|
Scione Brevibeccus
Scione or Skione () was an ancient Greek city in Pallene, the westernmost headland of Chalcidice, on the southern coast east of the modern town of Nea Skioni. Scione was founded by settlers from Achaea; the Scionaeans claimed their ancestors settled the place when their ships were blown there by the storm that caught the Achaeans on their way back from Troy. It "was situated on one summit of a two-crested hill and on the slopes toward the sea... The hill with the fortifications and the pottery fragments constituted the acropolis of ancient Scione and the hill beyond was that on which the defenders encamped 'before the city.'" It was a member of the Delian League. Its moment of historical importance came during the Peloponnesian War, when just after the truce between Sparta and Athens in early 423 BCE, Scione revolted against Athens and was encouraged by the Spartan general Brasidas with promises of support. The Athenians sent a fleet to retake Mende and Scione; after s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassandreia
Cassandreia or Cassandrea (, ''Kassándreia'') was once one of the most important cities in Ancient Macedonia, founded by and named after Cassander in 316 BC. It was located on the site of the earlier Ancient Greek city of Potidaea, at the isthmus of the Pallene peninsula.POTEIDAIA (Nea Poteidaia) Chalkidike, Greece entry in The Princeton Encyclopedia of Classical Sites. The fact that Cassander named it after himself suggests that he may have intended it to be his capital, and if the canal which cuts the peninsula at this point was dug or at least planned in his time, he may have intended to develop his naval forces using it as a base with a harbour on each of the east and west sides. Cassandreia soon became a great and powerful city, surpassing the other Mace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Members Of The Delian League
The members of the Delian League/Athenian Empire (c. 478-404 BC) can be categorized into two groups: the allied states (''symmachoi'') reported in the stone tablets of the Athenian tribute lists (454-409 BC), who contributed the ''symmachikos phoros'' ("allied tax") in money, and further allies, reported either in epigraphy or historiography, whose contribution consisted of ships, wood, grain, and military assistance; proper and occasional members, subject members and genuine allies. Analysis The study of the ''symmachikos phoros'' provides the following insights: The amount of tax paid by each state is written in Attic numerals. One-sixtieth is dedicated to Athena, the patron goddess of the city. The membership is not limited to Ionians or Greek city-states (see Ialysus, Mysians, Eteocarpathians and ''the Carians whom Tymnes rules''). Allied states of Western Greece are not categorized under a fiscal district the Thracian, Hellespontine, Insular, Carian and Ionian ''pho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achaean Colonies
Achaeans are the inhabitants of Achaea in Greece. However, the meaning of Achaea changed during the course of Ancient history, and thus ''Achaeans'' may refer to: *Achaeans (Homer), a name used by Homer in the Iliad for Mycenaean-era Greeks in general. *Achaeans (tribe), one of the major tribes of Greece according to the Hesiodic foundation myth *Achaea Phthiotis, a region of ancient Thessaly *Achaea Achaea () or Achaia (), sometimes transliterated from Greek language, Greek as Akhaia (, ''Akhaḯa'', ), is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the modern regions of Greece, region of Western Greece and is situated in the northwest ..., the modern Greek administrative unit See also * Achaea (other) {{Disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Colonies In Chalcidice
Greek may refer to: Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe: *Greeks, an ethnic group *Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family **Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all known varieties of Greek **Mycenaean Greek, most ancient attested form of the language (16th to 11th centuries BC) **Ancient Greek, forms of the language used c. 1000–330 BC **Koine Greek, common form of Greek spoken and written during Classical antiquity **Medieval Greek or Byzantine Language, language used between the Middle Ages and the Ottoman conquest of Constantinople **Modern Greek, varieties spoken in the modern era (from 1453 AD) *Greek alphabet, script used to write the Greek language *Greek Orthodox Church, several Churches of the Eastern Orthodox Church *Ancient Greece, the ancient civilization before the end of Antiquity * Old Greek, the language as spoken from Late Antiquity to around 1500 AD *Greek mythology, a body of myths o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Ancient Chalcidice
Geography (from Ancient Greek ; combining 'Earth' and 'write', literally 'Earth writing') is the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. Geography has been called "a bridge between natural science and social science disciplines." Origins of many of the concepts in geography can be traced to Greek Eratosthenes of Cyrene, who may have coined the term "geographia" (). The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as the title of a book by Greek scholar Claudius Ptolemy (100 – 170 AD). This work created the so-called "Ptolemaic tradition" of geography, which included "Ptolemaic cartographic theory." ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cities In Ancient Macedonia
A city is a human settlement of a substantial size. The term "city" has different meanings around the world and in some places the settlement can be very small. Even where the term is limited to larger settlements, there is no universally agreed definition of the lower boundary for their size. In a narrower sense, a city can be defined as a permanent and Urban density, densely populated place with administratively defined boundaries whose members work primarily on non-agricultural tasks. Cities generally have extensive systems for housing, transportation, sanitation, Public utilities, utilities, land use, Manufacturing, production of goods, and communication. Their density facilitates interaction between people, government organisations, government organizations, and businesses, sometimes benefiting different parties in the process, such as improving the efficiency of goods and service distribution. Historically, city dwellers have been a small proportion of humanity overall, bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Populated Places In Ancient Macedonia
Population is a set of humans or other organisms in a given region or area. Governments conduct a census to quantify the resident population size within a given jurisdiction. The term is also applied to non-human animals, microorganisms, and plants, and has specific uses within such fields as ecology and genetics. Etymology The word ''population'' is derived from the Late Latin ''populatio'' (a people, a multitude), which itself is derived from the Latin word ''populus'' (a people). Use of the term Social sciences In sociology and population geography, population refers to a group of human beings with some predefined feature in common, such as location, race, ethnicity, nationality, or religion. Ecology In ecology, a population is a group of organisms of the same species which inhabit the same geographical area and are capable of interbreeding. The area of a sexual population is the area where interbreeding is possible between any opposite-sex pair within the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
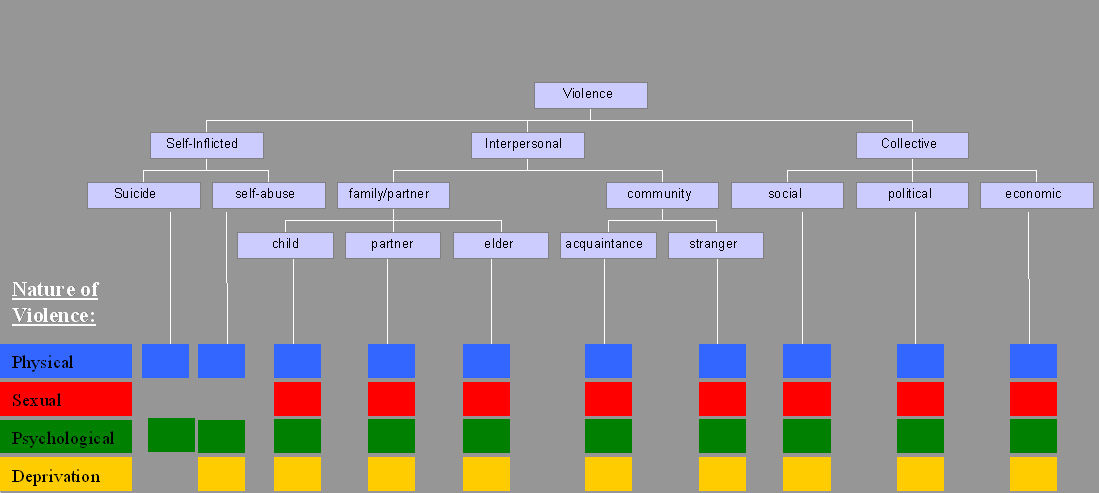
Violence Against Men In Greece
Violence is characterized as the use of physical force by humans to cause harm to other living beings, or property, such as pain, injury, disablement, death, damage and destruction. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines violence as "the intentional use of physical force or power, threatened or actual, against oneself, another person, or against a group or community, which either results in or has a high likelihood of resulting in injury, death, psychological harm, maldevelopment, or deprivation"; it recognizes the need to include violence not resulting in injury or death. Categories The World Health Organization (WHO) divides violence into three broad categories: self-directed, interpersonal, and collective. This categorization differentiates between violence inflicted to and by oneself, by another individual or a small group, and by larger groups such as states. Alternatively, violence can primarily be classified as either instrumental or hostile. Self-inflict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydna
Hydna of Scione (alternately called Hydne or Cyana) (fl. 480 BC) was an Ancient Greek swimmer and diver given credit for contributing to the destruction of the Persian navy in 480 BC. Biography According to Pausanias (''Description of Greece'', 10.19.1.), prior to the battle of Salamis. a critical naval battle with the Persians, Hydna and her father, Scyllias, volunteered to assist Greek forces by vandalizing the nearby Persian naval fleet. After reaching Greece, Persian king Xerxes I had moored his ships off the coast of Mount Pelion to wait out a storm prior to the Battle of Artemisium. Hydna was well known in Greece as a skilled swimmer, having been trained by her father, a professional swim instructor named Scyllias, from a young age. She was known for her ability to swim long distances and dive deep into the ocean. On the night of the attack, father and daughter swam roughly ten miles through rough, choppy waters to reach the ships. They silently swam among the boats, using k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aethilla
In Greek mythology, Aethilla or Aethylla (Ancient Greek: Αἴθιλλα or Αἴθυλλα) was Trojan princess as a daughter of King Laomedon and sister of Priam, Lampus, Hicetaon, Clytius, Hesione, Cilla, Astyoche, Proclia, Medesicaste and Clytodora.Dionysius of Halicarnassus, ''Antiquitates Romanae'1.62.2/ref> Mythology After the fall of Troy Aethilla became the prisoner of Protesilaus, who took her, together with other captives, with him on his voyage home. He landed in Thrace in order to take in fresh water. While Protesilaus had gone inland, Aethilla persuaded her fellow prisoners to set fire to the ships. As a result of this being done, the Greeks were forced to remain on the spot and founded the town of Scione. According to other authors, the event took place in Italy; in commemoration of it, the nearby river received the name Nauaethus ("of the burning ships"), while Aethilla, Astyoche, and Medesicaste were surnamed the ''Nauprestidai'' ("they who set fire to ships" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nea Skione
Nea Skioni (, ) is a village and a community in the peninsula of Kassandra, Chalkidiki, Macedonia, Greece. Nea Skioni is located 7 km southwest of Chaniotis, 7 km west of Agia Paraskevi and 90 km southeast of Thessaloniki. It is named after the ancient city of Scione Scione or Skione () was an ancient Greek city in Pallene, the westernmost headland of Chalcidice, on the southern coast east of the modern town of Nea Skioni. Scione was founded by settlers from Achaea; the Scionaeans claimed their ancestor ..., whose site was nearby to the east. Nea Skioni was established in 1918 where fisherman huts existed. In 1930, the old village “Tsaprani”, which was located in the mountain of Kassandra, was abandoned. The new village was named after the ancient Skioni, which was the oldest colony. According to Thucydides, it was built after the Trojan War by the Pellineis of Peloponnese, who were located there to spend the winter. The village is a popular tourist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |