|
San Pedro De Quemes Municipality
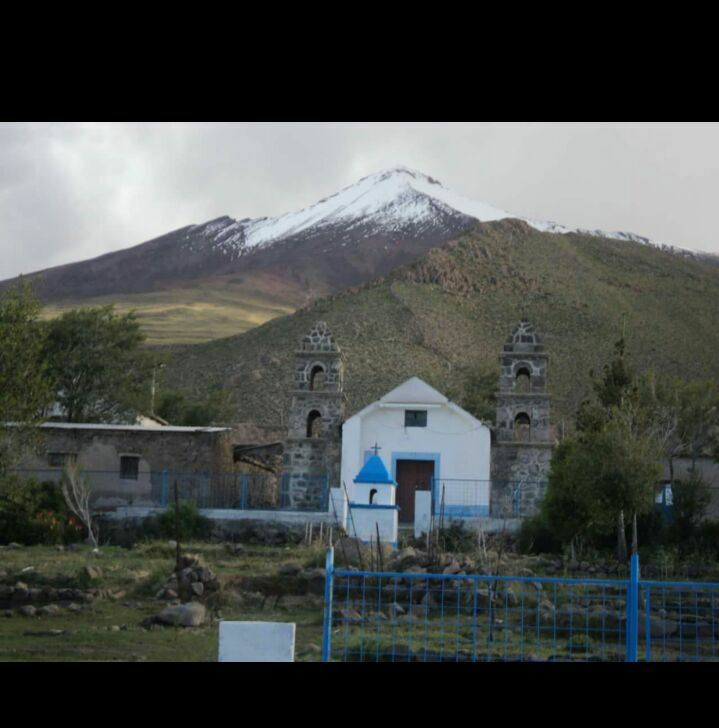
San Pedro de Quemes () is the second Municipalities of Bolivia, municipal section of the Nor Lípez Province in the Potosí Department in Bolivia. Its seat is San Pedro de Quemes. Geography The municipality lies at the Salar de Uyuni, Uyuni salt flat. Some of the highest mountains of the municipality are listed below: Many of the mountains and volcanoes are a natural border to Chile. Subdivision The municipality consists of the following cantons: * Cana - 44 inhabitants (''2001'') * Chiguana - 10 inhabitants * Pajancha - 52 inhabitants * Pelcoya Canton, Pelcoya - 135 inhabitants * San Pedro de Quemes Canton, San Pedro de Quemes- 574 inhabitants The people The people are mainly not Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous and 45,0% are citizens of Quechua people, Quechua descent.obd.descentralizacion.gov.bo/municipal/fichas/ (inactive) See also * Ch'iyar Quta, Nor Lípez, Ch'iyar Quta References External links San Pedro de Quemes Municipality: populatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
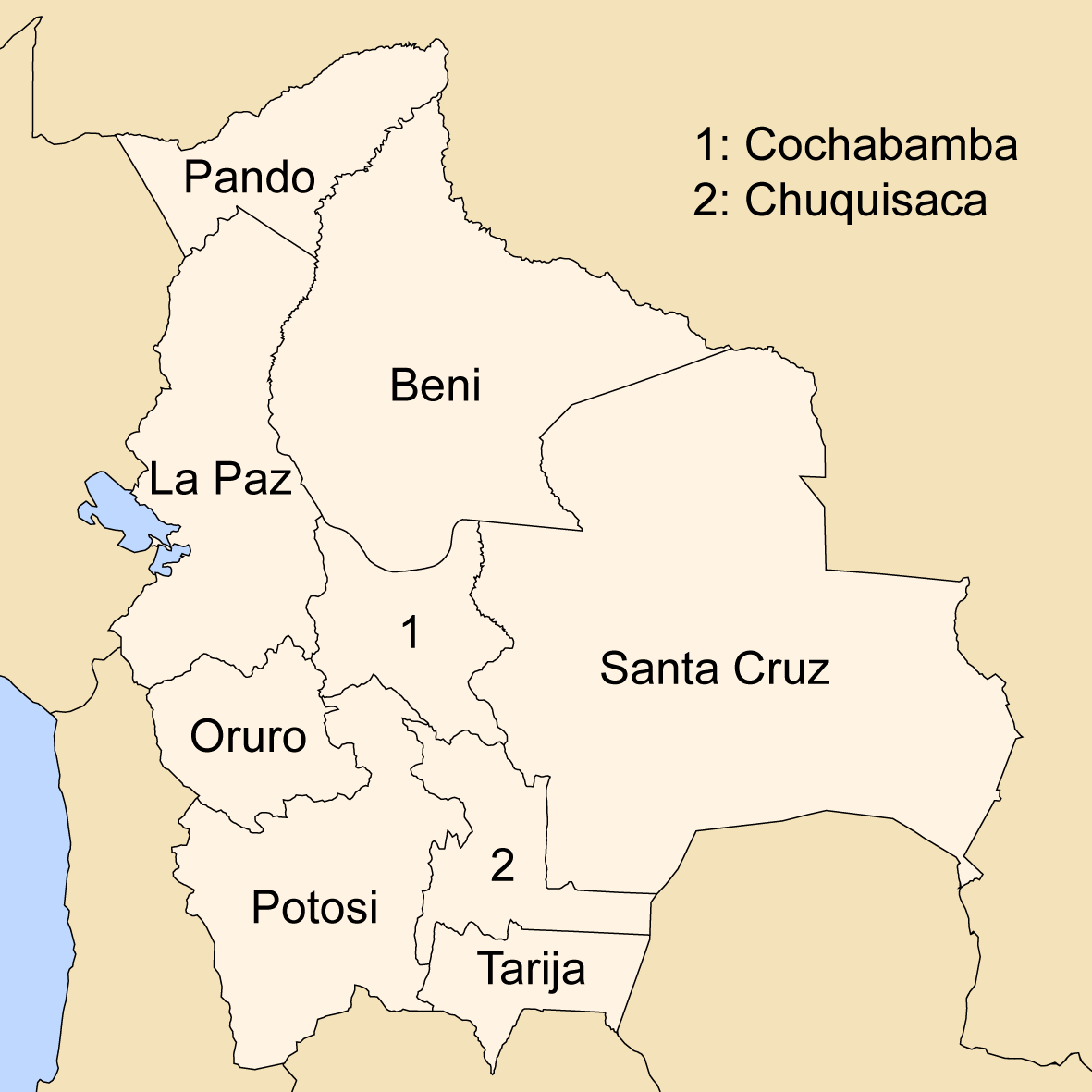
Departments Of Bolivia
Bolivia is a unitary state consisting of nine department (administrative division), departments (). Departments are the primary subdivisions of Bolivia, and possess certain rights under the Constitution of Bolivia. Each department is represented in the Plurinational Legislative Assembly—a bicameralism, bicameral legislature consisting of the Senate and the Chamber of Deputies. Each department is represented by four Senators, while Deputies are awarded to each department in proportion to their total population. Out of the nine departments, La Paz Department (Bolivia), La Paz was originally the most populous, with 2,706,351 inhabitants as of 2012 but the far eastern department of Santa Cruz Department (Bolivia), Santa Cruz has since surpassed it by 2020; Santa Cruz also claims the title as the largest, encompassing . Pando Department, Pando is the least populated, with a population of 110,436. The smallest in area is Tarija Department, Tarija, encompassing . Departments Forme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paruma
Paruma is a stratovolcano that lies on the border of Bolivia and Chile. It is part of a ridge that contains several stratovolcanos. Paruma lies at the eastern end of the ridge, with Olca to its west. The older volcano Paruma lies to east of Paruma. Paruma has clearly been active during the Holocene The Holocene () is the current geologic time scale, geological epoch, beginning approximately 11,700 years ago. It follows the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene to ..., with many morphologically young lava flows on its flanks. It also has persistent fumaroles. One lava flow in particular extends for 7 kilometres to the south-east of the peak. Historical activity along the ridge has been confined to one eruption from 1865 to 1867, the character of which is not precisely known. Sources * Subduction volcanoes Volcanoes of Potosí Department Stratovolcanoes of Chile Polygenetic volcanoes Bolivi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moxos People
Moxos may refer to: * Moxos plains, or ''Llanos de Moxos'', a region of Bolivia * Moxos Province, Bolivia * Moxo people, an indigenous people of Bolivia * Llanos de Moxos (archaeology) * Jesuit Missions of Moxos * Moxoene, or Moxos, an ancient Armenian province {{Disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guarani People
Guarani, Guaraní or Guarany may refer to Ethnography * Guaraní people, an indigenous people from South America's interior (Brazil, Argentina, Paraguay and Bolivia) * Guarani language, or Paraguayan Guarani, an official language of Paraguay * Guarani dialects, spoken in Argentina, Brazil, Bolivia, and Paraguay * Guarani languages, a group of languages, including Guarani, in the Tupí-Guaraní language subfamily * Eastern Bolivian Guaraní language, historically called Chiriguanos, living in the eastern Bolivian foothills of the Andes. Also called Ava Guarani. Economics * Paraguayan guaraní, the currency of Paraguay Education * The Guarini School of Graduate and Advanced Studies, a subunit of Dartmouth College Geography * Guarani, Minas Gerais, Brazil * Guarani de Goiás, Brazil * Guarani das Missões, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil * Guarani Aquifer, a large underground water reservoir in South America Literature and music * '' The Guarani'', an 1857 novel by Jos� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aymara People
The Aymara or Aimara (, ) people are an Indigenous people in the Andes and Altiplano regions of South America. Approximately 2.3 million Aymara live in northwest Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, and Peru. The ancestors of the Aymara lived in the region for many centuries before becoming a subject people of the Inca Empire in the late 15th or early 16th century and later of the Spanish in the 16th century. With the Spanish American wars of independence (1810–1825), the Aymaras became subjects of the new nations of Bolivia and Peru. After the War of the Pacific (1879–1883), Chile annexed territory with the Aymara population. Etymology The name of the Aymara people stems from the word ''Ayma-ra-mi'' meaning "a place with many communally owned farms". The word "Aymara" also refers to a group of language dialects of which the origin, spread and time-frame are debated. History Early history The early history of the Aymara people is uncertain. Various hypotheses have been voiced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quechuas
Quechua people (, ; ) , Quichua people or Kichwa people may refer to any of the Indigenous peoples of South America who speak the Quechua languages, which originated among the Indigenous people of Peru. Although most Quechua speakers are native to Peru, there are some significant populations in Ecuador, Bolivia, Chile, Colombia, and Argentina. The most common Quechua dialect is Southern Quechua. The Kichwa people of Ecuador speak the Kichwa language, Kichwa dialect; in Colombia, the Inga people speak Inga Kichwa. The Quechua word for a Quechua speaker is ''runa'' or ''nuna'' ("person"); the plural is ''runakuna'' or ''nunakuna'' ("people"). "Quechua speakers call themselves Runa -- simply translated, "the people". Some historical Quechua people are: * The Chanka people lived in the Huancavelica Region, Huancavelica, Ayacucho Region, Ayacucho, and Apurímac Region, Apurímac regions of Peru. * The Huanca people of the Junín Region of Peru spoke Quechua before the Incas did. * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples Of The Americas
In the Americas, Indigenous peoples comprise the two continents' pre-Columbian inhabitants, as well as the ethnic groups that identify with them in the 15th century, as well as the ethnic groups that identify with the pre-Columbian population of the Americas as such. These populations exhibit significant diversity; some Indigenous peoples were historically hunter-gatherers, while others practiced agriculture and aquaculture. Various Indigenous societies developed complex social structures, including pre-contact monumental architecture, organized city, cities, city-states, chiefdoms, state (polity), states, monarchy, kingdoms, republics, confederation, confederacies, and empires. These societies possessed varying levels of knowledge in fields such as Pre-Columbian engineering in the Americas, engineering, Pre-Columbian architecture, architecture, mathematics, astronomy, History of writing, writing, physics, medicine, Pre-Columbian agriculture, agriculture, irrigation, geology, minin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Pedro De Quemes Canton
San Pedro de Quemes is one of the cantons of the San Pedro de Quemes Municipality, the second municipal section of the Nor Lípez Province in the Potosí Department of Bolivia Bolivia, officially the Plurinational State of Bolivia, is a landlocked country located in central South America. The country features diverse geography, including vast Amazonian plains, tropical lowlands, mountains, the Gran Chaco Province, w .... During the census of 2001 it had 574 inhabitants.Instituto Nacional de Estadística, Bolivia (Spanish) Its seat is San Pedro de Quemes with a population of 490 in 2001. References External links [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelcoya Canton
Pelcoya is one of the cantons of the San Pedro de Quemes Municipality, the second municipal section of the Nor Lípez Province in the Potosí Department of Bolivia Bolivia, officially the Plurinational State of Bolivia, is a landlocked country located in central South America. The country features diverse geography, including vast Amazonian plains, tropical lowlands, mountains, the Gran Chaco Province, w .... During the census of 2001 it had 135 inhabitants.Instituto Nacional de Estadística, Bolivia (Spanish) Its seat is Pelcoya with a population of 79 in 2001. References External links [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wanaku (Potosí)
Wanaku ( Quechua for guanaco, Hispanicized spelling ''Huanaco, Huanacu'') is a mountain in the Andes of Bolivia, about high. It is situated in the Potosí Department, Nor Lípez Province, Quemes Municipality, Pelcoya Canton. Wanaku lies southeast of the Ollagüe Ollagüe () or Ullawi () is a massive andesite stratovolcano in the Andes on the Bolivia–Chile border, within the Antofagasta Region of Chile and the Potosí Department, Potosi Department of Bolivia. Part of the Central Volcanic Zone of the A ... (Ullawi) volcano and northeast of Ch'aska Urqu. References Mountains of Potosí Department Four-thousanders of the Andes {{Potosí-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olca
Olca is a stratovolcano on the border of Chile and Bolivia. It lies in the middle of a 15 km long ridge composed of several stratovolcanos. Cerro Minchincha lies to the west and Paruma to the east. It is also close to the pre-Holocene Cerro Paruma. It is andesitic and dacitic in composition, with lava flows extending several kilometres north of the peak. The only activity from the ridge during historical times was a flank eruption from 1865 to 1867. The exact source of this eruption is unclear. Gas emissions and composition The gasses emission is comprised by a single warm spring at the base and a persistent fumarole field over at the crater's dome for at least 60 years. The fumarolic field is about 0.1 km2 and the emissions measured in situ at the crater show a highly mixed magmatic system between high temperature gasses and hydrothermal fluids. The gas composition indicates low concentration of H2, CO and acidic gasses, and high concentration of H2S and hydroc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |