|
San Pedro Creek
San Pedro Creek (Spanish for ''St. Peter'') is a perennial stream in the City of Pacifica, San Mateo County, California in the San Francisco Bay Area whose tributaries originate on Sweeney Ridge in the Golden Gate National Recreation Area and Montara Mountain in the Santa Cruz Mountains.The creek mainstem flows through the San Pedro Valley to its mouth near Shelter Cove of the Pacific Ocean The stream is notable as the 1769 campsite for Gaspar de Portolà before he ascended Sweeney Ridge and discovered San Francisco Bay. The south fork of San Pedro Creek became a trout farm, operated by John Gay, until 1962, when storm rains washed out the entire operation. Today the south fork is a seasonal water source for the City of Pacifica. San Pedro Creek is also notable as the only major steelhead trout habitat for between San Francisco and Half Moon Bay, supporting fish of up to two feet in length. More recently, the Middle Valley has been used for grazing on its hillsides and commerci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine United States Minor Outlying Islands, Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in Compact of Free Association, free association with three Oceania, Pacific Island Sovereign state, sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Palau, Republic of Palau. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders Canada–United States border, with Canada to its north and Mexico–United States border, with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the List of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
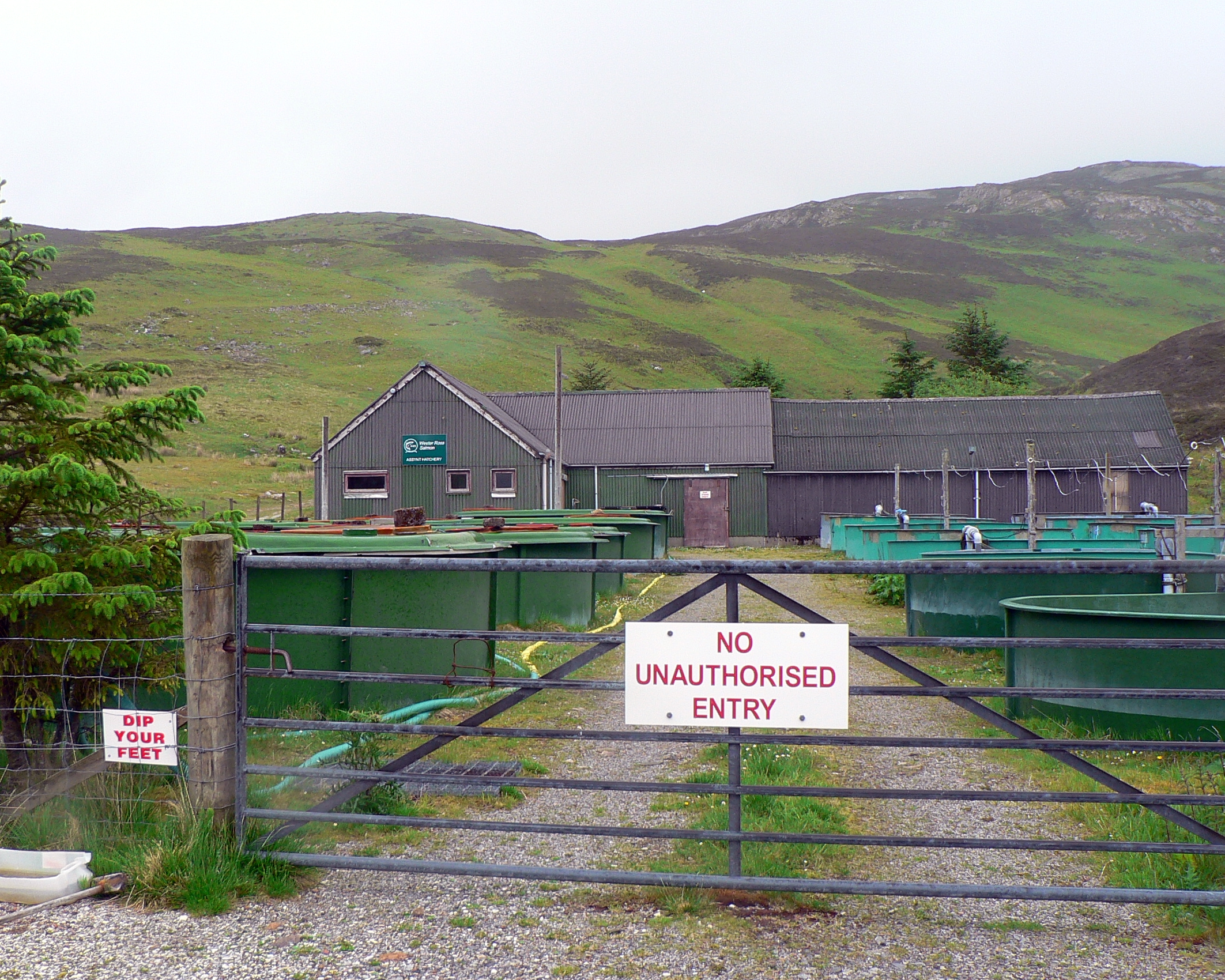
Trout Farm
The aquaculture of salmonids is the farming and harvesting of salmonids under controlled conditions for both commercial and recreational purposes. Salmonids (particularly salmon and rainbow trout), along with carp, and tilapia are the three most important fish species in aquaculture. The most commonly commercially farmed salmonid is the Atlantic salmon. In the U.S. Chinook salmon and rainbow trout are the most commonly farmed salmonids for recreational and subsistence fishing through the National Fish Hatchery System. In Europe, brown trout are the most commonly reared fish for recreational restocking. Commonly farmed nonsalmonid fish groups include tilapia, catfish, sea bass, and bream. In 2007, the aquaculture of salmonids was worth US$10.7 billion globally. Salmonid aquaculture production grew over ten-fold during the 25 years from 1982 to 2007. In 2012, the leading producers of salmonids were Norway, Chile, Scotland and Canada. Much controversy exists about the ecological a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ohlone
The Ohlone, formerly known as Costanoans (from Spanish meaning 'coast dweller'), are a Native American people of the Northern California coast. When Spanish explorers and missionaries arrived in the late 18th century, the Ohlone inhabited the area along the coast from San Francisco Bay through Monterey Bay to the lower Salinas Valley. At that time they spoke a variety of related languages. The Ohlone languages make up a sub-family of the Utian language family. Older proposals place Utian within the Penutian language phylum, while newer proposals group it as Yok-Utian. In pre-colonial times, the Ohlone lived in more than 50 distinct landholding groups, and did not view themselves as a single unified group. They lived by hunting, fishing, and gathering, in the typical ethnographic California pattern. The members of these various bands interacted freely with one another. The Ohlone people practiced the Kuksu religion. Prior to the Gold Rush, the northern California re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corylus Cornuta
''Corylus cornuta'', the beaked hazelnut (or just ''beaked hazel''), is a deciduous shrubby hazel with two subspecies found throughout most of North America. Description The beaked hazelnut can reach tall with stems thick with smooth gray bark, but it can also remain relatively small in the shade of other plants. It typically grows with several trunks. The leaves are green, rounded oval with a pointed tip, coarsely double-toothed, long and broad, with soft and hairy undersides. The male flowers are catkins that form in autumn, pollinating the single female flowers the following spring to allow the fruits to mature through the summer. The beaked hazelnut is named for its fruit, which is a nut enclosed in a husk with a tubular extension long that resembles a beak. Tiny filaments protrude from the husk and may stick into, and irritate, skin that contacts them. The spherical nuts are small and surrounded by a hard shell. The beaked hazel is the hardiest of all hazel spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctostaphylos Montaraensis
''Arctostaphylos montaraensis'', known by the common name Montara manzanita, is a species of manzanita in the family Ericaceae. Distribution This perennial evergreen shrub is endemic to California, native only to a few occurrences in northern San Mateo County on San Bruno Mountain and Montara Mountain, northern extensions of the Santa Cruz Mountains. It is found at elevations of on the two mountains, growing on decomposing granite and sandstone rock outcrops, in coastal chaparral and coastal sage scrub habitats. The plant is ranked as a critically endangered species by the California Native Plant Society Inventory of Rare and Endangered Plants of California, due to being threatened by new developments and off trail/road walking and vehicle (e.g. motorcycles, mountain bikes) habitat degradation. Description ''Arctostaphylos montaraensis'' is a mounding to erect shrub that can grow to heights from (on exposed granite outcrops) to . The multiple trunks and stems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coast Douglas-fir
''Pseudotsuga menziesii'' var. ''menziesii'', commonly known as Coast Douglas-fir, Pacific Douglas-fir, Oregon pine, or Douglas spruce, is an evergreen conifer native to western North America from west-central British Columbia, Canada southward to central California, United States. In Oregon and Washington its range is continuous from the Cascades crest west to the Pacific Coast Ranges and Pacific Ocean. In California, it is found in the Klamath and California Coast Ranges as far south as the Santa Lucia Mountains with a small stand as far south as the Purisima Hills, Santa Barbara County. In the Sierra Nevada it ranges as far south as the Yosemite region. It occurs from near sea level along the coast to in the California Mountains. Further inland, coast Douglas-fir is replaced by Rocky Mountain or interior Douglas-fir (''P. menziesii'' var. ''glauca''). Interior Douglas-fir intergrades with coast Douglas-fir in the Cascades of northern Washington and southern British Columb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
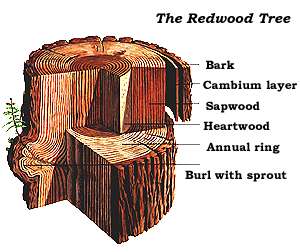
Coast Redwood
''Sequoia sempervirens'' ()''Sunset Western Garden Book,'' 1995:606–607 is the sole living species of the genus '' Sequoia'' in the cypress family Cupressaceae (formerly treated in Taxodiaceae). Common names include coast redwood, coastal redwood, and California redwood. It is an evergreen, long-lived, monoecious tree living 1,200–2,200 years or more. This species includes the tallest living trees on Earth, reaching up to in height (without the roots) and up to in diameter at breast height. These trees are also among the oldest living things on Earth. Before commercial logging and clearing began by the 1850s, this massive tree occurred naturally in an estimated along much of coastal California (excluding southern California where rainfall is not sufficient) and the southwestern corner of coastal Oregon within the United States. The name sequoia sometimes refers to the subfamily Sequoioideae, which includes ''S. sempervirens'' along with '' Sequoiadendron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Pedro Valley County Park
'San Pedro Valley County Park'' is a San Mateo County park located in Pacifica, California, which includes the headwaters of San Pedro Creekbr> Trails * Montara Mountain Trail, 2.1 miles, includes views of the Pacific Ocean The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contine .... * The Brooks Creek Trail, 1.0 mile, to Brooks Falls which is 175 feet tall in three tiers following rain storms during the winter and spring. * Hazelnut Trail, 3.7 miles * Valley View Trail, 1.4 miles * Weiler Ranch Road Trail, 1 mile known for wildlife viewing in the mornings and evenings. * Plaskon Nature Trail, 0.1 mile, wheelchair accessible. * Old Trout Farm Trail, .5 mile. Pacifica, California Parks in San Mateo County, California Regional parks in California {{SanMateoCountyCA-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landfill
A landfill site, also known as a tip, dump, rubbish dump, garbage dump, or dumping ground, is a site for the disposal of waste materials. Landfill is the oldest and most common form of waste disposal, although the systematic burial of the waste with daily, intermediate and final covers only began in the 1940s. In the past, refuse was simply left in piles or thrown into pits; in archeology this is known as a midden. Some landfill sites are used for waste management purposes, such as temporary storage, consolidation and transfer, or for various stages of processing waste material, such as sorting, treatment, or recycling. Unless they are stabilized, landfills may undergo severe shaking or soil liquefaction of the ground during an earthquake. Once full, the area over a landfill site may be reclaimed for other uses. Operations Operators of well-run landfills for non-hazardous waste meet predefined specifications by applying techniques to: # confine waste to as small an area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
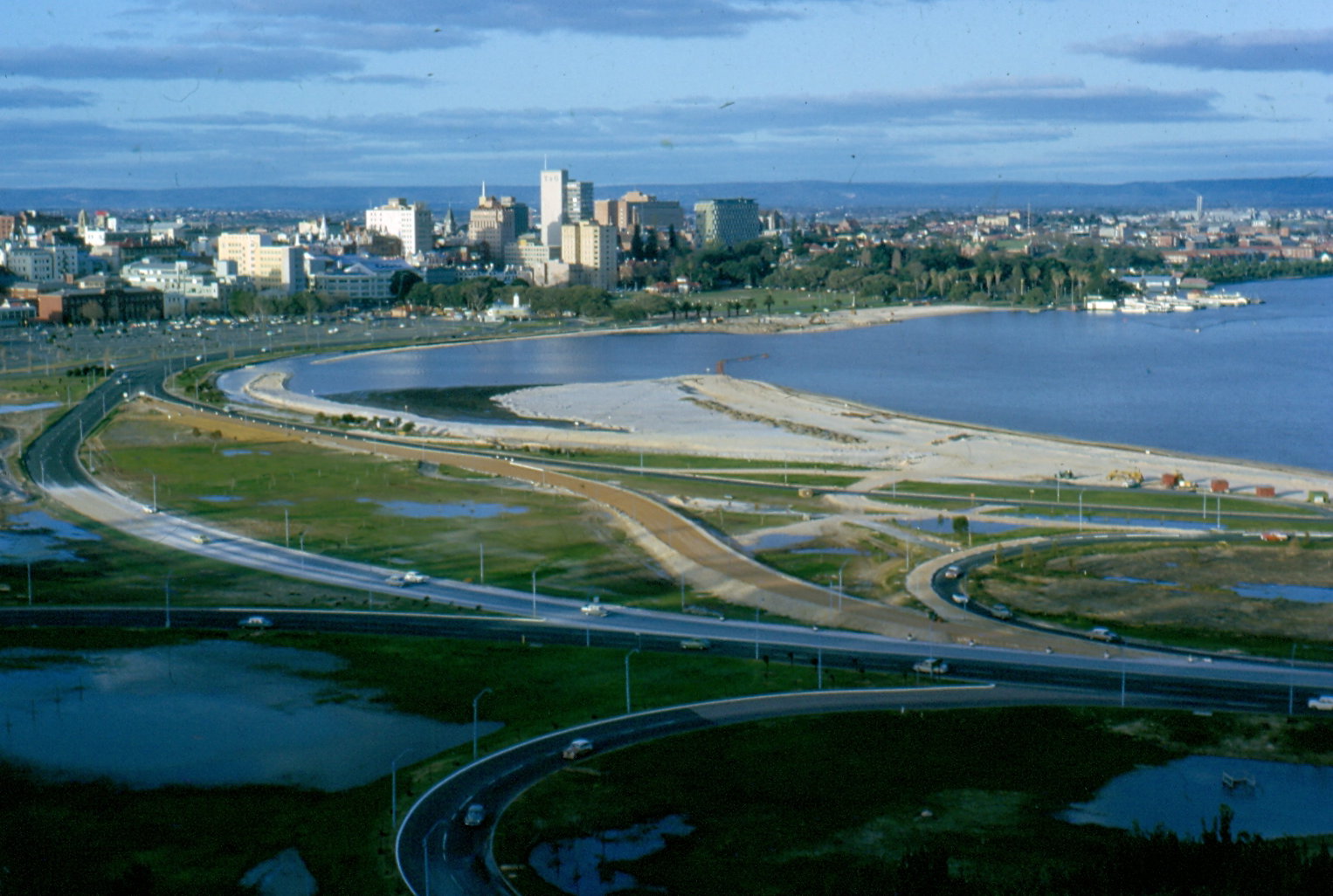
Land Reclamation
Land reclamation, usually known as reclamation, and also known as land fill (not to be confused with a waste landfill), is the process of creating new land from oceans, seas, riverbeds or lake beds. The land reclaimed is known as reclamation ground or land fill. In some jurisdictions, including parts of the United States, the term "reclamation" can refer to returning disturbed lands to an improved state. In Alberta, Canada, for example, reclamation is defined by the provincial government as "The process of reconverting disturbed land to its former or other productive uses." In Oceania, it is frequently referred to as land rehabilitation. History One of the earliest large-scale projects was the Beemster Polder in the Netherlands, realized in 1612 adding of land. In Hong Kong the Praya Reclamation Scheme added of land in 1890 during the second phase of construction. It was one of the most ambitious projects ever taken during the Colonial Hong Kong era.Bard, Solomon. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
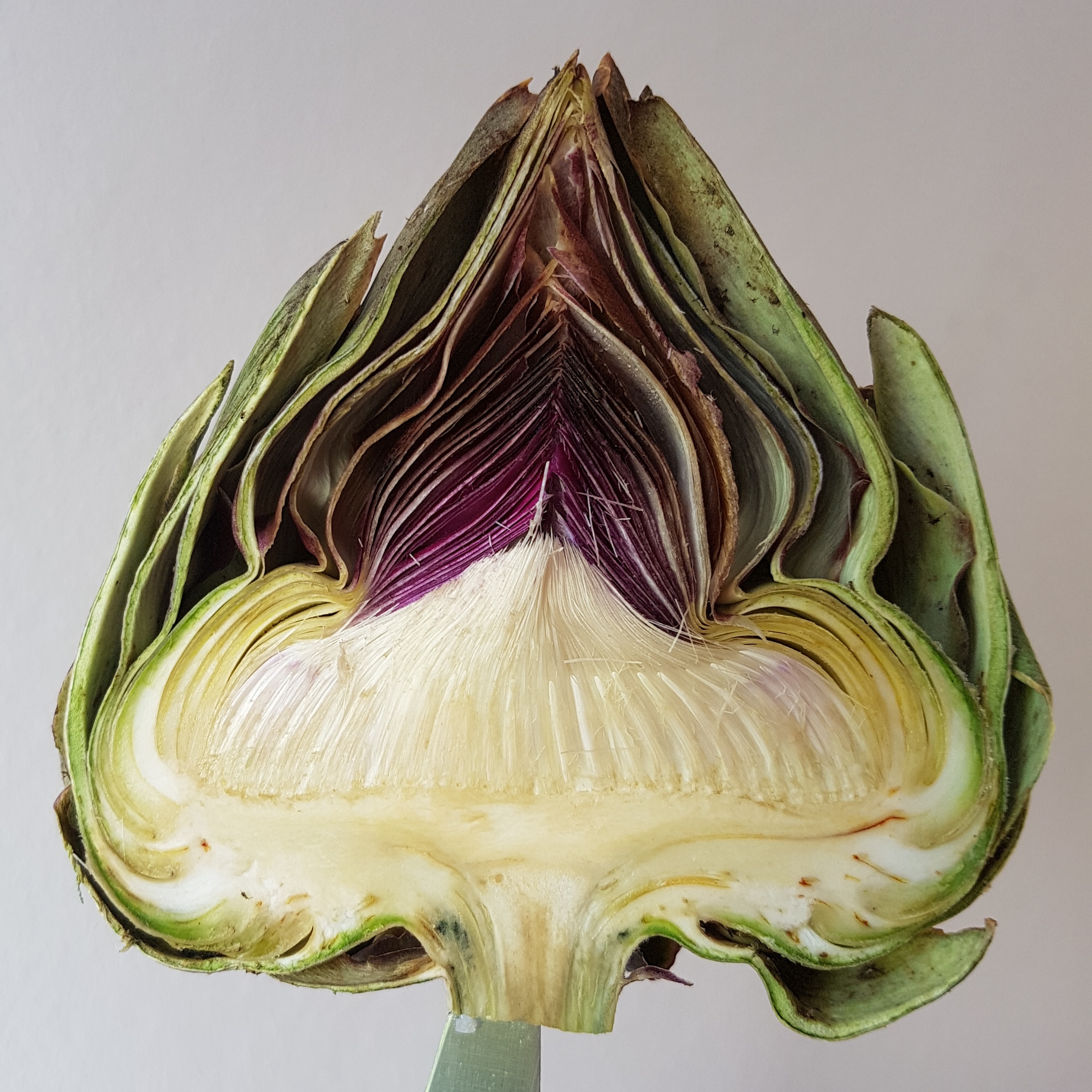
Artichokes
The globe artichoke ('' Cynara cardunculus'' var. ''scolymus'' ),Rottenberg, A., and D. Zohary, 1996: "The wild ancestry of the cultivated artichoke." Genet. Res. Crop Evol. 43, 53–58. also known by the names French artichoke and green artichoke in the U.S., is a variety of a species of thistle cultivated as food. The edible portion of the plant consists of the flower buds before the flowers come into bloom. The budding artichoke flower-head is a cluster of many budding small flowers (an inflorescence), together with many bracts, on an edible base. Once the buds bloom, the structure changes to a coarse, barely edible form. Another variety of the same species is the cardoon, a perennial plant native to the Mediterranean region. Both wild forms and cultivated varieties (cultivars) exist. Description This vegetable grows to tall, with arching, deeply lobed, silvery, glaucous-green leaves long. The flowers develop in a large head from an edible bud about diameter with nu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
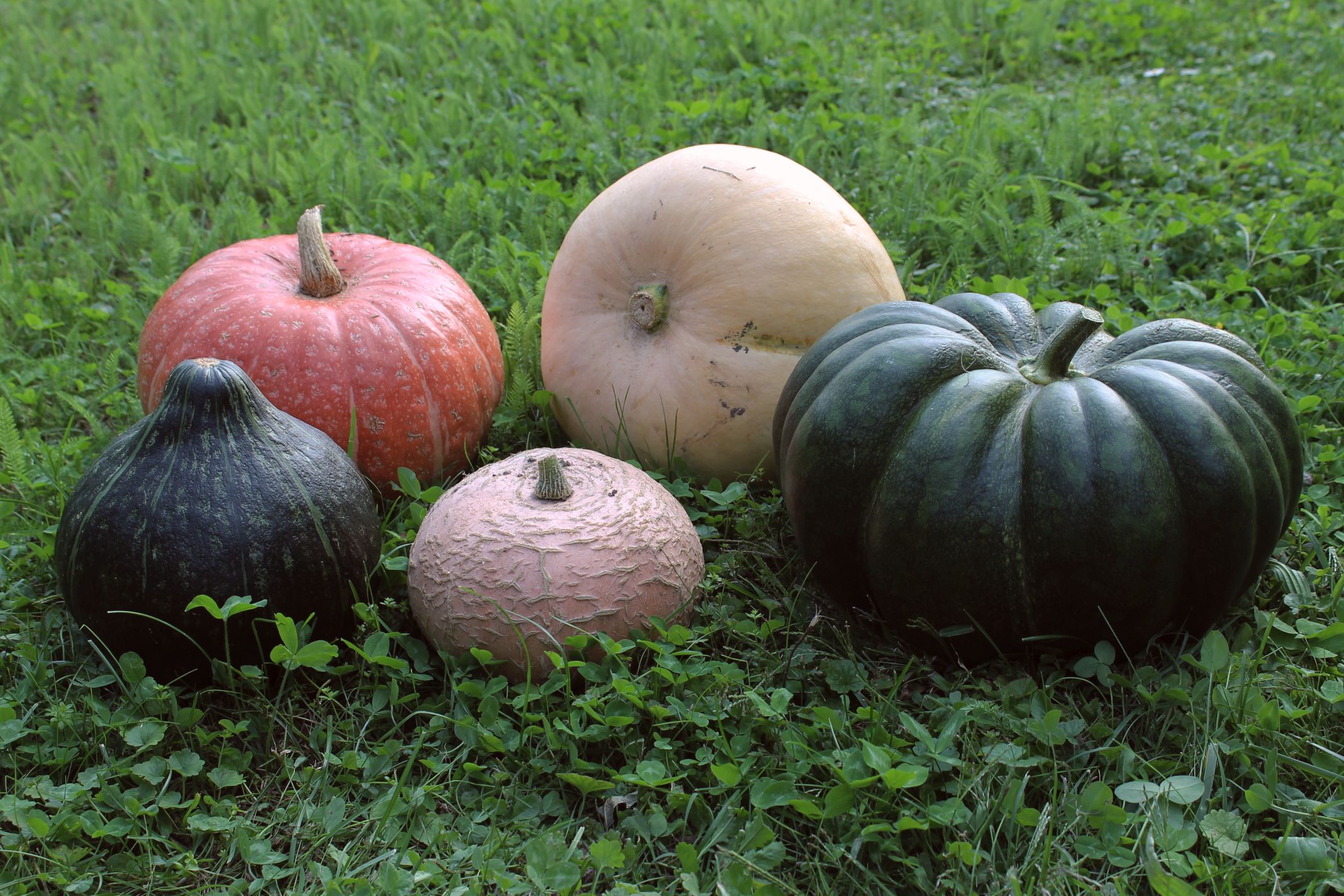
Pumpkin
A pumpkin is a vernacular term for mature winter squash of species and varieties in the genus '' Cucurbita'' that has culinary and cultural significance but no agreed upon botanical or scientific meaning. The term ''pumpkin'' is sometimes used interchangeably with "squash" or "winter squash", and is commonly used for cultivars of '' Cucurbita argyrosperma'', '' Cucurbita ficifolia'', '' Cucurbita maxima'', '' Cucurbita moschata'', and '' Cucurbita pepo''. Native to North America (northeastern Mexico and the southern United States), ''C. pepo'' pumpkins are one of the oldest domesticated plants, having been used as early as 7,000 to 5,500 BC. Today, pumpkins of varied species are widely grown for food, as well as for aesthetic and recreational purposes. The pumpkin's thick shell contains edible seeds and pulp. Pumpkin pie, for instance, is a traditional part of Thanksgiving meals in Canada and the United States, and pumpkins are frequently carved as jack-o'-lanterns for de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |