|
Scalpelling
Scalpelling is a body art procedure similar to body piercing for the creation of decorative perforations through the skin and other body tissue, and is most commonly used as a replacement for or enhancement of ear piercing. Whereas piercing is typically performed with a hollow piercing needle or an ear piercing instrument, scalpelling is performed by using a scalpel to cut a slit into the skin. Unlike dermal punching, no flesh is removed. The technique can immediately produce holes with a larger diameter than can be achieved by piercing. This is a more rapid means of accommodating larger gauge jewellery than stretching, a technique whereby piercings are enlarged by inserting gradually larger jewellery. Scalpelling is performed to quickly achieve a large-gauge piercing, when scar tissue is preventing further stretching, if tissue has thinned to the point where further stretching could cause it to break, or to combine two closely placed piercings into one hole. Though the wounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stretching (body Piercing)
Stretching, in the context of body piercing, is the deliberate expansion of a healed piercing for the purpose of wearing certain types of jewelry. Ear piercings are the most commonly stretched piercings, with nasal septum piercings, tongue piercings and lip piercings/ lip plates following close behind. While all piercings can be stretched to some degree, cartilage piercings are usually more difficult to stretch and more likely to form hypertrophic scars if stretched quickly. Dermal punching is generally the preferred method for accommodating larger jewelry in cartilage piercings. Stretching is usually done in small increments to minimize the potential for damaging the healed fistula or creating scar tissue. In North America, most stretching methods go up by a single even-sized gauge increment at a time. 0g (8 mm), is generally considered to be "the point of no return": a hole larger than this size will rarely close to a standard piercing size. Since each body is different, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Body Art
Body art is art in which the artist uses their human body as the primary medium.Oxford Dictionary of Modern and Contemporary Art, Oxford University, p. 88 Emerging from the context of Conceptual Art during the 1970s, Body art may include performance art. Body art is likewise utilized for investigations of the body in an assortment of different media including painting, casting, photography, film and video. More extreme body art can involve mutilation or pushing the body to its physical limits. In more recent times, the body has become a subject of much broader discussion and treatment than can be reduced to body art in its common understanding. Important strategies that question the human body are: implants, body in symbiosis with the new technologies, virtual avatar bodies, among others. Popular use of the term Body art has been expanded into the popular culture and now covers a wide spectrum of usage, including tattoos, body piercings, scarification, and body painting. Phot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ear Piercing
Earrings are jewelry that can be worn on one's ears. Earrings are commonly worn in a piercing in the earlobe or another external part of the ear, or by some other means, such as stickers or clip-ons. Earrings have been worn across multiple civilizations and historic periods, often carrying a cultural significance. Locations for piercings other than the earlobe include the rook, tragus, and across the helix (see image in the infobox). The simple term "ear piercing" usually refers to an earlobe piercing, whereas piercings in the upper part of the external ear are often referred to as "cartilage piercings". Cartilage piercings are more complex to perform than earlobe piercings and take longer to heal. Earring components may be made of any number of materials, including metal, plastic, glass, precious stone, beads, wood, bone, and other materials. Designs range from small hoops and studs to large plates and dangling items. The size is ultimately limited by the physical capacity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ear Piercing Instrument
An ear-piercing instrument (commonly referred to as a piercing gun or an ear-piercing gun) is a device designed to pierce earlobes by driving a pointed starter stud through the lobe. Piercing guns are typically used for ear piercing in mall jewelry shops, beauty salons, pharmacies, and doctors' offices. Piercing guns have been widely criticized as dangerous among professional body piercers. The use of older designs of piercing gun can possibly carry an increased risk of disease transmission, as compared to methods used by professional piercers. Piercing guns have been criticised for causing damage (sometimes mischaracterised as blunt-force trauma) to the skin and underlying tissue. Diminished air and blood circulation in tissue compressed by a piercing gun can lead to prolonged healing, minor complications and scarring. More modern designs of reusable ear-piercing instruments, such as Inverness and Studex System 75, use self-contained, single-use, sealed, and sterilised dispo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scalpel
A scalpel or bistoury is a small and extremely sharp bladed instrument used for surgery, anatomical dissection, podiatry and various handicrafts. A lancet is a double-edged scalpel. Scalpel blades are usually made of hardened and tempered steel, stainless steel, or high carbon steel; in addition, titanium, ceramic, diamond and even obsidian knives are not uncommon. For example, when performing surgery under MRI guidance, steel blades are unusable (the blades would be drawn to the magnets and would also cause image artifacts). Historically, the preferred material for surgical scalpels was silver. Scalpel blades are also offered by some manufacturers with a zirconium nitride–coated edge to improve sharpness and edge retention. Others manufacture blades that are polymer-coated to enhance lubricity during a cut. Scalpels may be single-use disposable or re-usable. Re-usable scalpels can have permanently attached blades that can be sharpened or, more commonly, removable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dermal Punching
Body modification (or body alteration) is the deliberate altering of the human anatomy or human physical appearance. In its broadest definition it includes skin tattooing, socially acceptable decoration (''e.g.'', common ear piercing in many societies), and religious rites of passage (e.g., circumcision in a number of cultures), as well as the modern primitive movement. Body modification is performed for a large variety of reasons, including aesthetics, sexual enhancement, rites of passage, religious beliefs, to display group membership or affiliation, in remembrance of lived experience, traditional symbolism such as axis mundi and mythology, to create body art, for shock value, and as self-expression, among other reasons. Background What counts as "body modification" varies in cultures. In western cultures, the cutting or removal of one's hair is not usually considered body modification. Body modification can be contrasted with body adornment by defining body modification a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scar
A scar (or scar tissue) is an area of fibrosis, fibrous tissue that replaces normal skin after an injury. Scars result from the biological process of wound repair in the skin, as well as in other Organ (anatomy), organs, and biological tissue, tissues of the body. Thus, scarring is a natural part of the healing process. With the exception of very minor lesions, every wound (e.g., after accident, disease, or surgery) results in some degree of scarring. An exception to this are animals with complete Regeneration (biology), regeneration, which regrow tissue without scar formation. Scar tissue is composed of the same protein (collagen) as the tissue that it replaces, but the fiber composition of the protein is different; instead of a random basketweave formation of the collagen fibers found in normal tissue, in fibrosis the collagen cross-links and forms a pronounced alignment in a single direction. This collagen scar tissue alignment is usually of inferior functional quality to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labret
A labret is a form of body piercing. Taken literally, it is any type of adornment that is attached to the lip (labrum). However, the term usually refers to a piercing that is below the bottom lip, above the chin. It is sometimes referred to as a "tongue pillar" or a "soul patch piercing". Pronunciation The traditional pronunciation of ''labret'' in anthropology is . It derives from the Latin ''labrum'' "lip" and the diminutive suffix ''-et.'' However, many in the body-piercing industry give it the pseudo-French pronunciation , though the French word is in fact borrowed from the English.''How do YOU Say L-a-b-r-e-t?'' (note: the etymology here is false.) Anthropology [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
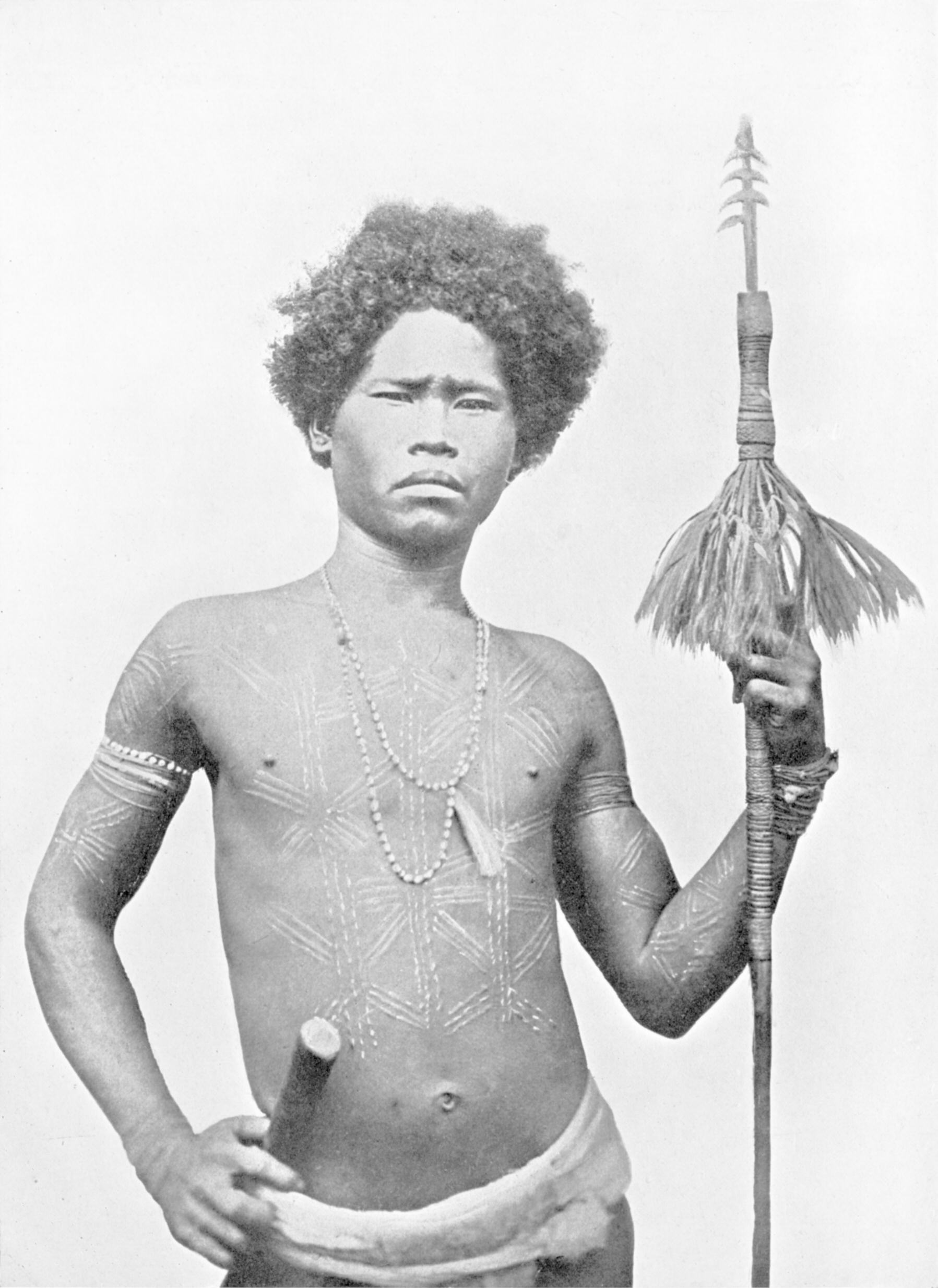
Scarification
Scarification involves scratching, etching, burning/ branding, or superficially cutting designs, pictures, or words into the skin as a permanent body modification or body art. The body modification can take roughly 6–12 months to heal. In the process of body scarification, scars are purposely formed by cutting or branding the skin by various methods (sometimes using further sequential aggravating wound-healing methods at timed intervals, like irritation). Scarification is sometimes called '' cicatrization''. History Scarification has been traditionally practiced by darker skinned cultures, possibly because it is usually more visible on darker skinned people than tattoos. It was common in indigenous cultures of Africa (especially in the west), Melanesia, and Australia. Some indigenous cultures in North America also practiced scarification, including the ancient Maya. Africa In Africa, European colonial governments and European Christian missionaries criminalized and sti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |