|
Schneider Et Cie
Schneider et Compagnie, also known as Schneider-Creusot for its birthplace in the French town of Le Creusot, was a historic iron and steel-mill company which became a major arms manufacturer. In the 1960s, it was taken over by the Belgian Empain group and merged with it in 1969 to form Empain-Schneider, which in 1980 was renamed Schneider SA and in 1999, after much restructuring, Schneider Electric. Origins In 1836, Adolphe Schneider and his brother Eugène Schneider bought iron-ore mines and forges at Le Creusot (Saône-et-Loire). They developed a business dealing in steel, railways, armaments, and shipbuilding. The Creusot steam hammer was built in 1877. Somua, a subsidiary located near Paris, made machinery and vehicles, including the SOMUA S35 tank. Armaments Vehicles *Schneider CA1, the first French tank *Schneider-Creusot 030-T steam locomotive *Schneider Coast Defense Train Ships *Ferré-class submarine, a pair of long Submarine, submarines in service with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palatine Rue Anjou
A palatine or palatinus (Latin; : ''palatini''; cf. derivative spellings below) is a high-level official attached to imperial or royal courts in Europe since Roman Empire, Roman times."Palatine" . From the ''Oxford English Dictionary''. Retrieved November 19, 2008. The term ''palatinus'' was first used in Ancient Rome for Chamberlain (office), chamberlains of the Emperor due to their association with the Palatine Hill. The imperial palace guard, after the rise of Constantine I, were also called the ''Scholae Palatinae'' for the same reason. In the Early Middle Ages the title became attached to courts beyond the imperial one; one of the highest level of officials in the papal administration were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
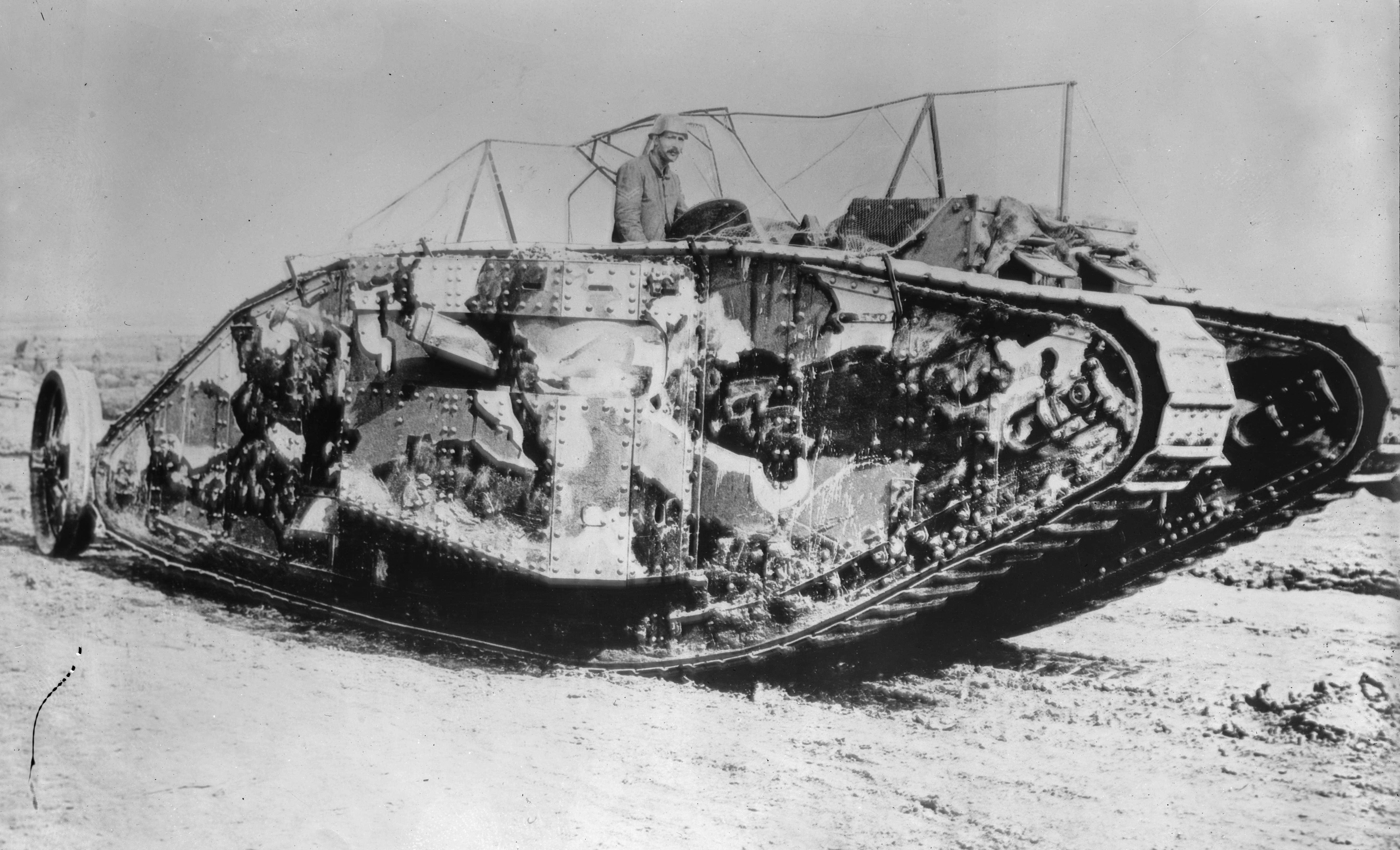
Tank
A tank is an armoured fighting vehicle intended as a primary offensive weapon in front-line ground combat. Tank designs are a balance of heavy firepower, strong armour, and battlefield mobility provided by tracks and a powerful engine; their main armament is often mounted within a turret. They are a mainstay of modern 20th and 21st century ground forces and a key part of combined arms combat. Modern tanks are versatile mobile land weapons platforms whose main armament is a large- calibre tank gun mounted in a rotating gun turret, supplemented by machine guns or other ranged weapons such as anti-tank guided missiles or rocket launchers. They have heavy vehicle armour which provides protection for the crew, the vehicle's munition storage, fuel tank and propulsion systems. The use of tracks rather than wheels provides improved operational mobility which allows the tank to overcome rugged terrain and adverse conditions such as mud and ice/snow better than wheele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canon De 75 Modèle 1912 Schneider
The Canon de 75 modele 1912 Schneider was a French World War I piece of 75 mm artillery, designed and manufactured by Schneider et Cie in Le Creusot. It entered service with the French horse-mounted artillery in 1912 and a number were sold to the army of Serbia. By the end of the war, all guns in French service were replaced with the more successful and standardised Canon de 75 modèle 1897 The French 75 mm field gun is a Quick-firing gun, quick-firing field artillery piece adopted in March 1898. Its official French designation was: Matériel de 75 mm Mle 1897. It was commonly known as the French 75, simply the 75 and S .... The remaining guns were then sold to Poland, where they were used in the Polish-Bolshevik War. Bibliography * {{DEFAULTSORT:Canon De 75 Modele 1912 Schneider Schneider Electric World War I field artillery of France World War I guns 75 mm artillery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canon De 75 Modèle 1905 Schneider
The Canon de 75 modèle 1905 Schneider, factory designation Matériel de campagne à tir rapide de 75 mm, modèle 1903 PR (''Puissant, système de récupération de recul à Ressort''), Bulgarian designation "75-мм скорострелно полско оръдие “Шнайдер” образец 1904 год, was a field gun developed by Gustave Canet and used by Bulgaria during World War I and World War II World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the wo .... Some 324 had been delivered by the end of 1907 and most were still in service in 1939.Chamberlain & Gander, p. 15 Notes References * Chamberlain, Peter & Gander, Terry. ''Light and Medium Field Artillery''. New York: Arco, 1975 Schneider-Canet 75mm 1904Canon de 75mm Mle 1904 Schneider-Canet PR World War II fiel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canon De 75 Modèle 1897
The French 75 mm field gun is a Quick-firing gun, quick-firing field artillery piece adopted in March 1898. Its official French designation was: Matériel de 75 mm Mle 1897. It was commonly known as the French 75, simply the 75 and Soixante-Quinze (French for "seventy-five"). The French 75 was designed as an anti-personnel weapon system for delivering large volumes of time-fused shrapnel shells on enemy troops advancing in the open. After 1915 and the onset of trench warfare, impact-detonated high-explosive shells prevailed. By 1918 the 75s became the main agents of delivery for Chemical warfare#Dispersion, toxic gas shells. The 75s also became widely used as truck mounted anti-aircraft artillery. They were the main armament of the Saint-Chamond (tank), Saint-Chamond tank in 1918 and the Char 2C. The French 75 is widely regarded as the first modern artillery piece.Priscilla Mary Roberts"French 75 gun" World War One, pg. 726 It was the first field gun to include a hyd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
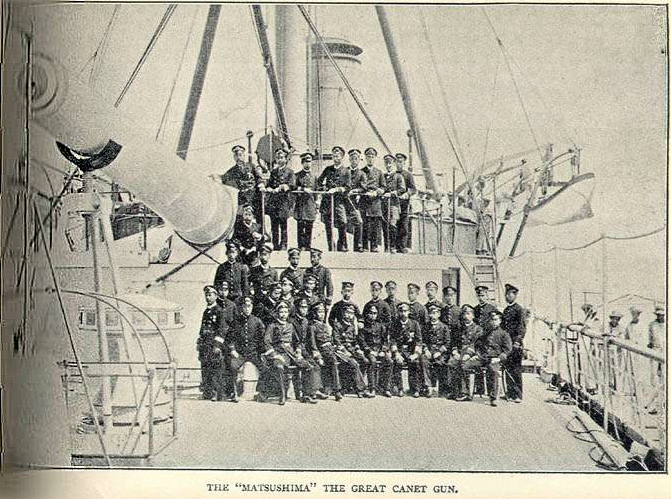
Canet Guns
The Canet guns were a series of weapon systems developed by the French engineer Gustave Canet (1846–1908), who worked as an engineer from 1872 to 1881 for the London Ordnance Works, then for Forges et Chantiers de la Méditerranée, and from 1897 to 1907 for Schneider et Cie of Le Creusot. 320 mm naval guns Canet developed a 38 cal naval gun, an extremely powerful weapon for its time, specifically for the export market. The gun was first selected by the Spanish Navy in 1884 as part of a large naval expansion program which called for six new battleships. The Spanish armaments firm Hontoria obtained a manufacturing license to produce the weapon, but due to budgetary reasons, only one vessel, the , was completed. Canet was more successful in sales to the Empire of Japan, when the gun was selected by the French military advisor and naval architect Louis-Émile Bertin as the main battery of the , new type of cruiser he had designed in 1887. The usage was consistent wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
76 Mm Mountain Gun M1909
The 76 mm Schneider-Danglis Mountain Gun Model 1909 (Russian 76-мм горная пушка Шнейдера-Данглиса, модель 1909) was a rapid-fire mountain gun based on the Schneider-Danglis mountain gun that was used by the Imperial Russian Army during World War I and the Red Army during World War II History In 1893, the Greek engineer Colonel Panagiotis Danglis developed a design for a 75 mm mountain cannon and submitted it to the Greek Ministry of War. However, he would have to wait ten years before his project was authorized. In 1905, Danglis proposed to the French firm Schneider that a prototype of his gun should be entered in the next competition for the Greek Army. Schneider developed its own carriage for the gun and the revised design was known as the Schneider-Danglis mountain gun. The prototype was tested in France in May 1906 and in April the gun was tested in Greece, after which the gun was adopted for service by the Greek Army. Early in 1909, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canon De 75 M(montagne) Modele 1928
The Canon de 75 Montagne modèle 1928 (75 mm M mle.28) was a French mountain gun, used by France, Poland and Nazi Germany during World War II. History It is a derivative of the Canon de 75 M(montagne) modele 1919 Schneider, upgraded based on feedback from the Rif War. According to Peter Chamberlain, the design of the mle 1928 "owed little to that of the mle 1919" while the French Army manuals insisted on it being "slightly modified" (). The mle 1928 featured a simpler shield. The mle 1928 fired the same ammunitions than the Canon de 75 modèle 1897 and the mle. 1919. It could be carried on seven mules or towed by three mules. The guns were also sold to Poland. After 1940, these weapons were used by the Germans as 7.5 cm GebK 283(f). The French used this weapon to equip the artillery batteries of the 4th Moroccan Mountain Division during 1944 and 1945. Some were later sent to alpine units but the gun was considered obsolete by that date. See also * List of mountai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canon De 75 M(montagne) Modele 1919 Schneider
The Canon de 75 M (montagne) modèle 1919 Schneider (75 mm mle.1919) was a French mountain gun designed as a replacement of the 65 mm mle 1906. The mle 1919 was manufactured by Schneider et Cie and used during World War II. For transport, the gun could be broken down into seven sections. This weapon was used by Brazil, Paraguay, Yugoslavia and Greece. When captured by the Germans in World War II, the French guns were designated 7.5 cm GebK 237(f); the Yugoslav guns were designated 7.5 cm GebK 283(j).Infantry, Mountain, and Airborne Guns - p.16 The gun crew was protected by an armoured shield. Greek service This gun was used by the Greek Army in the Greek–Italian War from October 1940 to April 1941. It was used in divisional service in conjunction with the Schneider 105 mountain gun. Each Greek division had an artillery regiment with 16 mountain 75 mm and 8 mountain 105 mm guns. A total of 192 Mle 1919 75mm were procured by Greece, that equipped 12 (of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panagiotis Danglis
Panagiotis Danglis (; – 9 March 1924) was a Greek military officer and politician. He is particularly notable for inventing the Schneider-Danglis mountain gun, his service as chief of staff in the Balkan Wars, and participation in the Triumvirate of the Provisional Government of National Defence during the First World War. Life Origin and early life Panagiotis Danglis was born in Atalanti on 17 November 1853, where his father was serving in an infantry battalion. His family was of Souliot origin, speaking the Soulotic dialect of Albanian at home, and had a long and distinguished history: Panagiotis was named after his grandfather, Giotis Danglis, a Souliot chieftain who had begun serving under Napoleon during the second French occupation of the Ionian Islands, and had become a general during the Greek War of Independence. His son, Georgios Danglis (1809–1896), was born in exile in Corfu, entered the Hellenic Army in 1828 in time to fight in the last campaigns of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
75 Mm Schneider-Danglis 06/09
The 75 mm Schneider-Danglis 06/09 (Greek: Ορειβατικό πυροβόλο των 75χιλ. Schneider-Δαγκλής, υποδ. 1908) (French: Matériel de montagne à tir rapide de 75mm, type MPD) was a 75mm mountain gun used by multiple countries prior to, during and after World War I. The gun was designed by a Greek artillery officer, Major Panagiotis Danglis, in 1893. It featured an inner barrel which could be removed from a combination outer barrel & breech mechanism, making for easier transportation. The carriage had rotating cranked axle stubs, allowing for high or low elevation. Underneath the gun was a cradle with a hydro-pneumatic recoil system, as well as an S-shaped shield and hinged box trail, the latter of which allowed the gun to be drawn by horses from fitted shafts. It was used by Greece during the Greco-Turkish War (1919–1922), Balkan Wars, World War I, and World War II. The Russian Empire purchased several guns from Schneider-Creusot in France, but a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circé-class Submarine (1925)
The ''Circé''-class submarines were a sub-class of the 600 Series of submarines built for the French Navy prior to World War II. There were four vessels in the class, built to a Schneider- Laubeuf design. They were ordered in 1925 and completed by 1927.Conway p.273 The four boats of the ''Circé'' class saw action during the Second World War, from September 1939 until the French armistice in June 1940. General characteristics The ''Circé'' class had a displacement of 615 tons surfaced and 776 tons submerged. They had an endurance of 3,500 miles at , with a maximum surface speed of , and a submerged speed of . Their armament was seven torpedo tubes (three forward, two midships, and two aft) with an outfit of 13 torpedoes. As with all French submarines of this period, the midships torpedo tubes were fitted externally in trainable mounts. They had a single deck gun and two machine guns, and were manned by crews of 41 men. Ships * was at Bizerte in June 1940. She was se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |