|
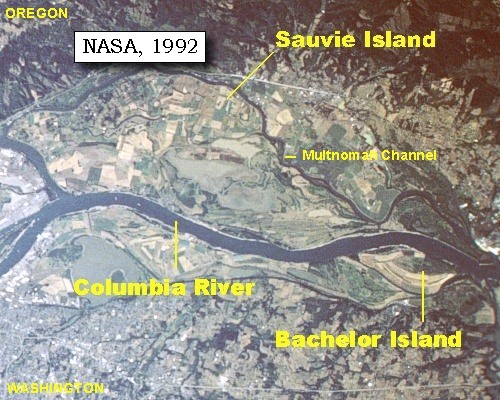
Sauvie Island
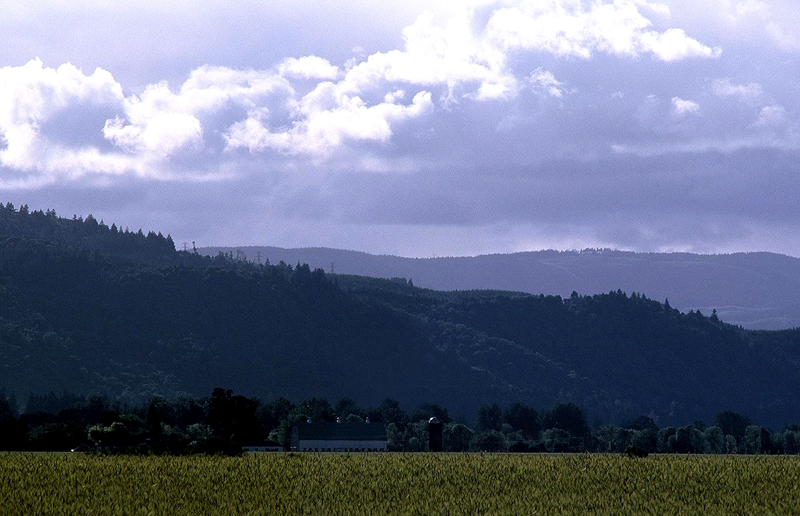
Sauvie Island is in the U.S. state of Oregon, originally named as Wapato Island or Wappatoo Island. It is the largest island along the Columbia River, at , and one of the largest river islands in the United States. It lies approximately northwest of downtown Portland, between the Columbia River to the east, the Multnomah Channel to the west, and the Willamette River to the south. A large portion of the island is designated as the Sauvie Island Wildlife Area. Sturgeon Lake, in the north central part of the island, is the most prominent water feature. The land area is , or . Most of the island is in Multnomah County, but the northern third is in Columbia County. The Wapato Bridge provides access across the Multnomah Channel from U.S. Route 30 and was completed in June 2008, replacing the first bridge to connect the island to the mainland which was opened on December 30, 1950. The island received the name "Sauvés Island" after Laurent Sauvé dit Laplante, a French-Canad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multnomah People
The Multnomah are a tribe of Chinookan people who live in the area of Portland, Oregon, in the United States. Multnomah villages were located throughout the Portland basin and on both sides of the Columbia River. The Multnomah speak a dialect of the Upper Chinookan language in the Oregon Penutian family. History The Multnomah people are a band of the Chinookan peoples who originally resided on and near Sauvie Island in Oregon. The Multnomah and the related Clackamas tribes lived in a series of villages along the river near the mouth of the Willamette River on the Columbia River (the Willamette was also called the "Multnomah" in the early 19th century). According to archaeologists, the villages in the area were home to approximately 3,400 people year-round, and as many as 8,000 during fishing and wappato-harvesting seasons (wappato is a marsh-grown plant like a potato or onion and a staple food). In 1830, a disease generally thought to have been malaria devastated the Multn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinookan Peoples
Chinookan peoples include several groups of Indigenous people of the Pacific Northwest in the United States who speak the Chinookan languages. Since at least 11,500 BCE, Chinookan peoples and their ancestors have resided along the upper and Middle Columbia River (Wimahl) ("Great River") from the river's gorge (near the present town of The Dalles, Oregon) downstream (west) to the river's mouth, and along adjacent portions of the coasts, from Tillamook Head of present-day Oregon in the south, north to Willapa Bay in southwest Washington. In 1805 the Lewis and Clark Expedition encountered the Chinook Tribe on the lower Columbia. The term "Chinook" also has a wider meaning in reference to the Chinook Jargon, which is based on Chinookan languages, in part, and so the term "Chinookan" was coined by linguists to distinguish the older language from its offspring, Chinuk Wawa. There are several theories about where the name "Chinook" came from. Some say it is a Chehalis word ''Tsi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as inactive or latent tuberculosis. A small proportion of latent infections progress to active disease that, if left untreated, can be fatal. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with hemoptysis, blood-containing sputum, mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms. Tuberculosis is Human-to-human transmission, spread from one person to the next Airborne disease, through the air when people who have active TB in their lungs cough, spit, speak, or sneeze. People with latent TB do not spread the disease. A latent infection is more likely to become active in those with weakened I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measles
Measles (probably from Middle Dutch or Middle High German ''masel(e)'', meaning "blemish, blood blister") is a highly contagious, Vaccine-preventable diseases, vaccine-preventable infectious disease caused by Measles morbillivirus, measles virus. Other names include ''morbilli'', ''rubeola'', ''9-day measles, red measles'', and ''English measles''. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, Rhinitis, runny nose, and conjunctivitis, inflamed eyes. Small white spots known as Koplik's spots, Koplik spots may form inside the mouth two or three days after the start of symptoms. A red, flat rash which usually starts on the face and then spreads to the rest of the body typically begins three to five days after the start of symptoms. Common complications include diarrhea (in 8% of cases), Otitis media, middle ear infection (7%), and pneumonia (6%). These occur i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms depend on the stage it presents: primary, secondary, latent syphilis, latent or tertiary. The primary stage classically presents with a single chancre (a firm, painless, non-itchy Ulcer_(dermatology), skin ulceration usually between 1 cm and 2 cm in diameter), though there may be multiple sores. In secondary syphilis, a diffuse rash occurs, which frequently involves the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. There may also be sores in the mouth or vagina. Latent syphilis has no symptoms and can last years. In tertiary syphilis, there are Gumma (pathology), gummas (soft, non-cancerous growths), neurological problems, or heart symptoms. Syphilis has been known as "The Great Imitator, the great imitator", because it may cause symptoms similar to many other diseases. Syphilis is most commonly spread through human sexual activi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by Variola virus (often called Smallpox virus), which belongs to the genus '' Orthopoxvirus''. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) certified the global eradication of the disease in 1980, making smallpox the only human disease to have been eradicated to date. The initial symptoms of the disease included fever and vomiting. This was followed by formation of ulcers in the mouth and a skin rash. Over a number of days, the skin rash turned into the characteristic fluid-filled blisters with a dent in the center. The bumps then scabbed over and fell off, leaving scars. The disease was transmitted from one person to another primarily through prolonged face-to-face contact with an infected person or rarely via contaminated objects. Prevention was achieved mainly through the smallpox vaccine. Once the disease had developed, certain antiviral medications could poten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native Americans In The United States
Native Americans (also called American Indians, First Americans, or Indigenous Americans) are the Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous peoples of the United States, particularly of the Contiguous United States, lower 48 states and Alaska. They may also include any Americans whose origins lie in any of the indigenous peoples of North or South America. The United States Census Bureau publishes data about "American Indians and Alaska Natives", whom it defines as anyone "having origins in any of the original peoples of North and South America ... and who maintains tribal affiliation or community attachment". The census does not, however, enumerate "Native Americans" as such, noting that the latter term can encompass a broader set of groups, e.g. Native Hawaiians, which it tabulates separately. The European colonization of the Americas from 1492 resulted in a Population history of Indigenous peoples of the Americas, precipitous decline in the size of the Native American ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broadleaf Arrowhead
''Sagittaria latifolia'' is a plant found in shallow wetlands and is sometimes known as broadleaf arrowhead, duck-potato, Indian potato, or wapato. This plant produces edible tubers that have traditionally been extensively used by Native Americans. Description ''Sagittaria latifolia'' is a variably sized perennial that may reach as much as in height, but is more typically . The plants often grow together in crowded colonies and spread by runners (stolons) at or just under the soil surface. In late summer the plants produce tubers that are twice as long as wide, each typically measuring in diameter. The plant produces rosettes of leaves and an inflorescence on a long rigid scape. The leaves are extremely variable, from in length and thin to wedge-shaped like those of '' S. cuneata''. Spongy and solid, the leaves have parallel venation meeting in the middle and the extremities. The inflorescence is a raceme about above water and composed of white flowers whorled by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lewis And Clark
Lewis may refer to: Names * Lewis (given name), including a list of people with the given name * Lewis (surname), including a list of people with the surname Music * Lewis (musician), Canadian singer * " Lewis (Mistreated)", a song by Radiohead from ''My Iron Lung'' Places * Lewis (crater), a crater on the far side of the Moon * Isle of Lewis, the northern part of Lewis and Harris, Western Isles, Scotland United States * Lewis, Colorado * Lewis, Indiana * Lewis, Iowa * Lewis, Kansas * Lewis Wharf, Boston, Massachusetts * Lewis, Missouri * Lewis, Essex County, New York * Lewis, Lewis County, New York * Lewis, North Carolina * Lewis, Vermont * Lewis, Wisconsin Ships * USS ''Lewis'' (1861), a sailing ship * USS ''Lewis'' (DE-535), a destroyer escort in commission from 1944 to 1946 Science * Lewis structure, a diagram of a molecule that shows the bonding between the atoms * Lewis acids and bases * Lewis antigen system, a human blood group system * Lewis number, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Hood, 1st Viscount Hood
Admiral (Royal Navy), Admiral Samuel Hood, 1st Viscount Hood (12 December 1724 – 27 January 1816) was a Royal Navy officer and politician. As a junior officer he saw action during the War of the Austrian Succession. While in temporary command of , Hood drove a French ship ashore in Audierne, Audierne Bay, and captured two privateers in 1757 during the Seven Years' War. He held senior command as North America and West Indies Station, Commander-in-Chief, North American Station and then as Leeward Islands Station, Commander-in-Chief, Leeward Islands Station. During the American Revolutionary War, Hood led the British fleet to victory at the Battle of the Mona Passage in April 1782. He went on to be Commander-in-Chief, Portsmouth, then First Sea Lord, First Naval Lord and, after briefly returning to the Portsmouth command, became Mediterranean Fleet, Commander-in-Chief, Mediterranean Fleet during the French Revolutionary Wars. His younger brother was Admiral Alexander Hood, 1st Vi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Hood
Mount Hood, also known as Wy'east, is an active stratovolcano in the Cascade Range and is a member of the Cascade Volcanic Arc. It was formed by a subduction zone on the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast and rests in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is located about east-southeast of Portland, Oregon, Portland, on the border between Clackamas County, Oregon, Clackamas and Hood River County, Oregon, Hood River counties, and forms part of the Mount Hood National Forest. Much of the mountain outside the ski areas is part of the Mount Hood Wilderness. With a summit elevation of 11,249 ft (3,429 m), it is the highest mountain in the U.S. state of Oregon and is the fourth highest in the Cascade Range. Ski areas on the mountain include Timberline Lodge ski area which offers the only year-round lift-served skiing in North America, Mount Hood Meadows, Mount Hood Skibowl, Summit Ski Area, and Cooper Spur ski area. Mt. Hood attracts an estimated 10,0 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oregon Historical Society
The Oregon Historical Society (OHS) is an organization that encourages and promotes the study and understanding of the history of the State of Oregon, within the broader context of U.S. history. Incorporated in 1898, the Society collects, preserves, and makes available materials of historical character and interest, and collaborates with other groups and individuals with similar aims. The society operates the Oregon History Center that includes the Oregon Historical Society Museum in downtown Portland. History The Society was organized on December 17, 1898, in Portland at the Portland Library Building.Corning, Howard M. ''Dictionary of Oregon History''. Binfords & Mort Publishing, 1956. Its mission, as expressed in the first volume of its '' Oregon Historical Quarterly'', was to "bring together in the most complete measure possible the data for the history of the commonwealth, and to stimulate the widest and highest use of them." The first president was Harvey W. Scott, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |