|
Sayyid Muhammad Qanauji
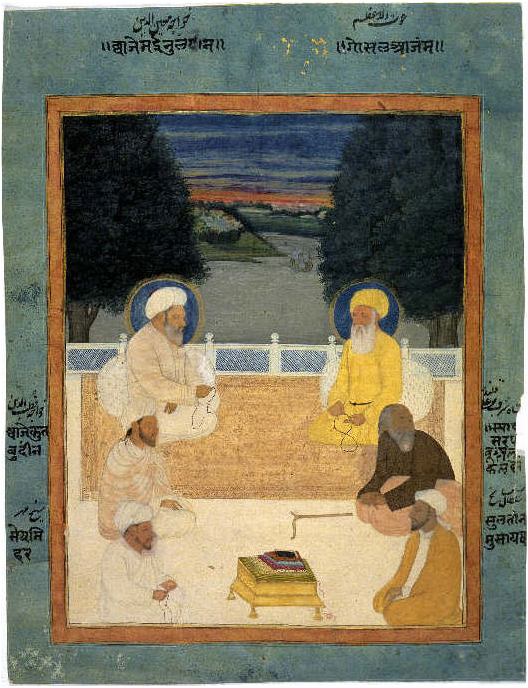
Mir Sayyid Muhammad Qanauji was a Sufi scholar who was chaplain to the Mughal emperor Shah Jahan (1592–1666) and teacher of his son, the emperor Aurangzeb (1618–1707). Life Sayyid Muhammad Qanauji was the chaplain of the Mughal emperor Shah Jahan (1592–1666). Sayyid Qannauji and Sayyid Fazil attended Shah Jahan during the last seven years of his life, when Shah Jahan was imprisoned in the fort at Akbarabad. Sayyid and the emperor's eldest daughter Jahanara were present with Shah Jahan during his last days, providing spiritual comfort and nursing. When the emperor knew he was dying, he praised Sayyid for his faithful service and asked if there was any way he could reward him. Sayyid asked him to forgive his son Aurangzeb (1618–1707), and the emperor reluctantly agreed. After Shah Jahan's death Sayyid Muhammad helped prepare the body for burial, which was done with little ceremony since Aurangzeb had not ordered a state funeral. Sayyid Qannauji taught Aurangzeb, and a letter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mir (title)
Mir (, , ) (which is derived from the Arabic title ''Emir'' 'elite, general, prince') is a Persian, Kurdish and Balochi title with variable connotations. Etymology The term Mir has its roots in the Arabic equivalent Emir, which means Prince or General. ''Emir'' is derived from the Arabic root a-m-r, "command". Its other variations are Miran (plural of Mir), Mirzadeh, and Mirza Tribal Princes of the Persian Sunni Sayyids Mir is the Persian version of the title of tribal leaders of Sayyids, that are addressed in the arabic world as Naqib. Examples for Persian Miran (Plural of Mir) are Mir Sayyid Ali Hamadani and the family of the Mir Sayyid Hasan bin Azimullah and Hazrat Ishaan, that are today known as Dakik Family. Tribal Princes of the Kurdish Yazidis In the Yazidi culture, the Mîr is the religious and also the administrative authority from the Qatani branch of the Sheikh caste. The former Mir was Tahseen Said Beg, whose son Hazim bin Tahsin Said and nephew Naif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sufi
Sufism ( or ) is a mysticism, mystic body of religious practice found within Islam which is characterized by a focus on Islamic Tazkiyah, purification, spirituality, ritualism, and Asceticism#Islam, asceticism. Practitioners of Sufism are referred to as "Sufis" (from , ), and historically typically belonged to "orders" known as (pl. ) — congregations formed around a grand (saint) who would be the last in a Silsilah, chain of successive teachers linking back to Muhammad, with the goal of undergoing (self purification) and the hope of reaching the Maqam (Sufism), spiritual station of . The ultimate aim of Sufis is to seek the pleasure of God by endeavoring to return to their original state of purity and natural disposition, known as . Sufism emerged early on in Islamic history, partly as a reaction against the expansion of the early Umayyad Caliphate (661–750) and mainly under the tutelage of Hasan al-Basri. Although Sufis were opposed to dry legalism, they strictly obs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shah Jahan
Shah Jahan I, (Shahab-ud-Din Muhammad Khurram; 5 January 1592 – 22 January 1666), also called Shah Jahan the Magnificent, was the Emperor of Hindustan from 1628 until his deposition in 1658. As the fifth Mughal emperor, his reign marked the zenith of Mughal architectural and cultural achievements. The third son of Jahangir (), Shah Jahan participated in the military campaigns against the Sisodia dynasty, Sisodia Rajputs of Mewar and the rebel Lodi (Pashtun tribe), Lodi nobles of the Deccan Plateau, Deccan. After Jahangir's death in October 1627, Shah Jahan defeated his youngest brother Shahryar Mirza and crowned himself emperor in the Agra Fort. In addition to Shahryar, Shah Jahan executed most of his rival claimants to the throne. He commissioned many monuments, including the Red Fort, Shah Jahan Mosque, Thatta, Shah Jahan Mosque and the Taj Mahal, where his favorite consort Mumtaz Mahal is entombed. In foreign affairs, Shah Jahan presided over the aggressive campaigns agai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
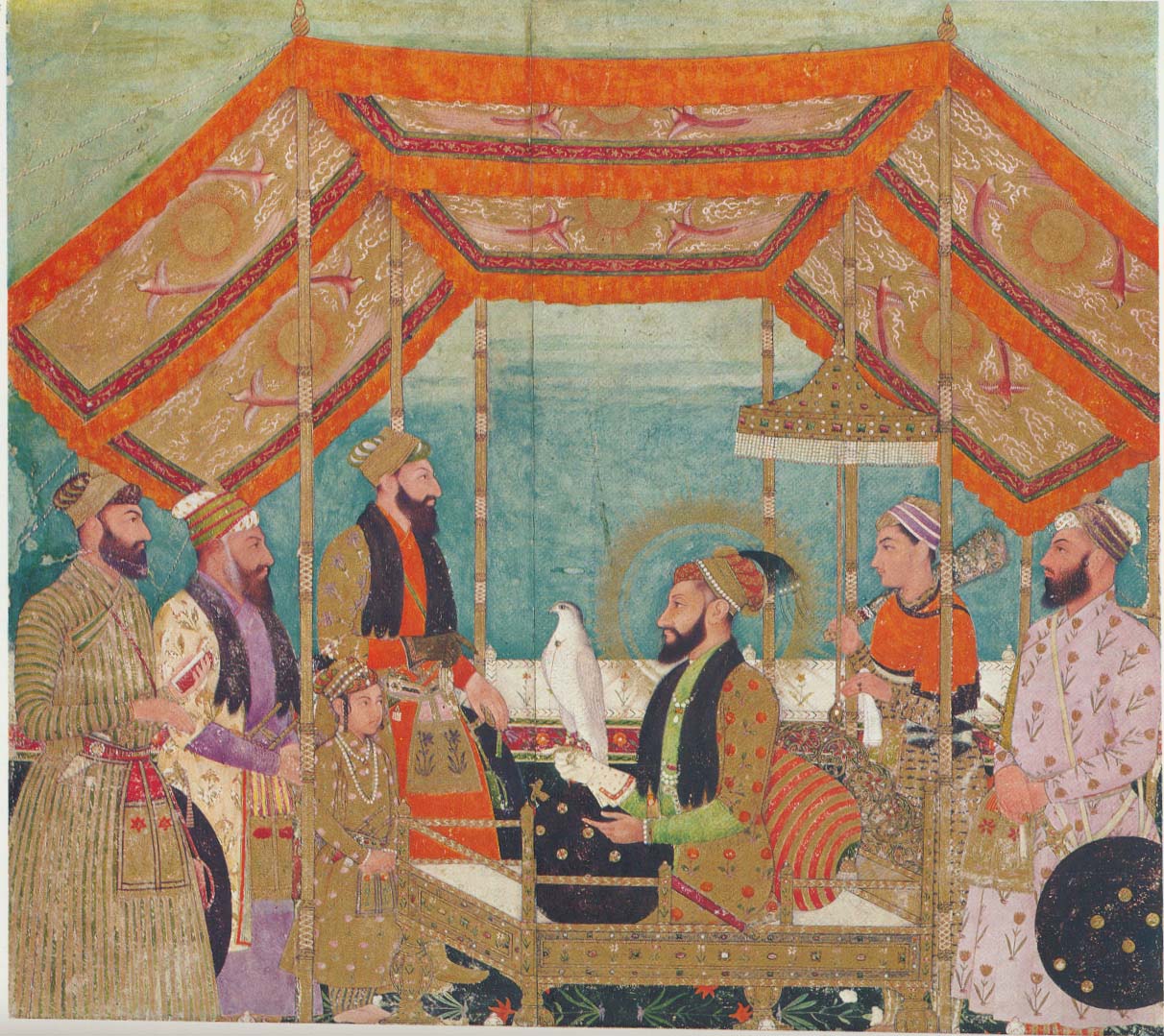
Aurangzeb
Alamgir I (Muhi al-Din Muhammad; 3 November 1618 – 3 March 1707), commonly known by the title Aurangzeb, also called Aurangzeb the Conqueror, was the sixth Mughal emperors, Mughal emperor, reigning from 1658 until his death in 1707, becoming the second longest-ruling emperor of Hindustan (48 years and 7 months). Under his reign, the Mughal Empire reached its greatest extent, with territory spanning nearly the entirety of the Indian subcontinent. Aurangzeb and the Mughals belonged to a branch of the Timurid dynasty. He held administrative and military posts under his father Shah Jahan () and gained recognition as an accomplished military commander. Aurangzeb served as the viceroy of the Viceroy of the Deccan, Deccan in 1636–1637 and the governor of Gujarat under Mughal Empire, Gujarat in 1645–1647. He jointly administered the provinces of Subah of Multan, Multan and Sind State, Sindh in 1648–1652 and continued expeditions into the neighboring Safavid Iran, Safavid ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. Muhammad in Islam, According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the tawhid, monotheistic teachings of Adam in Islam, Adam, Noah in Islam, Noah, Abraham in Islam, Abraham, Moses in Islam, Moses, Jesus in Islam, Jesus, and other Prophets and messengers in Islam, prophets. He is believed to be the Seal of the Prophets in Islam, and along with the Quran, his teachings and Sunnah, normative examples form the basis for Islamic religious belief. Muhammad was born in Mecca to the aristocratic Banu Hashim clan of the Quraysh. He was the son of Abdullah ibn Abd al-Muttalib and Amina bint Wahb. His father, Abdullah, the son of tribal leader Abd al-Muttalib ibn Hashim, died around the time Muhammad was born. His mother Amina died when he was six, leaving Muhammad an orphan. He was raised under the care of his grandfather, Abd al-Muttalib, and paternal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannauj
Kannauj (Hindustani language, Hindustani pronunciation: ) is an ancient city, administrative headquarters and a municipal board or Nagar palika, Nagar Palika Parishad in Kannauj district in the Indian States and territories of India, state of Uttar Pradesh. It is located 113 km (71 mi) from Etawah, 93 km (58 mi) from Kanpur, 129 km (81 mi) from Lucknow. The city's name is an evolved form of the classical name ''Kanyakubja''. During the ancient Vedic period, it was the capital city of the Pañcāla, Panchala Kingdom during the reign of king Vajrayudha. In the medieval era, it formed the core of the Kingdom of Kannauj and was ruled by multiple successive royal families. It was also known as ''Mahodaya'' during the time of Mihira Bhoja. It is situated 104 kilometres west of the state capital, Lucknow. Kannauj is famous for distilling of scents and perfumes. It is known as "India's perfume capital" and is famous for its traditional Kannauj Perfume, a g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhibullah Allahabadi
Muhibullah Allahabadi, or Muhibb ullah Ilahabadi (; मुहिबउल्लाह इलाहाबादी 1587–30 July 1648) was a Sufi saint and scholar who was active in Allahabad in northern India during the reign of the Mughul emperor Shah Jahan. He is noted as a leading proponent of the Sufi doctrine of '' Wahdat al-Wujud'', sometimes called "Oneness of Being". Life Muhibullah was born in 1587in India. He was a descendant of Fariduddin Ganjshakar. His home was in Sadarpur in Awadh. There he compiled a commentary in Arabic on Ibn Arabi's Fusus ul-Hikam. He was initiated into the Sabiriya branch of the Chishti Order of Sufis with the help of Shaikh Abu Said Gangohi, and visited major Chishti places of pilgrimage and centers before settling in Allahabad in 1628, where he spent the rest of his life. He was active during the reign of the Mogul emperor Shah Jahan (r. 1628–58). Muhibullah founded the Indo-Islamic literary culture in Allahabad, with his many writings on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharia
Sharia, Sharī'ah, Shari'a, or Shariah () is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition based on Islamic holy books, scriptures of Islam, particularly the Quran, Qur'an and hadith. In Islamic terminology ''sharīʿah'' refers to immutable, intangible divine law; contrary to ''fiqh'', which refers to its interpretations by Ulama, Islamic scholars. Sharia, or fiqh as traditionally known, has always been used alongside urf, customary law from the very beginning in Islamic history; has been elaborated and developed over the centuries by fatwa, legal opinions issued by mufti, qualified jurists – reflecting the tendencies of Schools of Fiqh, different schools – and integrated and with various economic, penal and administrative laws issued by Muslims, Muslim rulers; and implemented for centuries by Qadi, judges in the courts until recent times, when secularism was widely adopted in Islamic societies. Traditional Principles of Islamic jurisprudence, theory o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatawa-e-Alamgiri
Fatawa 'Alamgiri, also called Al-Fatawa al-Hindiyyah (; ), Fatawa-e-Alamgiri or Al-Fatawa al-'Alamkiriyyah (; ), is a 17th-century sharia based compilation on statecraft, general ethics, military strategy, economic policy, justice and punishment, that served as the law and principal regulating body of the Mughal Empire, during the reign of the Mughal Empire, Mughal emperor Aurangzeb, Muhammad Muhiuddin Aurangzeb Alamgir.Jamal Malik (2008), Islam in South Asia: A Short History, Brill Academic, , pp. 194-197 It subsequently went on to become the reference legal text to enforce sharia in colonial South Asia in the 18th century through early 20th century,David Arnold and Peter Robb, Institutions and Ideologies: A SOAS South Asia Reader, Psychology Press, pp. 171-176 and has been heralded as "the greatest digest of Muslim law during the Mughal empire, Mughal India". Outline Fatawa-e-Alamgiri was the work of many prominent scholars from different parts of the world, including Hejaz, pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad Azam Shah
Mirza Abu'l Fayaz Qutb-ud-Din Mohammad Azam (28 June 1653 – 20 June 1707), commonly known as Azam Shah, was briefly the seventh Mughal emperor from 14 March to 20 June 1707. He was the third son of the sixth Mughal emperor Aurangzeb and his chief consort Dilras Banu Begum. Azam was appointed as the heir-apparent (''Shahi Ali Jah'') to his father on 12 August 1681 and retained that position until Aurangzeb's death. During his long military career, he served as the viceroy of Berar Subah, Malwa, Bengal, Gujarat and the Deccan. Azam ascended the Mughal throne in Ahmednagar upon the death of his father on 14 March 1707. However, he and his three sons, Bidar Bakht, Jawan Bakht and Sikandar Shan, were later defeated and killed by Azam Shah's older half-brother, Shah Alam (later crowned as Bahadur Shah I), during the Battle of Jajau on 20 June 1707. Early life Birth Qutb-ud-Din Muhammad Azam was born on 28 June 1653 in Burhanpur to Prince Muhi-ud-Din (later known as 'Aurangze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muhammad Sultan (Mughal Prince)
Mirza Muhammad Sultan (Persian: میرزا محمد سلطان) (30 December 1639 – 14 December 1676) was the eldest son of Mughal emperor Aurangzeb and his second wife Nawab Bai. His younger brother Muazzam later became Emperor as Bahadur Shah I in 1707. Life In April 1656, Muhammad Sultan was appointed Heir Apparent by his father-in-law Abdullah Qutb Shah, Sultan of Golconda and Hyderabad. When the succession war of the Mughal Empire began in 1657, he joined his father-in-law Shah Shuja, and was appointed Chief-in-Commander and Principal Counsellor in 1659. He rejoined his father on 20 February 1660, and was imprisoned at Salimgarh Fort in Delhi, 8 May 1660. On the orders of his father Emperor Aurangzeb, he was transferred to Gwalior Fort and imprisoned there from January 1661 to December 1672. He died on 14 December 1676, in confinement at Salimgarh Fort in Delhi. Marriages In 1656, during the siege of Golconda negotiations for peace were carried out between Auran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jizya
Jizya (), or jizyah, is a type of taxation levied on non-Muslim subjects of a state governed by Sharia, Islamic law. The Quran and hadiths mention jizya without specifying its rate or amount,Sabet, Amr (2006), ''The American Journal of Islamic Social Sciences'' 24:4, Oxford; pp. 99–100. and the application of jizya varied in the course of Islamic history. However, scholars largely agree that early Muslim rulers adapted some of the existing systems of taxation and modified them according to Islamic religious law.online Historically, the jizya tax has been understood in Islam as a fee for protection provided by the Muslim ruler to non-Muslims, for the exemption from military service for non-Muslims, for the permission to practice a non-Muslim faith with some communal autonomy in a Muslim state, and as material proof of the non-Muslims' allegiance to the Muslim state and its laws. The majority of Muslim jurists required adult, free, sane men, males among the dhimma community to pay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |