|
Saudi Arabian Military Industries
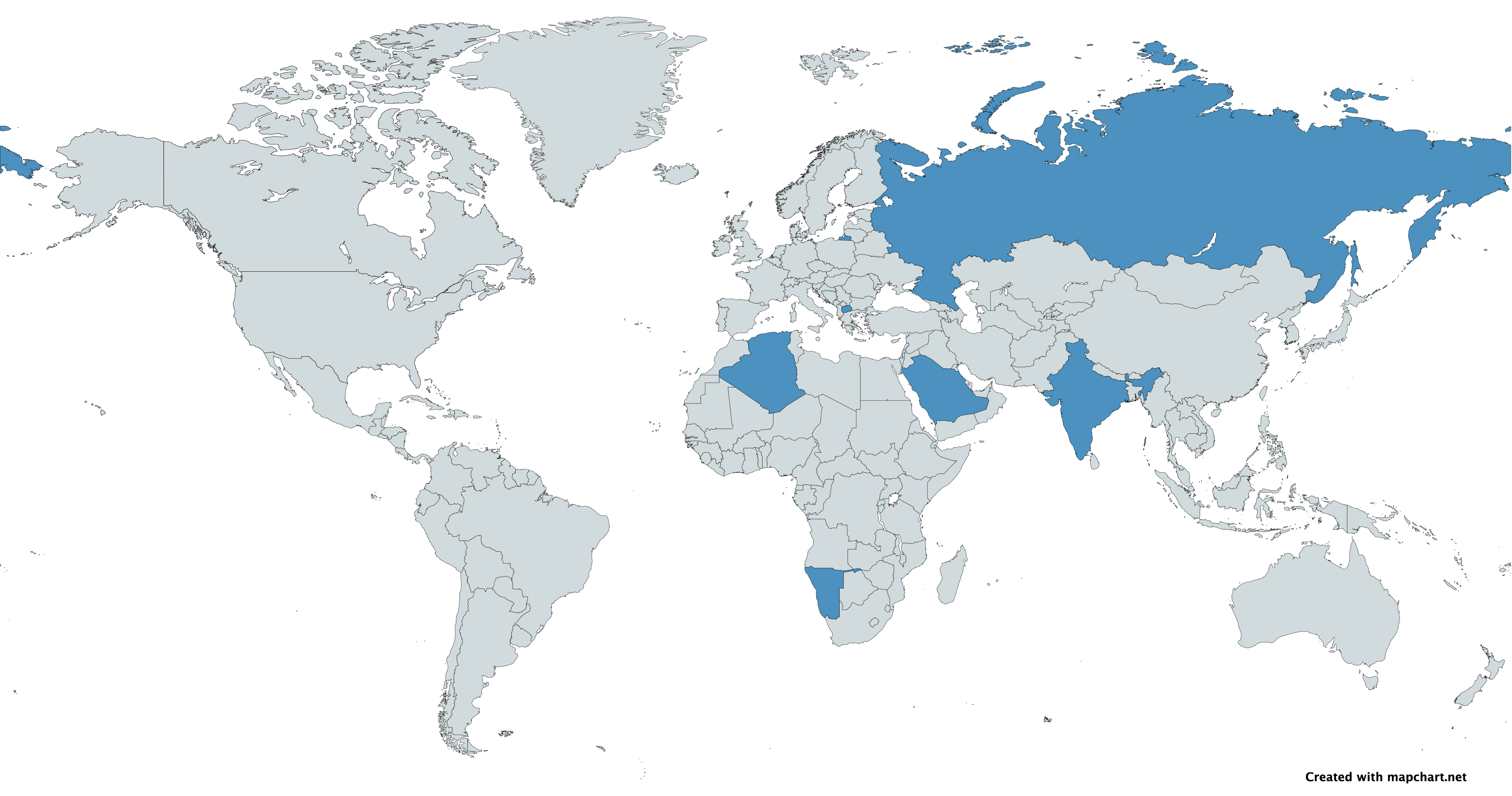
Saudi Arabian Military Industries (SAMI), (Arabic:الشركة السعودية للصناعات العسكرية), is a state-owned defense company based in Saudi Arabia. Activities SAMI was established to provide defense products and services in Saudi Arabia and to reduce the country’s reliance on imported defense products. The company operates across aerospace, electronics, defense systems, sea, and land systems. SAMI’s reported targets include the contribution of 14 billion riyals (US$3.7 billion) to the Saudi economy by 2030, 6 billion riyals (US$1.6 billion) investment in research and development and the creation of 40,000 jobs. Partnerships In May 2017, SAMI signed Memoranda of Understanding (MOUs) with defense contractors Boeing, Lockheed Martin, Raytheon and General Dynamics. In October 2017, SAMI signed a Memorandum of Understanding with Russia's Rosoboronexport to manufacture military equipment in Saudi Arabia. The agreement provides for the transfer of te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Privately Held Company
A privately held company (or simply a private company) is a company whose Stock, shares and related rights or obligations are not offered for public subscription or publicly negotiated in their respective listed markets. Instead, the Private equity, company's stock is offered, owned, traded or exchanged privately, also known as "over-the-counter (finance), over-the-counter". Related terms are unlisted organisation, unquoted company and private equity. Private companies are often less well-known than their public company, publicly traded counterparts but still have major importance in the world's economy. For example, in 2008, the 441 list of largest private non-governmental companies by revenue, largest private companies in the United States accounted for $1.8 trillion in revenues and employed 6.2 million people, according to ''Forbes''. In general, all companies that are not owned by the government are classified as private enterprises. This definition encompasses both publ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Dynamics
General Dynamics Corporation (GD) is an American publicly traded aerospace and defense corporation headquartered in Reston, Virginia. As of 2020, it was the fifth largest defense contractor in the world by arms sales and fifth largest in the United States by total sales. The company is a ''Fortune'' 100 company and was ranked in 2022. Formed in 1952 with the merger of submarine manufacturer Electric Boat and aircraft manufacturer Canadair, the corporation today consists of ten subsidiary companies with operations in 45 countries. The company's products include Gulfstream business jets, and nuclear-powered submarines, guided-missile destroyers, M1 Abrams tanks, and Stryker armored fighting vehicles. In 2024, General Dynamics had worldwide sales of $47.7 billion and a workforce of approximately 117,000 full-time employees. The current chairman and chief executive officer (CEO) is Phebe Novakovic. History Electric Boat General Dynamics traces its ancestry to John Philip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guided Bomb
A guided bomb (also known as a smart bomb, guided bomb unit, or GBU) is a precision-guided munition designed to achieve a smaller circular error probable (CEP). The creation of precision-guided munitions resulted in the retroactive renaming of older bombs as unguided bombs or "dumb bombs". Guidance Guided bombs carry a guidance system which is usually monitored and controlled from an external device. A guided bomb of a given weight must carry fewer explosives to accommodate the guidance mechanisms. Radio The Germans were first to introduce precision guided munitions (PGMs) in combat, using the 1,400-kg (3,100 lb) MCLOS-guidance Fritz X to successfully attack the Italian battleship ''Roma'' in September 1943. The closest Allied equivalents were the 1,000-lb (454 kg) AZON (AZimuth ONly), used in both Europe and the CBI Theater, and the US Navy's Bat, primarily used in the Pacific Theater of World War II which used autonomous, on-board radar guidance. In addi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counter-battery Radar
A counter-battery radar or weapon tracking radar is a radar system that detects artillery projectiles fired by one or more guns, howitzers, Mortar (weapon), mortars or rocket launchers and, from their trajectories, locates the position on the ground of the weapon that fired it. Such radars are a subclass of the wider class of target acquisition radars. Early counter-battery radars were generally used against mortars, whose lofted trajectories were highly symmetrical and allowed easy calculation of the launcher's location. Starting in the 1970s, digital computers with improved calculation capabilities allowed more complex trajectories of long-range artillery to also be determined. Normally, these radars would be attached to friendly artillery units or their support units, allowing them to quickly arrange counter-battery fire. With the aid of modern communications systems, the information from a single radar can be rapidly disseminated over long distances. This allows the radar t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Cockerill (company)
John Cockerill, formerly Cockerill Maintenance & Ingénierie (CMI), is a mechanical engineering group headquartered in Seraing, Belgium. It produces machinery for steel plants, industrial heat recovery equipment and boilers, as well as shunting locomotives and military equipment. History In 1817, an iron foundry was established in Seraing by John Cockerill (industrialist), John Cockerill and his brother, James Cockerill, Charles James Cockerill. As well as creating an iron works, John Cockerill also began machine-building activities, following in the footsteps of his father, William Cockerill, who had made his fortune constructing machines for the textile industry in the Liège Province, Liège region. In 1825, the enterprise became known as John Cockerill & Cie. The company produced the primary industrial machinery of the day – steam engines, blast furnace blowers, etc. In 1835, the company produced the first Belgian steam locomotive, ''Le Belge (locomotive), Le Belge'', begi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thales Group
Thales S.A., Trade name, trading as Thales Group (), is a French multinational corporation, multinational aerospace and defence industry, defence corporation specializing in electronics. It designs, develops and manufactures a wide variety of aerospace and military systems, devices and equipment but also operates in the computer security, cybersecurity and formerly civil ground transportation sectors. The company is headquartered in Paris' business district, La Défense, and its stock is listed on Euronext Paris. Founded as Thomson-CSF in 1968, the group was rebranded ''Thales'' (named after the Greek philosopher Thales , pronounced as in French language, French) in 2000 due to the company's desire to simplify and improve the group's brand. Thales is partially owned by the Agence des participations de l'État, French state and operates in more than 68 countries. In 2023, the company generated €18,42 billion in revenue and was the 17th largest defence contractor in the world, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jane's Defence Weekly
''Jane's Defence Weekly'' (abbreviated as ''JDW'') is a weekly magazine reporting on military and corporate affairs, edited by Peter Felstead. It is one of a number of military-related publications named after John F. T. Jane, an Englishman who first published '' Jane's All the World's Fighting Ships'' in 1898. It is a unit of Janes Information Services. The magazine is frequently cited in publications worldwide. History ''Jane's Defence Weekly'' was established in 1984 replacing the now-defunct '' Jane's Defence Review''. The latter was started in 1978 and was published on a monthly basis. Award winning international journalist Clifford Beal is a former editor of the magazine. Samuel Loring Morison In 1984, only months after the magazine was established, ''Jane's Defence Weekly'' gained worldwide attention after printing several images from an American spy satellite of the Nikolaiev 444 shipyard in the Black Sea The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Medite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AK-103
The AK-103 is an assault rifle designed by Russian small arms designer Mikhail Kalashnikov. History The AK-103 was officially offered for export on March 13, 1993. Design details It is an AK-100 derivative of the AK-74M that is chambered for the 7.62x39mm M43 cartridge, similar to the AKM. The AK-103 can be fitted with a variety of sights, including night vision and telescopic sights, plus a knife-bayonet or a grenade launcher like the GP-34. Newer versions can fit Picatinny rails, allowing more accessories to be mounted. The AK-103 uses plastic components where possible instead of wood or metal, with such components being the pistol grip On a firearm or other tools, a pistol grip is a distinctly protruded handle underneath the main mechanism, to be held by the user's hand at a more vertical (and thus more ergonomic) angle, similar to how one would hold a conventional pistol. ..., handguards, folding stock and depending on the type, the magazine. Protectiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AGS-30
The AGS-30 is a Russian automatic grenade launcher currently in production in Russia and in service with the Russian armed forces. Description Designed on the basis of AGS-17, the AGS-30 provides better mobility, longer range and better accuracy during firing. Significantly lighter than its previous version, the AGS-30 weighs 30 kg loaded, meaning it can be carried by one person. Using a specially designed GPD-30 grenade, the AGS-30 can engage targets at 2100m. Recoil is lessened with a smoother grenade ejection mechanism. An adjustable SAG-30 tripod mount (GRAU index 6P17) is also included. Development After the success of the AGS-17 in Afghanistan, the KBP Instrument Design Bureau began work on a new grenade launcher. The Russian army needed a weapon that could easily flush militants out of their fortified building hideouts. The new design proved to be effective, and it was officially adopted in 2002, and was later adopted by the Russian Interior Ministry Troops. Ammunit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TOS-1
TOS-1 Buratino (, Heavy Flamethrower System) is a Soviet 220 mm 30-barrel (original system, Object 634 or TOS-1M) or 24-barrel (Object 634B or TOS-1A Solntsepyok) multiple rocket launcher capable of using thermobaric warheads, mounted on a T-72 / T-90 tank chassis. TOS-1 was designed to attack enemy fortified positions and lightly armored vehicles and transports, particularly in open terrain. The system’s first combat tests took place in 1988 and 1989 in the Panjshir Valley during the Soviet–Afghan War. The TOS-1 was shown for the first time in public in 1999 in Omsk. TOS-1 is not assigned to the artillery units of the Russian Armed Forces but is found in Russian NBC Protection Troops. Development The idea of a heavy short-range MLRS to launch rockets equipped with incendiary and thermobaric warheads arose in the late 1970s. The combat system consisting of the combat vehicle, rockets, and loading vehicle was developed in early 1980s at KBTM in Omsk and was named T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |