|
Science And Technology In Nazi Germany
The position of science and technology in Nazi Germany was completely determined by party instructions and the political atmosphere established in the country. The state and party apparatuses, largely educated people from the lower classes of society, due to their inherent distrust and unfriendly attitude towards any knowledge, in principle did not contribute to the progress of science. On May 1, 1934, Bernhard Rust was appointed ''Reichs- und preußischen Minister für Wissenschaft, Erziehung und Volksbildung'' ( Reich Minister of Science, Education and Culture). He was charged with the responsibility of leading science in the spirit of party ideology and preparing for war. The regime encouraged, mainly, only science that gives an obvious result. The significance of fundamental science was not understood by the leaders of Nazi Germany. After the spectacular victory over France in 1940, Hitler considered his immediate political tasks (see ''Mein Kampf'') completed, and decreed t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synthetic Rubber
A synthetic rubber is an artificial elastomer. They are polymers synthesized from petroleum byproducts. About of rubber is produced annually in the United States, and of that amount two thirds are synthetic. Synthetic rubber, just like natural rubber, has many uses in the automotive industry for tires, door and window profiles, seals such as O-rings and gaskets, hoses, belts, matting, and flooring. They offer a different range of physical and chemical properties which can improve the reliability of a given product or application. Synthetic rubbers are superior to natural rubbers in two major respects: thermal stability, and resistance to oils and related compounds. They are more resistant to oxidizing agents, such as oxygen and ozone which can reduce the life of products like tires. History The expanded use of bicycles, and particularly their pneumatic tires, starting in the 1890s, created increased demand for rubber. In 1909, a team headed by Fritz Hofmann, working at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
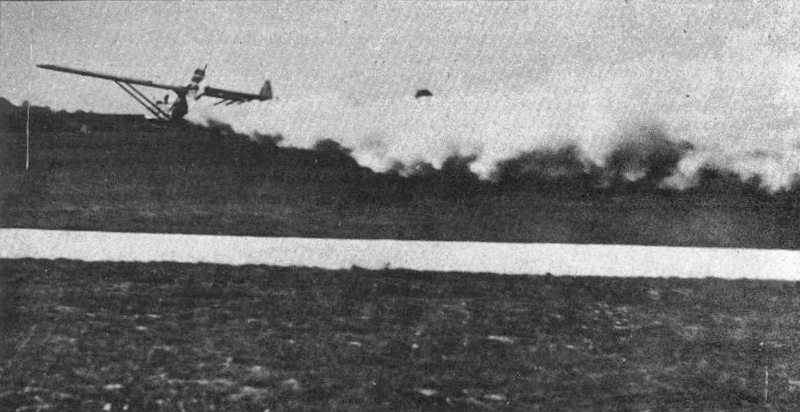
Heinkel He 176
The Heinkel He 176 was a German experimental rocket-powered aircraft. It was the world's first aircraft to be propelled solely by a liquid-fueled rocket, making its first powered flight on 20 June 1939 with Erich Warsitz at the controls. The He 176 was developed as a private venture by the Heinkel company in accordance with director Ernst Heinkel's emphasis on developing technology for high-speed flight. Work on the project began in 1936 after testing with a modified He 72 and a pair of He 112s had shown rocket propulsion to have some viability. The He 176 was purpose-built to harness this propulsion, rather than a modification of existing piston engined-types. The resulting aircraft, largely composed of wood, was of relatively simple build in some aspects, and relatively compact. It incorporated some novel concepts, such as an unconventional reclined seating position for the pilot and a unique jettisonable nose escape system for emergencies. In December 1937 the aircraft was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jet Engine
A jet engine is a type of reaction engine, discharging a fast-moving jet (fluid), jet of heated gas (usually air) that generates thrust by jet propulsion. While this broad definition may include Rocket engine, rocket, Pump-jet, water jet, and hybrid propulsion, the term typically refers to an internal combustion airbreathing jet engine, air-breathing jet engine such as a turbojet, turbofan, ramjet, pulse jet engine, pulse jet, or scramjet. In general, jet engines are internal combustion engines. Air-breathing jet engines typically feature a Axial compressor, rotating air compressor powered by a turbine, with the leftover power providing thrust through the propelling nozzle—this process is known as the Brayton cycle, Brayton thermodynamic cycle. Jet aircraft use such engines for long-distance travel. Early jet aircraft used turbojet engines that were relatively inefficient for subsonic flight. Most modern subsonic jet aircraft use more complex High-bypass turbofan, high-bypas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar
Radar is a system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), direction ( azimuth and elevation angles), and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It is a radiodetermination method used to detect and track aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, map weather formations, and terrain. The term ''RADAR'' was coined in 1940 by the United States Navy as an acronym for "radio detection and ranging". The term ''radar'' has since entered English and other languages as an anacronym, a common noun, losing all capitalization. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwave domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna (often the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving) and a receiver and processor to determine properties of the objects. Radio waves (pulsed or continuous) from the transmitter reflect off the objects and return to the receiver, giving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Power
Nuclear power is the use of nuclear reactions to produce electricity. Nuclear power can be obtained from nuclear fission, nuclear decay and nuclear fusion reactions. Presently, the vast majority of electricity from nuclear power is produced by nuclear ''fission'' of uranium and plutonium in nuclear power plants. Nuclear ''decay'' processes are used in niche applications such as radioisotope thermoelectric generators in some space probes such as ''Voyager 2''. Reactors producing controlled fusion power, ''fusion'' power have been operated since 1958 but have yet to generate net power and are not expected to be commercially available in the near future. The first nuclear power plant was built in the 1950s. The global installed nuclear capacity grew to 100GW in the late 1970s, and then expanded during the 1980s, reaching 300GW by 1990. The 1979 Three Mile Island accident in the United States and the 1986 Chernobyl disaster in the Soviet Union resulted in increased regulation and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insecticide
Insecticides are pesticides used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. The major use of insecticides is in agriculture, but they are also used in home and garden settings, industrial buildings, for vector control, and control of insect parasites of animals and humans. Acaricides, which kill mites and ticks, are not strictly insecticides, but are usually classified together with insecticides. Some insecticides (including common bug sprays) are effective against other non-insect arthropods as well, such as scorpions, spiders, etc. Insecticides are distinct from insect repellents, which repel but do not kill. Sales In 2016 insecticides were estimated to account for 18% of worldwide pesticide sales. Worldwide sales of insecticides in 2018 were estimated as $ 18.4 billion, of which 25% were neonicotinoids, 17% were pyrethroids, 13% were diamides, and the rest were many other classes which sold for less th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarin
Sarin (NATO designation GB nerve_agent#G-series.html" ;"title="hort for nerve agent#G-series">G-series, "B" is an extremely toxic organophosphorus compound.Sarin (GB) Emergency Response Safety and Health Database. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. Accessed April 20, 2009. that has been often used as a due to its extreme potency as a . Sarin is a volatile, colorless and odorless liquid. Exposure can be lethal even at very low concentrations, and death can occur within one to ten minutes after direct inhalation of a leth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fritz Strassmann
Friedrich Wilhelm Strassmann (; 22 February 1902 – 22 April 1980) was a German chemist who, with Otto Hahn in December 1938, identified the element barium as a product of the bombardment of uranium with neutrons. Their observation was the key piece of evidence necessary to identify the previously unknown phenomenon of nuclear fission, as was subsequently recognized and published by Lise Meitner and Robert Frisch. In their second publication on nuclear fission in February 1939, Strassmann and Hahn predicted the existence and liberation of additional neutrons during the fission process, opening up the possibility of a nuclear chain reaction. Early life Friedrich Wilhelm (Fritz) Strassmann was born in Boppard, Germany, to Richard Strassmann and Julie Strassmann (née Bernsmann). He was the youngest of nine children. Growing up in Düsseldorf, he developed an interest in chemistry at a young age and conducted chemistry experiments in his parents' home. His family was of modes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otto Hahn
Otto Hahn (; 8 March 1879 – 28 July 1968) was a German chemist who was a pioneer in the field of radiochemistry. He is referred to as the father of nuclear chemistry and discoverer of nuclear fission, the science behind nuclear reactors and nuclear weapons. Hahn and Lise Meitner discovered isotopes of the radioactive elements isotopes of radium, radium, Isotopes of thorium, thorium, isotopes of protactinium, protactinium and isotopes of uranium, uranium. He also discovered the phenomena of atomic recoil and nuclear isomerism, and pioneered rubidium–strontium dating. In 1938, Hahn, Meitner and Fritz Strassmann Discovery of nuclear fission, discovered nuclear fission, for which Hahn alone was awarded the 1944 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. A graduate of the University of Marburg, which awarded him a doctorate in 1901, Hahn studied under Sir William Ramsay at University College London and at McGill University in Montreal under Ernest Rutherford, where he discovered several new radi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olympia, Greece
Olympia ( ; ), officially Archaia Olympia ( ), is a small town in Elis (regional unit), Elis on the Peloponnese peninsula in Greece, famous for the nearby archaeological site of the same name. The site was a major Panhellenic sanctuary, Panhellenic religious sanctuary of ancient Greece, where the ancient Olympic Games were held every Olympiad, four years throughout classical antiquity, from the 8th century BC to the 4th century AD. They were Olympic Games, restored on a global basis in 1894 in honor of the ideal of peaceful international contention for excellence. The sacred precinct, named the Altis, was primarily dedicated to Zeus, although other gods were worshipped there. The games conducted in his name drew visitors from all over the Greek world as one of a group of such "Panhellenic" centres, which helped to build the identity of the ancient Greeks as a nation. Despite the name, it is nowhere near Mount Olympus in northern Greece, where the twelve Olympians, the major deit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nylon 6
Nylon 6 or polycaprolactam is a polymer, in particular semicrystalline polyamide. Unlike most other nylons, nylon 6 is not a condensation polymer, but instead is formed by ring-opening polymerization; this makes it a special case in the comparison between condensation and addition polymers. Its competition with nylon 66 and the example it set have also shaped the economics of the synthetic fibre industry. It is sold under numerous trade names including Perlon (Germany), Dederon (former East Germany), Nylatron, Capron, Ultramid, Akulon, Kapron (former Soviet Union and satellite states), Rugopa (Turkey) and Durethan. History Polycaprolactam was developed by Paul Schlack at IG Farben in late 1930s (first synthesized in 1938) to reproduce the properties of Nylon 66 without violating the patent on its production. (Around the same time, Kohei Hoshino at Toray also succeeded in synthesizing nylon 6.) It was marketed as Perlon, and industrial production with a capacity of 3,500 tons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |