|
Saturn IB-CE
The Saturn IB-CE rocket was a variant of the Saturn IB rocket studied in 1965 by Douglas. However unlike the Saturn IB the Saturn IB-CE was to be a three-stage rocket. The IB-CE used the same configuration as the Saturn IB for the first two stages however with the addition of a Centaur D/E rocket as the third stage. It was to be capable of delivering 22,000 kg to low Earth orbit and 5,590 kg into a translunar trajectory. Although this version never flew, a similar rocket, the Titan IIIE, built primarily for the U.S. Air Force, but launching a few NASA payloads, including the ''Viking'' and ''Voyager Voyager may refer to: Computing and communications * LG Voyager, a mobile phone model manufactured by LG Electronics * NCR Voyager, a computer platform produced by NCR Corporation * Voyager (computer worm), a computer worm affecting Oracle ...'' spacecraft, had the same equivalent thrust as the Saturn IB-CE. References {{Saturns Saturn IB ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturn IB
The Saturn IB (also known as the uprated Saturn I) was an American launch vehicle commissioned by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) for the Apollo program. It uprated the Saturn I by replacing the S-IV second stage (, 43,380,000 lb-sec total impulse), with the S-IVB (, 96,000,000 lb-sec total impulse). The S-IB first stage also increased the S-I baseline's thrust from to and propellant load by 3.1%. This increased the Saturn I's low Earth orbit payload capability from to , enough for early flight tests of a half-fueled Apollo command and service module (CSM) or a fully fueled Apollo Lunar Module (LM), before the larger Saturn V needed for lunar flight was ready. By sharing the S-IVB upper stage, the Saturn IB and Saturn V provided a common interface to the Apollo spacecraft. The only major difference was that the S-IVB on the Saturn V burned only part of its propellant to achieve Earth orbit, so it could be restarted for trans-lunar injectio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas Aircraft Company
The Douglas Aircraft Company was an American aerospace manufacturer, aerospace and military, defense company based in Southern California. Founded in 1921 by Donald Wills Douglas Sr., it merged with McDonnell Aircraft in 1967 to form McDonnell Douglas, where it operated as a division. History 1920s The company was founded as the Douglas Company by Donald Wills Douglas Sr. on July 22, 1921, in Santa Monica, California, following dissolution of the Davis-Douglas Company. An early claim to fame was the first aerial circumnavigation, first circumnavigation of the world by air in Douglas airplanes in 1924. In 1923, the U.S. Army Air Service was interested in carrying out a mission to circumnavigate the Earth for the first time by aircraft, a program called "World Flight". Donald Douglas proposed a modified Douglas DT to meet the Army's needs. The two-place, open cockpit DT biplane torpedo bomber had previously been produced for the United States Navy, U.S. Navy.Rumerman, Judy. "The D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centaur (rocket Stage)
The Centaur is a family of rocket propelled upper stages that has been in use since 1962. It is currently produced by U.S. launch service provider United Launch Alliance, with one main active version and one version under development. The diameter Common Centaur/Centaur III flies as the upper stage of the Atlas V launch vehicle, and the diameter Centaur V has been developed as the upper stage of ULA's new Vulcan rocket. Centaur was the first rocket stage to use liquid hydrogen (LH2) and liquid oxygen (LOX) propellants, a high-energy combination that is ideal for upper stages but has significant handling difficulties. Characteristics Common Centaur is built around stainless steel pressure stabilized balloon propellant tanks with thick walls. It can lift payloads of up to . The thin walls minimize the mass of the tanks, maximizing the stage's overall performance. A common bulkhead separates the LOX and LH2 tanks, further reducing the tank mass. It is made of two stainless ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
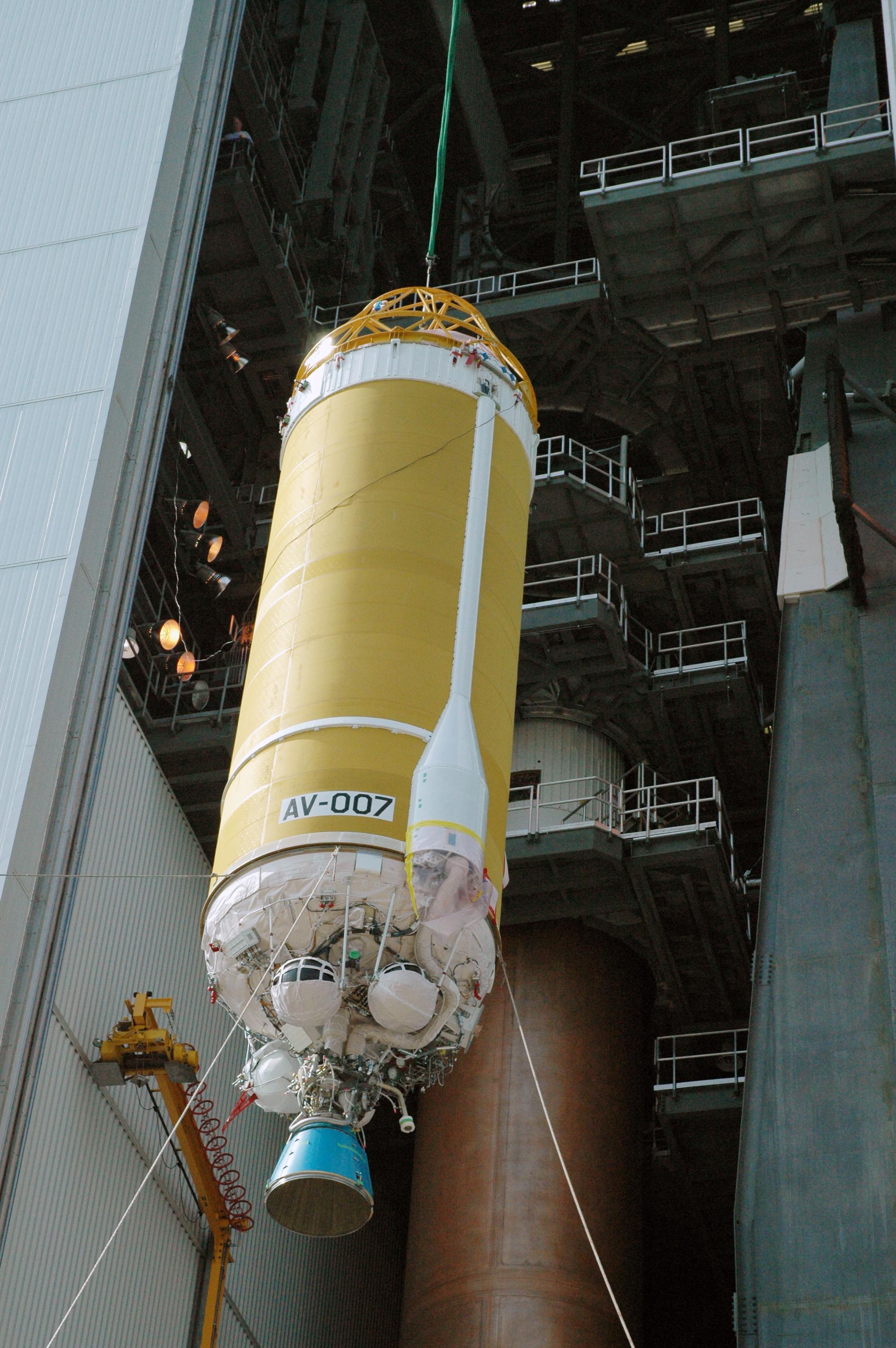
Titan IIIE
The Titan IIIE or Titan 3E, also known as the Titan III-Centaur, was an American expendable launch system. Launched seven times between 1974 and 1977, it enabled several high-profile NASA missions, including the Voyager and Viking planetary probes and the joint West Germany-U.S. Helios spacecraft. All seven launches were conducted from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Launch Complex 41 in Cape Canaveral, Florida. Development In the early 1960s, NASA's long-range plan was to continue using Atlas-Centaur until a reusable launch system or a nuclear-powered upper stage could be developed. To help fund the escalating Vietnam War and the new War on Poverty, Congress drastically reduced the funding of the civilian space program. In addition, further development of the reusable launch vehicle was postponed. NASA needed a launch vehicle more powerful than Atlas-Centaur to send heavier planetary probes like Viking and Voyager into space in the 1970s. So, NASA began in 1967 to consid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viking Program
The ''Viking'' program consisted of a pair of identical American space probes, ''Viking 1'' and ''Viking 2'' both launched in 1975, and landed on Mars in 1976. The mission effort began in 1968 and was managed by the NASA Langley Research Center.Soffen, G. A. (July–August 1978). "Mars and the Remarkable Viking Results." ''Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets''. 15 (4): 193-200. Each spacecraft was composed of two main parts: an orbiter spacecraft which photographed the surface of Mars from orbit, and a Lander (spacecraft), lander which studied the planet from the surface. The orbiters also served as communication relays for the landers once they touched down. The Viking program grew from NASA's earlier, even more ambitious, Voyager program (Mars), Voyager Mars program, which was not related to the successful Voyager program, Voyager deep space probes of the late 1970s. ''Viking 1'' was launched on August 20, 1975, and the second craft, ''Viking 2'', was launched on September 9, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
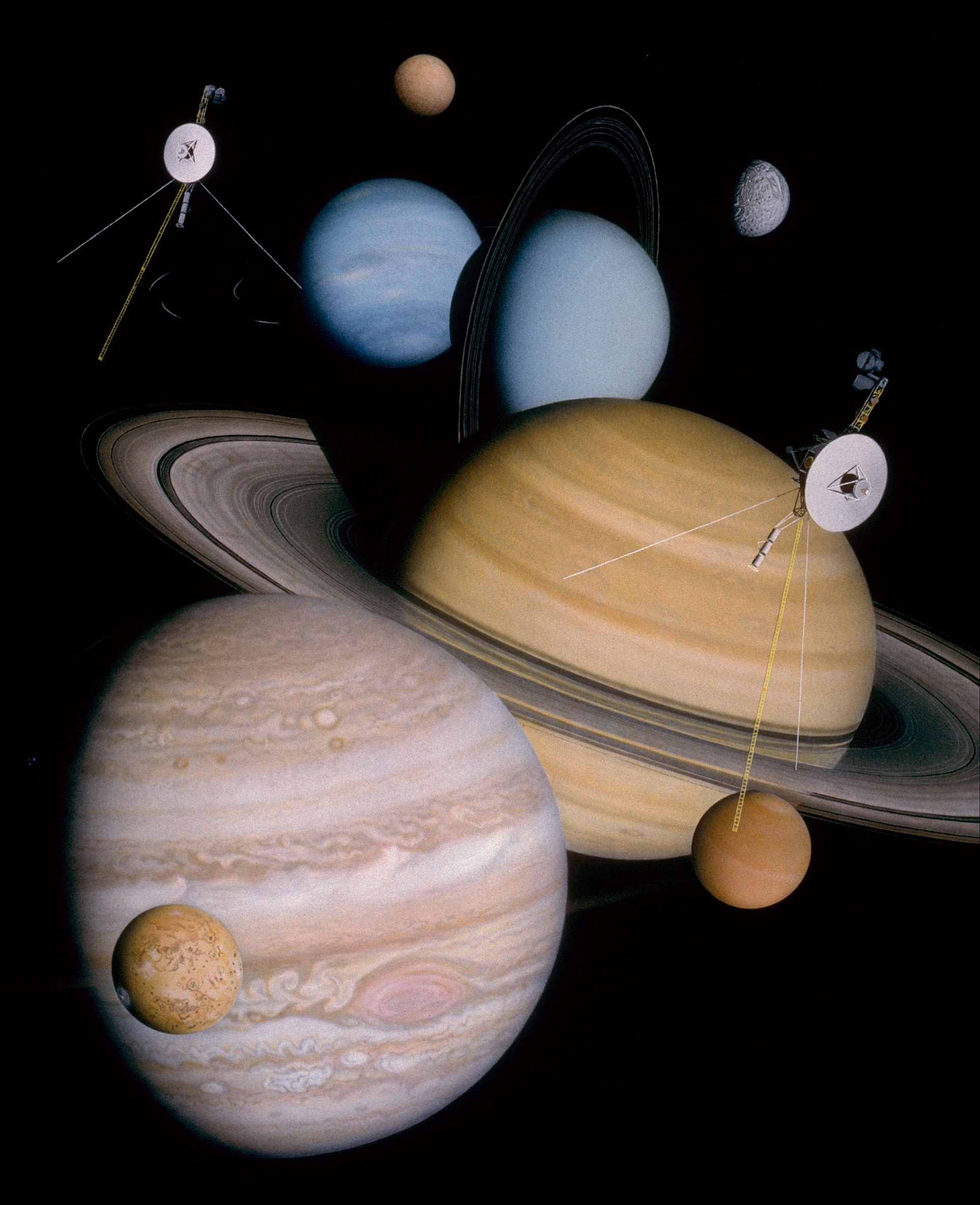
Voyager Program
The Voyager program is an American scientific program that employs two interstellar probes, ''Voyager 1'' and ''Voyager 2''. They were launched in 1977 to take advantage of a favorable planetary alignment to explore the two gas giants Jupiter and Saturn and potentially also the ice giants, Uranus and Neptune—to Flyby (spaceflight), fly near them while collecting data for transmission back to Earth. After ''Voyager 1'' successfully completed its flyby of Saturn and its moon Titan (moon), Titan, it was decided to send ''Voyager 2'' on flybys of Uranus and Neptune. After the planetary flybys were complete, decisions were made to keep the probes in operation to explore Outer space, interstellar space and the outer regions of the Solar System. On 25 August 2012, data from ''Voyager 1'' indicated that it had entered interstellar space. On 5 November 2019, data from ''Voyager 2'' indicated that it also had entered interstellar space. On 4 November 2019, scientists reported that on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |