|
Sangeeta N. Bhatia
Sangeeta N. Bhatia (born 1968) is an American biological engineer and the John J. and Dorothy Wilson Professor at MIT’s Institute for Medical Engineering and Science and Electrical Engineering and Computer Science (EECS) at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Bhatia's research investigates applications of micro- and nano-technology for tissue repair and regeneration. She applies ideas from computer technology and engineering to the design of miniaturized biomedical tools for the study and treatment of diseases, in particular liver disease, hepatitis, malaria and cancer. In 2003, she was named by the ''MIT Technology Review'' as one of the top 100 innovators in the world under the age of 35. She was also named a "Scientist to Watch" by '' The Scientist'' in 2006. She has received multiple awards and has been elected to the National Academy of Sciences, the National Academy of Engineering, the National Academy of Medic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is the manipulation of matter with at least one dimension sized from 1 to 100 nanometers (nm). At this scale, commonly known as the nanoscale, surface area and quantum mechanical effects become important in describing properties of matter. This definition of nanotechnology includes all types of research and technologies that deal with these special properties. It is common to see the plural form "nanotechnologies" as well as "nanoscale technologies" to refer to research and applications whose common trait is scale. An earlier understanding of nanotechnology referred to the particular technological goal of precisely manipulating atoms and molecules for fabricating macroscale products, now referred to as molecular nanotechnology. Nanotechnology defined by scale includes fields of science such as surface science, organic chemistry, molecular biology, semiconductor physics, energy storage, engineering, microfabrication, and molecular engineering. The associated rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malaria
Malaria is a Mosquito-borne disease, mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and ''Anopheles'' mosquitoes. Human malaria causes Signs and symptoms, symptoms that typically include fever, Fatigue (medical), fatigue, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, Epileptic seizure, seizures, coma, or death. Symptoms usually begin 10 to 15 days after being bitten by an infected ''Anopheles'' mosquito. If not properly treated, people may have recurrences of the disease months later. In those who have recently survived an infection, reinfection usually causes milder symptoms. This partial Immunity (medical), resistance disappears over months to years if the person has no continuing exposure to malaria. The mosquitoes themselves are harmed by malaria, causing reduced lifespans in those infected by it. Malaria is caused by protozoa, single-celled microorganisms of the genus ''Plasmodium''. It is spread exclusively through bites of infected female ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Organs
An artificial organ is a human-made organ device or Tissue (biology), tissue that is Implant (medicine), implanted or integrated into a humaninterfacing with living tissueto replace a natural Organ (anatomy), organ, to duplicate or augment a specific function or functions so the patient may return to a normal life as soon as possible. The replaced function does not have to be related to life support, but it often is. For example, replacement bones and joints, such as those found in hip replacements, could also be considered artificial organs. Implied by definition, is that the device must not be continuously tethered to a stationary power supply or other stationary resources such as filters or chemical processing units. (Periodic rapid recharging of batteries, refilling of chemicals, and/or cleaning/replacing of filters would exclude a device from being called an artificial organ.) Thus, a Kidney dialysis, dialysis machine, while a very successful and critically important life sup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Broadcasting Service
The Public Broadcasting Service (PBS) is an American public broadcaster and non-commercial, free-to-air television network based in Arlington, Virginia Arlington County, or simply Arlington, is a County (United States), county in the U.S. state of Virginia. The county is located in Northern Virginia on the southwestern bank of the Potomac River directly across from Washington, D.C., the nati .... PBS is a publicly funded nonprofit organization and the most prominent provider of educational television, educational programs to public television stations in the United States, distributing shows such as ''Nature (TV program), Nature'', ''Nova (American TV program), Nova'', ''Frontline (American TV program), Frontline'', ''PBS News Hour'', ''Masterpiece (TV series), Masterpiece'', ''Mister Rogers' Neighborhood'', ''Sesame Street'', ''Barney & Friends'', ''Arthur (TV series), ''Arthur'''' and ''American Experience''. Certain stations also provide spillover service to Canada. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrasound Machine
Medical ultrasound includes Medical diagnosis, diagnostic techniques (mainly medical imaging, imaging) using ultrasound, as well as therapeutic ultrasound, therapeutic applications of ultrasound. In diagnosis, it is used to create an image of internal body structures such as tendons, muscles, joints, blood vessels, and internal organs, to measure some characteristics (e.g., distances and velocities) or to generate an informative audible sound. The usage of ultrasound to produce visual images for medicine is called medical ultrasonography or simply sonography, or echography. The practice of examining pregnant women using ultrasound is called obstetric ultrasonography, and was an early development of clinical ultrasonography. The machine used is called an ultrasound machine, a sonograph or an echograph. The visual image formed using this technique is called an ultrasonogram, a sonogram or an echogram. Ultrasound is composed of sound waves with frequency, frequencies greater than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernhard Palsson
Bernhard Örn Pálsson is the Galletti Professor of Bioengineering and an adjunct professor of Medicine at the University of California, San Diego.http://gcrg.ucsd.edu/Researchers/Palsson Bernhard Palsson at USCD Education Palsson received his PhD from the University of Wisconsin–Madison in 1984 under the supervision of Edwin N. Lightfoot. Research Upon graduation Palsson joined the chemical engineering faculty at University of Michigan where he served as a professor until 1995. In 1995, he joined the department of Bioengineering at University of California, San Diego and was named the Galetti Chair of Bioengineering in 2004. In 2005 he became a faculty member of Keio University. Palsson has authored or co-authored over 300 peer-reviewed scientific articles and is the holder of over 35 patents. His research interests include metabolic network modelling, systems biology, tissue engineering and cell culture, the development of analysis procedures for genome-scale models, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
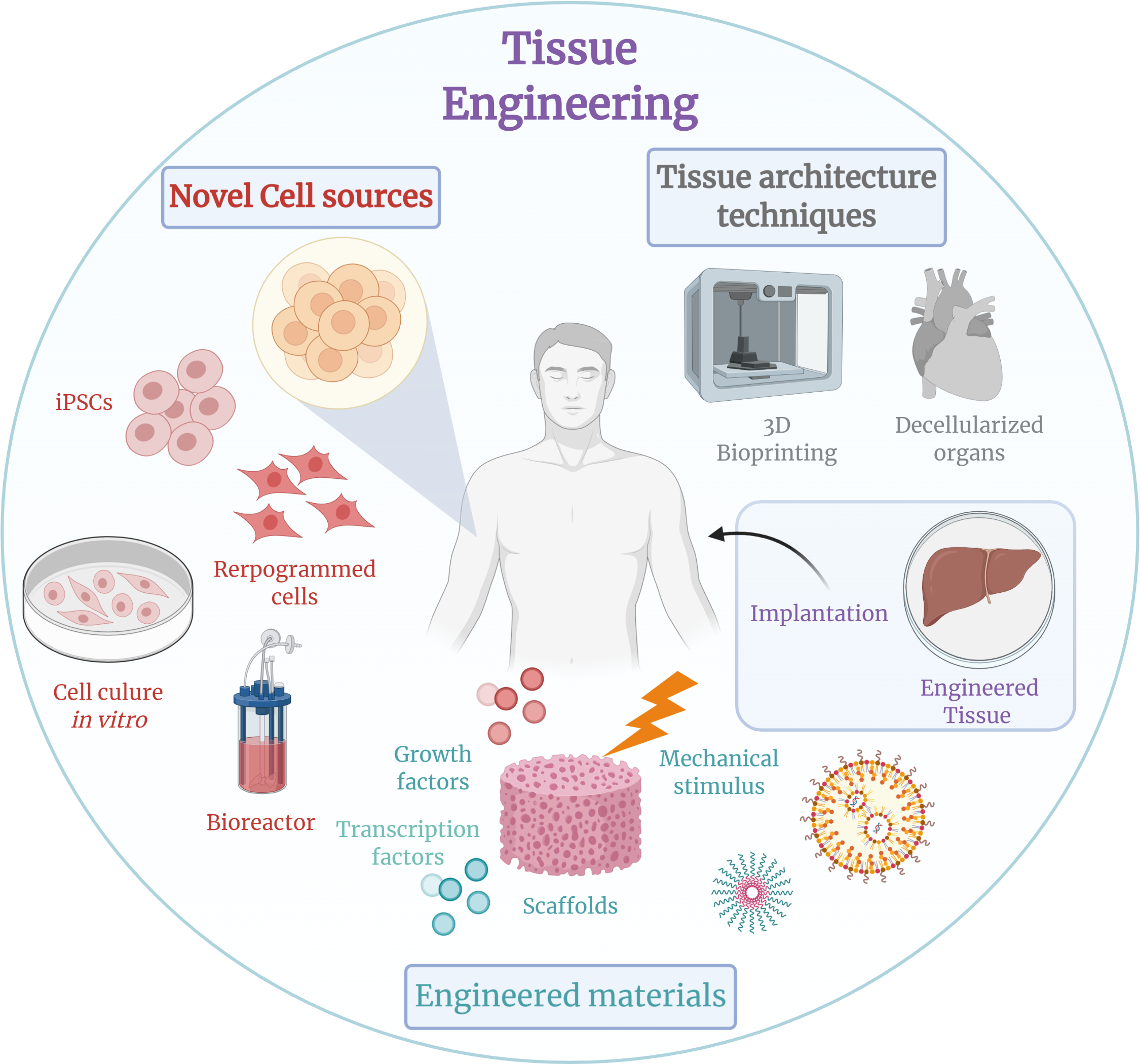
Tissue Engineering
Tissue engineering is a biomedical engineering discipline that uses a combination of cells, engineering, materials methods, and suitable biochemical and physicochemical factors to restore, maintain, improve, or replace different types of biological tissues. Tissue engineering often involves the use of cells placed on tissue scaffolds in the formation of new viable tissue for a medical purpose, but is not limited to applications involving cells and tissue scaffolds. While it was once categorized as a sub-field of biomaterials, having grown in scope and importance, it can be considered as a field of its own. While most definitions of tissue engineering cover a broad range of applications, in practice, the term is closely associated with applications that repair or replace portions of or whole tissues (i.e. organs, bone, cartilage, blood vessels, bladder, skin, muscle etc.). Often, the tissues involved require certain mechanical and structural properties for proper functioning. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Academy Of Inventors
The National Academy of Inventors (NAI) is a US non-profit organization dedicated to encouraging inventors in academia, following the model of the National Academies of the United States. It was founded at the University of South Florida in 2010. Starting in 2012, the NAI has inducted 757 Fellows into the organization. Fellows must be named as an inventor on at least one US patent and are selected by the NAI Fellows Committee. The NAI also includes colleges and universities as institutional members, beginning with 9 such institutions in 2012; it now has over 200, including 30 outside the United States.. Since 2013, the National Academy of Inventors and the Intellectual Property Owners Association have released an annual report listing the top 100 universities by the number of US patents. The University of California has topped the list each year. The NAI has held a yearly national conference since 2011. In 2017, US Representative Dennis A. Ross Dennis Alan Ross (born ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Academy Of Medicine
The National Academy of Medicine (NAM), known as the Institute of Medicine (IoM) until 2015, is an American nonprofit, non-governmental organization. The National Academy of Medicine is a part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Sciences (NAS), National Academy of Engineering (NAE), and the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM). Operating outside the framework of the U.S. federal government, it relies on a volunteer workforce of scientists and other experts, operating under a formal peer-review system. As a national academy, the organization annually elects new members with the help of its current members; the election is based on the members' distinguished and continuing achievements in a relevant field as well as for their willingness to participate actively. History The institute was founded in 1970, under the congressional charter of the National Academy of Sciences as the Institu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Academy Of Engineering
The National Academy of Engineering (NAE) is an American Nonprofit organization, nonprofit, NGO, non-governmental organization. It is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine (NASEM), along with the National Academy of Sciences (NAS) and the National Academy of Medicine (NAM). The NAE operates engineering programs aimed at meeting national needs, encourages education and research, and recognizes the superior achievements of engineers. New members are annually elected by current members, based on their distinguished and continuing achievements in original research. The NAE is autonomous in its administration and in the selection of its members, sharing with the rest of the National Academies the role of advising the federal government. History The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine#History, National Academy of Sciences was created by an Act of Incorporation dated March 3, 1863, which was signed by then president of the United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Academy Of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, NGO, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the National Academy of Medicine (NAM). As a national academy, new members of the organization are elected annually by current members, based on their distinguished and continuing achievements in original research. Election to the National Academy is one of the highest honors in the scientific field in the United States. Member of the National Academy of Sciences, Members of the National Academy of Sciences serve ''pro bono'' as "advisers to the nation" on science, engineering, and medicine. The group holds a congressional charter under Title 36 of the United States Code. Congress legislated and President Abraham Lincoln signed an Act of Congress (1863) establishing the National Academy of Sciences as an independent, trusted nongovernmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |