyotype, wherein chromosomes are generally organized in pairs, ordered by size and position of centromere for chromosomes of the same size. Karyotyping generally combines light microscopy and photography in the metaphase of the cell cycle, and results in a photomicrographic (or simply micrographic) karyogram. In contrast, a schematic karyogram is a designed graphic representation of a karyotype. In schematic karyograms, just one of the sister chromatids of each chromosome is generally shown for brevity, and in reality they are generally so close together that they look as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Here ''sets of chromosomes'' refers to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectively, in each homologous chromosome pair—the form in which chromosomes naturally exist. Somatic cells, tissues, and individual organisms can be described according to the number of sets of chromosomes present (the "ploidy level"): monoploid (1 set), diploid (2 sets), triploid (3 sets), tetraploid (4 sets), pentaploid (5 sets), hexaploid (6 sets), heptaploid or septaploid (7 sets), etc. The generic term polyploid is often used to describe cells with three or more sets of chromosomes. Virtually all sexually reproducing organisms are made up of somatic cells that are diploid or greater, but ploidy level may vary widely between different organisms, between different tissues within the same organism, and at different stages in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fundamental Number
A karyotype is the general appearance of the complete set of chromosomes in the cells of a species or in an individual organism, mainly including their sizes, numbers, and shapes. Karyotyping is the process by which a karyotype is discerned by determining the chromosome complement of an individual, including the number of chromosomes and any abnormalities. A karyogram or idiogram is a graphical depiction of a karyotype, wherein chromosomes are generally organized in pairs, ordered by size and position of centromere for chromosomes of the same size. Karyotyping generally combines light microscopy and photography in the metaphase of the cell cycle, and results in a photomicrographic (or simply micrographic) karyogram. In contrast, a schematic karyogram is a designed graphic representation of a karyotype. In schematic karyograms, just one of the sister chromatids of each chromosome is generally shown for brevity, and in reality they are generally so close together that they look as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iquitos
Iquitos (; ) is the capital city of Peru's Maynas Province, Peru, Maynas Province and Loreto Region. It is the largest metropolis in the Peruvian Amazon, east of the Andes, as well as the List of cities in Peru, ninth-most populous city in Peru. Iquitos is the largest city in the world that cannot be reached by road that is not on an island; it is only accessible by river and air. It is known as the "capital of the Peruvian Amazon". The city is located in the Great Plains of the Amazon Basin, fed by the Amazon River, Amazon, Nanay River, Nanay, and Itaya River, Itaya rivers. Overall, it constitutes the Iquitos metropolitan area, a conurbation of 471,993 inhabitants consisting of four districts: Iquitos District, Iquitos, Punchana District, Punchana, Belén District, Maynas, Belén, and San Juan Bautista District, Maynas, San Juan Bautista. The area has long been inhabited by indigenous peoples. According to Spanish historical documents, Iquitos was established around 1757 as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lepidocaryum
''Lepidocaryum'' is a monotypic genus of flowering plant in the palm family from South America where the lone species, ''Lepidocaryum tenue'', is commonly called poktamui. Nine species names have been published, but palm taxonomists currently agree that just one variable species includes them all.Riffle, Robert L. and Craft, Paul (2003) ''An Encyclopedia of Cultivated Palms''. Portland: Timber Press. / The most reduced member of the Lepidocaryeae, it is similar in appearance to two closely related genera, ''Mauritia'' and '' Mauritiella'', as well as to the former genus ''Lytocaryum'' (now included in '' Syagrus'').Uhl, Natalie W. and Dransfield, John (1987) ''Genera Palmarum - A classification of palms based on the work of Harold E. Moore''. Lawrence, Kansas: Allen Press. / The genus name combines the Greek words for "scale" and "nut" and the species epithet is Latin for "thin". Description At just 2.5 cm in width, the clustering trunks reach no higher than 3.5 m and ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |