|
Sati Sulochana
''Sati Sulochana'' () is a 1934 Indian Kannada-language film directed by Y. V. Rao. The film was released on 3 March 1934 and is the first talkie film in Kannada language.Dr.Raj's impact on Kannada cinema Rediff.com It is also the first film to be screened in the erstwhile . It is a . Though initially it was believed that the movie had 18 songs, a gramophone record jacket found in private archives showed that the movie had as many as 30 songs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinema Of Andhra Pradesh
Telugu cinema, also known as Tollywood, is the segment of Indian cinema dedicated to the production of motion pictures in the Telugu language, widely spoken in the states of Andhra Pradesh and Telangana. Based in Film Nagar, Hyderabad, Telugu cinema is the second largest film industry in India by box-office revenue as of 2023, following Bollywood. Telugu films sold 23.3 crore (233 million) tickets in 2022, the highest among all Indian film industries. As of 2023, Andhra Pradesh has the highest number of movie screens in India. Since 1909, filmmaker Raghupathi Venkaiah Naidu was involved in producing short films and exhibiting them in different regions of South Asia. He established the first Indian-owned cinema halls in South India. In 1921, he produced the silent film, '' Bhishma Pratigna'', generally considered to be the first Telugu feature film. As the first Telugu film producer and exhibitor, Naidu is regarded as the 'Father of Telugu cinema'. The first Telugu talkie film ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rama
Rama (; , , ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the seventh and one of the most popular avatars of Vishnu. In Rama-centric Hindu traditions, he is considered the Supreme Being. Also considered as the ideal man (''maryāda'' ''puruṣottama''), Rama is the male protagonist of the Hindu epic '' Ramayana''. His birth is celebrated every year on Rama Navami, which falls on the ninth day of the bright half ( Shukla Paksha) of the lunar cycle of Chaitra (March–April), the first month in the Hindu calendar. According to the ''Ramayana'', Rama was born to Dasaratha and his first wife Kausalya in Ayodhya, the capital of the Kingdom of Kosala. His siblings included Lakshmana, Bharata, and Shatrughna. He married Sita. Born in a royal family, Rama's life is described in the Hindu texts as one challenged by unexpected changes, such as an exile into impoverished and difficult circumstances, and challenges of ethical questions and moral dilemmas. The most not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kolhapur
Kolhapur () is a city on the banks of the Panchganga River in the southern part of the Indian state of Maharashtra. Kolhapur is one of the most significant cities in South Maharashtra and has been a hub of historical, religious, and cultural activities for centuries. It is famous for its unique food culture, including its signature Kolhapuri cuisine. The city is situated in the western part of Maharashtra and is often referred to as "Dakshin Kashi" or "Mahateerth". It boasts a rich history, which has given it various other names, including Kollagiri, Kolladigiripattan and Kollpur, all meaning "valley" Around 2 CE Kolhapur's name was 'Kuntal'. Kolhapur is known as Dakshin Kashi''' or Kashi of the South because of its spiritual history and the antiquity of its shrine Mahalaxmi, better known as Ambabai. The region is known for the production of the famous handcrafted and braided leather slippers called Kolhapuri chappal, which received the Geographical Indication designatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jalore District
Jalore District is a district of Rajasthan States and territories of India, state in western India. The city of Jalore is the administrative headquarters of the district. The district has an area of (3.11 percent of Rajasthan's area), and a population of 1,828,730 (2011 census), with a population density of 136 persons per square kilometre. History In ancient times Jalore was known as Jabalipura - named after the Hindu saint Jabali. The town was also known as Suvarngiri or Songir, the Golden Mount, on which the fort stands. It was a flourishing town in the 8th century, and according to some historical sources, in the 8th-9th centuries, one branch of the Pratihara dynasty, pratihara empire ruled at Jablipur (Jalore). Raja Man Pratihara dynasty, Pratihar was ruling Bhinmal in Jalore when Paramara dynasty, Parmara Emperor Vakpati Munja (972-990 CE) invaded the region — after this conquest he divided these conquered territories among his Parmara princes - his son Aranyaraj Parmar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahor
Ahore or Ahor (Aavar) is a city in the Jalore District of the Indian state of Rajasthan. Strategically located at intersection of Sanderao-Jalore and Jalore-Jodhpur Highway and is a great commercial hub catering to almost all nearby villages and towns. Nearby Railway Stations are Jalore (18 km), Falna (50 km) and Jodhpur (120 km) and Jodhpur is the nearest Airport. Ahore Ahore was a Thikana of 10 villages of Rathore sub clan Champawat Rajputs. Thakur Jagannath Singh, the first Thakur of Ahore, was granted the Ahor estate in 1706 by Maharaja Ajit Singh of Marwar following the Battle of Dunada. Geography It is located 18 KM east of Jalore on NH 325 between Jalore and Sanderao. It is the headquarters of the tehsil of the same name. This town can be found at the intersection that connects Jalore, the District Headquarters, and Jodhpur, a major city. The Ahor tehsil has 41 Gram Panchayats. The Gram Panchayats are: Agawari, Ahore, Aipura, Ajeetpura, Bala, Bankli, Badanwar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
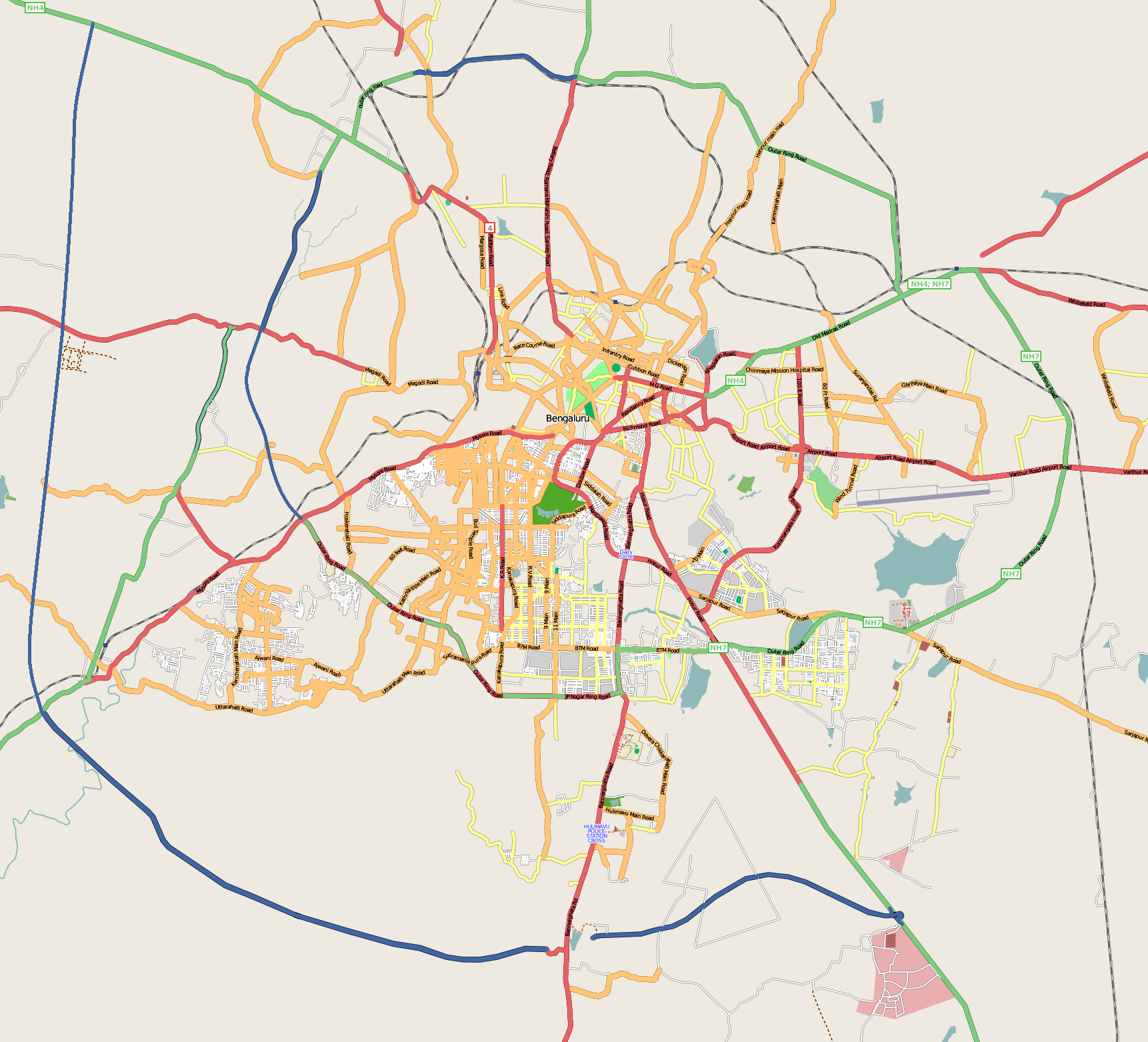
Bangalore
Bengaluru, also known as Bangalore (List of renamed places in India#Karnataka, its official name until 1 November 2014), is the Capital city, capital and largest city of the southern States and union territories of India, Indian state of Karnataka. As per the 2011 Census of India, 2011 census, the city had a population of 8.4 million, making it the List of cities in India by population, third most populous city in India and the most populous in South India. The Bengaluru metropolitan area had a population of around 8.5 million, making it the List of million-plus urban agglomerations in India, fifth most populous urban agglomeration in the country. It is located near the center of the Deccan Plateau, at a height of above sea level. The city is known as India's "Garden City", due to its parks and greenery. Archaeological artifacts indicate that the human settlement in the region happened as early as 4000 Common Era, BCE. The first mention of the name "Bengalooru" is from an ol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marwaris
The Marwari or Marwadi (Devanagari: मारवाड़ी) are an Indo-Aryan ethno-linguistic group that originate from the Marwar region of Rajasthan, India. Their language, also called Marwari, comes under the umbrella of Rajasthani languages, which is part of the Western Zone of Indo-Aryan languages. Apart from India, they have sizeable presence in the neighbouring countries of Pakistan and Nepal. Etymology The term ''Marwari'' once referred to the area encompassed by the former princely state of Marwar, also called the Jodhpur region of southwest Rajasthan in India. It formed from the two constituent words, Maru (region of Thar desert) and Wadi (enclosure), effectively indicating the western part of modern day Rajasthan. It has evolved to be a designation for the Rajasthani people in general but it is used particularly with reference to certain jātis that fall within the Bania community. The most prominent among these communities are the Agrawals, Khandelwal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indubala
Indubala (1898 – 30 November 1984), sometimes credited as Miss Indubala, Indubālā Debī, or Indubala Devi, was a Bengali singer and actress. She received the Sangeet Natak Akademi Award in 1975. Early life Indubala was born in Amritsar, the daughter of Motilal Bose and Rajabala. Her parents were with the Great Bengal Circus, and separated soon after her birth. She lived with her mother in Calcutta. She trained as a singer in Calcutta with several teachers, including Gauhar Jaan, Kamal Dasgupta, and Kazi Nazrul Islam. Career Indubala is considered one of the great Bengali women singers. She made her first of hundreds of recordings for Gramaphone Records in 1915 or 1916. She performed on stage with her mother's company, the Rambagan Female Kali Theatre, and at the Star Theatre. She sang on All India Radio beginning in 1927, on the broadcaster's second day on the air, and regularly through the 1930s. In 1936 she was appointed court musician to the Maharaja of Mysore. Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Narada
Narada (, ), or Narada Muni, is a sage-divinity, famous in Hinduism, Hindu traditions as a travelling musician and storyteller, who carries news and enlightening wisdom. He is one of the Manasputra, mind-created children of Brahma, the creator god. He appears in a number of Hindu texts, notably the Mahabharata, telling Yudhishthira the story of Prahlada, Prahalada, and he also appears in the Ramayana and the Puranas. A common theme in Vaishnavism is the accompaniment of a number of deities such as Narada to offer aid to Vishnu upon his descent to earth to combat the forces of evil, or to enjoy a close view of epochal events. He is also referred to as ''Rishiraja'', meaning the king of all sages. He was gifted with the boon of knowledge regarding the past, present, and the future. Hinduism In Indian texts, Narada travels to distant worlds and realms (Sanskrit: ''lokas''). He is depicted carrying a khartal (musical instrument) and the veena, and is generally regarded as one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandodari
Mandodari (, , lit. "soft-bellied";) was the queen consort of Ravana, the king of Lanka, according to the Hindu epic ''Ramayana''. The ''Ramayana'' describes her as beautiful, pious, and righteous. She is extolled as one of the ''Panchakanya'', the recital of whose names is believed to dispel sin. Mandodari was the daughter of Mayasura, the King of the Asuras (demons), and the ''apsara'' (celestial nymphs) Hema. She marries Ravana and bears three sons: Meghanada ( Indrajit), Atikaya and Akshayakumara. Despite her husband's faults, Mandodari loves him and advises him to follow the path of righteousness. She repeatedly advises Ravana to return Sita to Rama, but her advice falls on deaf ears. Her love and loyalty to Rāvana are praised in the ''Rāmāyana''. In a version of Ramayana, Hanuman tricks her into disclosing the location of a magical arrow which Rama uses to kill Ravana. Many versions of Ramayana state that after Ravana's death, Vibhishana—Ravana's younger brother ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sati (practice)
Sati or suttee is a practice, a chiefly historical one, Quote: Between 1943 and 1987, some thirty women in Rajasthan (twenty-eight, according to official statistics) immolated themselves on their husband's funeral pyre. This figure probably falls short of the actual number. (p. 182) in which a Hindu widow burns alive on her deceased husband's funeral pyre, the death by burning entered into voluntarily, by coercion, or by a perception of the lack of satisfactory options for continuing to live. Although it is debated whether it received scriptural mention in early Hinduism, it has been linked to related Hindu practices in the Indo-Aryan-speaking regions of India, which have diminished the rights of women, especially those to the inheritance of property. A cold form of sati, or the neglect and casting out of Hindu widows, has been prevalent from ancient times. Quote: Sati is a particularly relevant social practice because it is often used as a means to prevent inheritance of pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanjeevani (plant)
Sanjivani () or the Mrtasanjivani () is a medicinal herb featured in the Hindu epic Ramayana. Literature The herb is mentioned in the Ramayana when Ravana's son, Indrajit, hurls a powerful weapon at Lakshmana. Lakshmana is badly wounded, and is killed by this attack. In the Kamba Ramayanam, Sushen Vaidh instructs Hanuman to fetch the sanjeevani herb by flying to the northern side of Mount Meru, where he would find the Nīla-mahāgiri, the great blue mountain, beyond which he would find the Ṛṣabhādri, the ox-shaped mountain, with two peaks. This mountain is described to bear four medicinal herbs, including sanjeevani. Unable to identify the herb, and due to time being of the essence, Hanuman lifts the entire mountain and carries it to the dead Lakshmana, who is healed and revived after its application. The mountain that bears the sanjeevani is also called the Oshadhiparvata. Identification The mountain of herbs is identified as the Valley of Flowers near Badri in Utt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |