|
Scintillant
A scintillator ( ) is a material that exhibits scintillation, the property of luminescence, when excited by ionizing radiation. Luminescent materials, when struck by an incoming particle, absorb its energy and scintillate (i.e. re-emit the absorbed energy in the form of light). Sometimes, the excited state is metastable, so the relaxation back down from the excited state to lower states is delayed (necessitating anywhere from a few nanoseconds to hours depending on the material). The process then corresponds to one of two phenomena: delayed fluorescence or phosphorescence. The correspondence depends on the type of transition and hence the wavelength of the emitted optical photon. Principle of operation A scintillation detector or scintillation counter is obtained when a scintillator is coupled to an electronic light sensor such as a photomultiplier tube (PMT), photodiode, or silicon photomultiplier. PMTs absorb the light emitted by the scintillator and re-emit it in the form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoelectric Effect
The photoelectric effect is the emission of electrons from a material caused by electromagnetic radiation such as ultraviolet light. Electrons emitted in this manner are called photoelectrons. The phenomenon is studied in condensed matter physics, solid state, and quantum chemistry to draw inferences about the properties of atoms, molecules and solids. The effect has found use in electronic devices specialized for light detection and precisely timed electron emission. The experimental results disagree with classical electromagnetism, which predicts that continuous light waves transfer energy to electrons, which would then be emitted when they accumulate enough energy. An alteration in the intensity of light would theoretically change the kinetic energy of the emitted electrons, with sufficiently dim light resulting in a delayed emission. The experimental results instead show that electrons are dislodged only when the light exceeds a certain frequency—regardless of the ligh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cost
Cost is the value of money that has been used up to produce something or deliver a service, and hence is not available for use anymore. In business, the cost may be one of acquisition, in which case the amount of money expended to acquire it is counted as cost. In this case, money is the input that is gone in order to acquire the thing. This acquisition cost may be the sum of the cost of production as incurred by the original producer, and further costs of transaction as incurred by the acquirer over and above the price paid to the producer. Usually, the price also includes a mark-up for profit over the cost of production. More generalized in the field of economics Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the Production (economics), production, distribution (economics), distribution, and Consumption (economics), consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interac ..., cost is a metric that is totaling up as a result of a process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the ratio of a substance's mass to its volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' (or ''d'') can also be used: \rho = \frac, where ''ρ'' is the density, ''m'' is the mass, and ''V'' is the volume. In some cases (for instance, in the United States oil and gas industry), density is loosely defined as its weight per unit volume, although this is scientifically inaccurate this quantity is more specifically called specific weight. For a pure substance, the density is equal to its mass concentration. Different materials usually have different densities, and density may be relevant to buoyancy, purity and packaging. Osmium is the densest known element at standard conditions for temperature and pressure. To simplify comparisons of density across different systems of units, it is sometimes replaced by the dimensionless quantity "relative den ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioactive Contamination
Radioactive contamination, also called radiological pollution, is the deposition of, or presence of Radioactive decay, radioactive substances on surfaces or within solids, liquids, or gases (including the human body), where their presence is unintended or undesirable (from the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) definition). Such contamination presents a hazard because the radioactive decay of the contaminants produces ionizing radiation (namely alpha particle, alpha, beta particle, beta, gamma rays and free neutrons). The degree of hazard is determined by the concentration of the contaminants, the energy of the radiation being emitted, the type of radiation, and the proximity of the contamination to organs of the body. It is important to be clear that the contamination gives rise to the radiation hazard, and the terms "radiation" and "contamination" are not interchangeable. The sources of radioactive pollution can be classified into two groups: natural and man-made. Follo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Survey Meter
Survey meters in radiation protection are hand-held ionising radiation measurement instruments used to check such as personnel, equipment and the environment for radioactive contamination and ambient radiation. The hand-held survey meter is probably the most familiar radiation measuring device owing to its wide and visible use. Types The most commonly used hand-held survey meters are the scintillation counter, which is used in the measurement of alpha, beta and neutron particles; the Geiger counter, widely used for the measurement of alpha, beta and gamma levels; and the ion chamber, which is used for beta, gamma and X-ray measurements. Functional design The instruments are designed to be hand-held, are battery powered and of low mass to allow easy manipulation. Other features include an easily readable display, in counts or radiation dose, and an audible indication of the count rate. This is usually the “click” associated with the Geiger type instrument, and can also be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optoelectric Nuclear Battery
An optoelectric nuclear battery (also radiophotovoltaic device, radioluminescent nuclear battery or radioisotope photovoltaic generator) is a type of nuclear battery in which nuclear energy is converted into light, which is then used to generate electrical energy. This is accomplished by letting the ionizing radiation emitted by the radioactive isotopes hit a luminescent material ( scintillator or phosphor), which in turn emits photons that generate electricity upon striking a photovoltaic cell. The technology was developed by researchers of the Kurchatov Institute in Moscow. Description A beta emitter such as technetium-99 or strontium-90 is suspended in a gas or liquid containing luminescent gas molecules of the excimer type, constituting a "dust plasma". This permits a nearly lossless emission of beta electrons from the emitting dust particles. The electrons then excite the gases whose excimer line is selected for the conversion of the radioactivity into a surroundi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
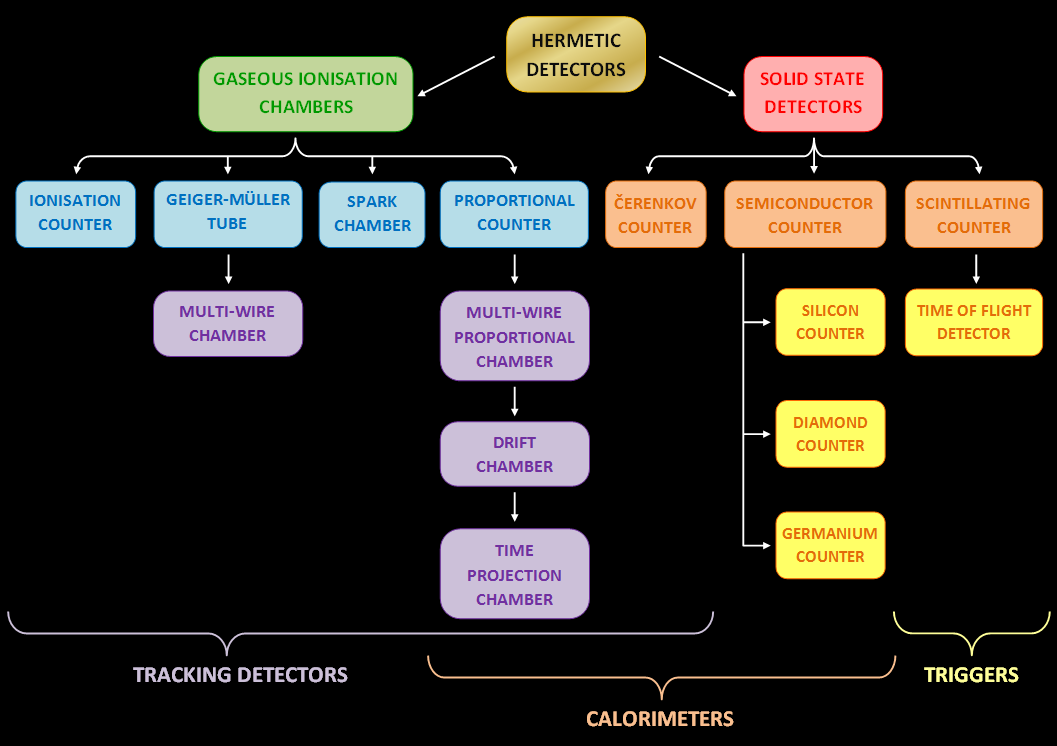
Particle Detector
In experimental and applied particle physics, nuclear physics, and nuclear engineering, a particle detector, also known as a radiation detector, is a device used to detect, track, and/or identify ionizing elementary particle, particles, such as those produced by nuclear decay, cosmic radiation, or reactions in a particle accelerator. Detectors can measure the particle energy and other attributes such as momentum, spin, charge, particle type, in addition to merely registering the presence of the particle. The operating of a nuclear radiation detector The operating principle of a nuclear radiation detector can be summarized as follows: The detector identifies high-energy particles or photons—such as alpha, beta, gamma radiation, or neutrons—through their interactions with the atoms of the detector material. These interactions generate a primary signal, which may involve ionization of gas, the creation of electron-hole pairs in semiconductors, or the emission of light in scint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US Navy 070208-N-9132D-002 Electronics Technician 2nd Class Shea Thompson Tests An Alpha Particle Dection Probe
US or Us most often refers to: * ''Us'' (pronoun), the objective case of the English first-person plural pronoun ''we'' * US, an abbreviation for the United States US, U.S., Us, us, or u.s. may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Albums * ''Us'' (Brother Ali album) or the title song, 2009 * ''Us'' (Empress Of album), 2018 * ''Us'' (Mull Historical Society album), 2003 * ''Us'' (Peter Gabriel album), 1992 * ''Us'' (EP), by Moon Jong-up, 2021 * ''Us'', by Maceo Parker, 1974 * ''Us'', mini-album by Peakboy, 2019 Songs * "Us" (James Bay song), 2018 * "Us" (Jennifer Lopez song), 2018 * "Us" (Regina Spektor song), 2004 * "Us" (Gracie Abrams song), 2024 * "Us", by Azealia Banks from '' Fantasea'', 2012 * "Us", by Celine Dion from ''Let's Talk About Love'', 1997 * "Us", by Gucci Mane from '' Delusions of Grandeur'', 2019 * "Us", by Spoon from '' Hot Thoughts'', 2017 Other media * US Festival, two 1980s California music festivals organized by Steve Wozniak * ''Us'' (1991 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photomultiplier
A photomultiplier is a device that converts incident photons into an electrical signal. Kinds of photomultiplier include: * Photomultiplier tube, a vacuum tube converting incident photons into an electric signal. Photomultiplier tubes (PMTs for short) are members of the class of vacuum tubes, and more specifically vacuum phototubes, which are extremely sensitive detectors of light in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum. ** Magnetic photomultiplier, developed by the Soviets in the 1930s. ** Electrostatic photomultiplier, a kind of photomultiplier tube demonstrated by Jan Rajchman of RCA Laboratories in Princeton, NJ in the late 1930s which became the standard for all future commercial photomultipliers. The first mass-produced photomultiplier, the Type 931, was of this design and is still commercially produced today. * Silicon photomultiplier, a solid-state device converting incident photons into an electric signal. Silicon photomul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Curran
Sir Samuel Crowe Curran, FRS, FRSE (23 May 1912 – 15 February 1998) was a Scottish physicist and academic who was the first Principal and Vice-Chancellor of the University of Strathclyde – the first of the new technical universities in Britain. He is the inventor of the scintillation counter, the proportional counter, and the proximity fuze. To date, Curran remains the longest serving principal and vice chancellor of the University of Strathclyde, holding the post for 16 years, not counting his previous five years as principal of the Royal College of Science and Technology. Life Samuel Curran was born on 23 May 1912 at Ballymena in Ireland, the son of John Hamilton Curran (from Kinghorn in Fife), and his wife, Sarah Carson Crowe (some sources state Sarah Owen Crowe). The family moved to Scotland soon after for his father to work as foreman of a steelworks near Wishaw. His brother Robert Curran, later a famous pathologist, was born soon after. He had two other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinthariscope
A spinthariscope () is a device for observing individual Radioactive decay, nuclear disintegrations caused by the interaction of ionizing radiation with a phosphor (see radioluminescence) or scintillator. Invention The spinthariscope was invented by William Crookes in 1903. While observing the apparently uniform fluorescence on a zinc sulfide screen created by the radioactive emissions (mostly alpha radiation) of a sample of radium bromide, he spilled some of the sample, and, owing to its extreme rarity and cost, he was eager to find and recover it. Upon inspecting the zinc sulfide screen under a microscope, he noticed separate flashes of light created by individual alpha particle collisions with the screen. Crookes took his discovery a step further and invented a device specifically intended to view these scintillations. It consisted of a small screen coated with zinc sulfide affixed to the end of a tube, with a tiny amount of radium salt suspended a short distance from the scree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |