|
San (letter)
San () is an archaic letter of the Greek alphabet. Its shape is similar to Latin and Greek Mu (Greek letter), mu (), and can be described as a sigma () turned sideways. It was used as an alternative to sigma to denote the sound . Unlike sigma, whose position in the alphabet is between Rho (letter), rho and Tau (letter), tau, san appeared between Pi (letter), pi and Qoppa (letter), koppa in alphabetic order. In addition to denoting the archaic character, the name "san" also came to be used for sigma itself. Historical use Sigma and san The existence of the two competing letters sigma and san is traditionally believed to have been due to confusion during the adoption of the Greek alphabet from the Phoenician alphabet, Phoenician script, because Phoenician had more sibilant sounds than Greek had. According to one theory, the distribution of the sibilant letters in Greek is due to pair-wise confusion between the sounds and alphabet positions of the four Phoenician sibilant sign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corinthian Incised Shard
Corinthian or Corinthians may refer to: *Several Pauline epistles, books of the New Testament of the Bible: **First Epistle to the Corinthians **Second Epistle to the Corinthians **Third Epistle to the Corinthians (Orthodox) *A demonym relating to the ancient city-state of Ancient Corinth, Corinth *A demonym relating to the modern-day port of Corinth or the regional unit of Corinthia in Greece *Corinthian order, a classical order of ancient Greek and Roman architecture *Residents or people from the town of Corinth (town), New York *The League of Corinth, a federation of ancient Greek states *Corinthian Colleges, a post secondary education company in North America currently under criminal investigation in the US. *Corinthian (comics), a character in ''The Sandman'' comics *The Corinthian (novel), novel by Georgette Heyer *The Corinthian (New York), a skyscraper in New York City *The Corinthian helmet, a style of helmet worn by hoplites in classical Greece *Corinthian leather, a mark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigma (letter)
Sigma ( ; uppercase Σ, lowercase σ, lowercase in word-final position ς; ) is the eighteenth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 200. In general mathematics, uppercase Σ is used as an operator for summation. When used at the end of a letter-case word (one that does not use all caps), the final form (ς) is used. In ' (Odysseus), for example, the two lowercase sigmas (σ) in the center of the name are distinct from the word-final sigma (ς) at the end. The Latin letter S derives from sigma while the Cyrillic letter Es derives from a lunate form of this letter. History The shape (Σς) and alphabetic position of sigma is derived from the Phoenician letter ( ''shin''). Sigma's original name may have been ''san'', but due to the complicated early history of the Greek epichoric alphabets, ''san'' came to be identified as a separate letter in the Greek alphabet, represented as Ϻ. Herodotus reports that "san" was the name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
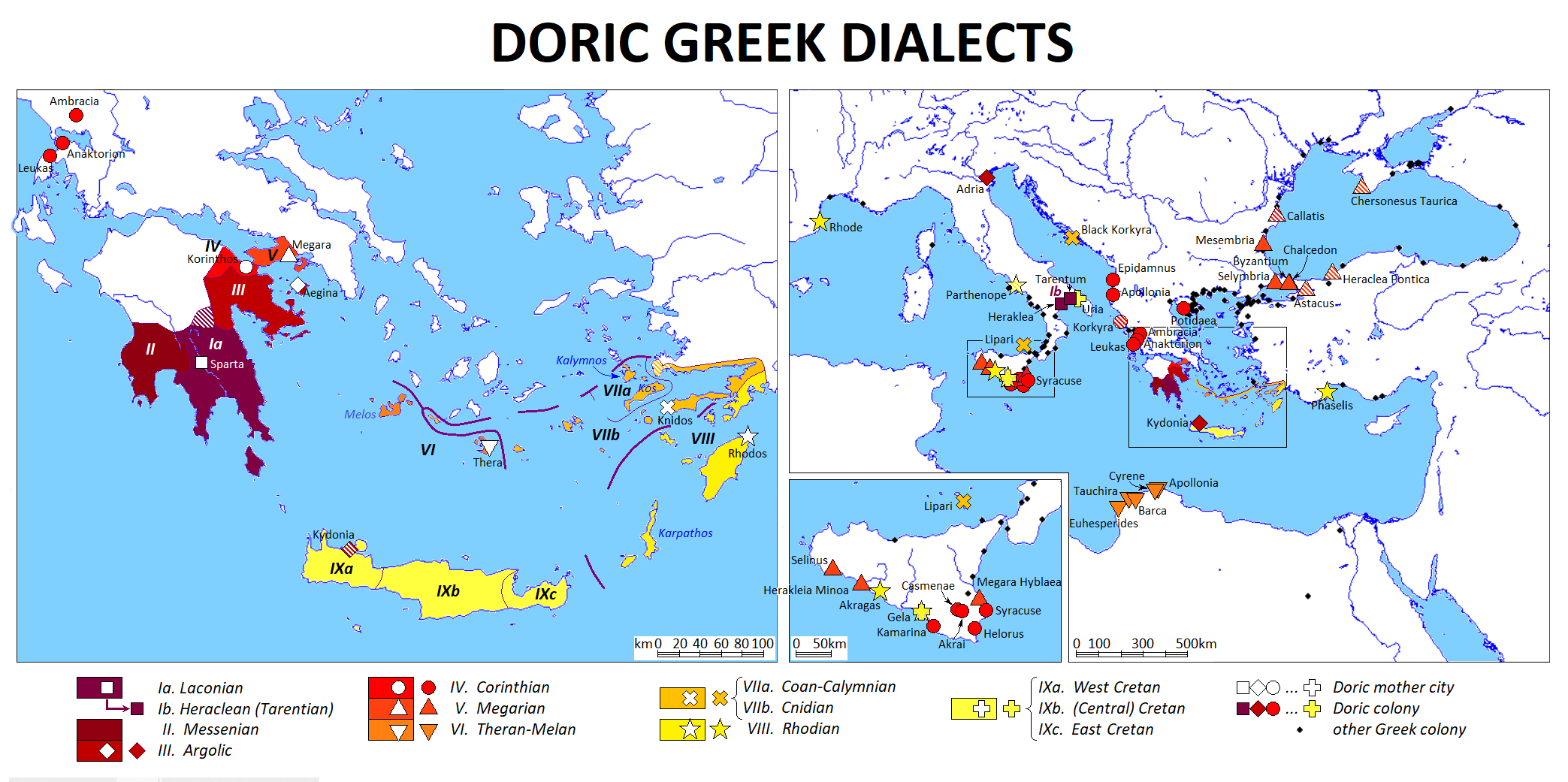
Doric Greek
Doric or Dorian (), also known as West Greek, was a group of Ancient Greek dialects; its Variety (linguistics), varieties are divided into the Doric proper and Northwest Doric subgroups. Doric was spoken in a vast area, including northern Greece (Acarnania, Aetolia, Epirus, Ozolian Locris, western and Opuntian Locris, eastern Locris, Phocis (ancient region), Phocis, Doris (Greece), Doris, and possibly Macedonia (ancient kingdom), ancient Macedonia), most of the Regions of ancient Greece#Peloponnese, Peloponnese (Achaea (ancient region), Achaea, Ancient Elis, Elis, Messenia (ancient region), Messenia, Laconia, Argolid, Aegina, Corinthia (ancient region), Corinthia, and Megara), the Southern Aegean (Kythira, Milos, Santorini, Thera, Crete, Karpathos, and Rhodes), as well as the colonies of some of those regions in Cyrene, Libya, Cyrene, Magna Graecia, the Greek colonisation#Black Sea and Propontis, Black Sea, Greek colonisation#Ionian Sea, Adriatic Sea, and Illyria, the Ionian Sea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abecedarium
An abecedarium (also known as an abecedary or ABCs or simply an ABC) is an inscription consisting of the letters of an alphabet, almost always listed in order. Typically, abecedaria (or abecedaries) are practice exercises. Non-Latin alphabets Some abecedaria include obsolete letters which are not otherwise attested in inscriptions. For example, abecedaria in the Etruscan alphabet from Marsiliana (the Tuscan town) include the letters B, D, and O, which indicate sounds not present in the Etruscan language and are therefore not found in Etruscan inscriptions. Others, such as those known from Safaitic inscriptions, list the letters of the alphabet in different orders, suggesting that the script was casually rather than formally learned. Some abecedaria found in the Athenian Agora appear to be deliberately incomplete, consisting of only the first three to six letters of the Greek alphabet, and these may have had a magical or ritual significance. A deliberately incomplete abeced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek San Slanted
Greek may refer to: Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe: *Greeks, an ethnic group *Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family **Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all known varieties of Greek **Mycenaean Greek, most ancient attested form of the language (16th to 11th centuries BC) **Ancient Greek, forms of the language used c. 1000–330 BC **Koine Greek, common form of Greek spoken and written during Classical antiquity **Medieval Greek or Byzantine Language, language used between the Middle Ages and the Ottoman conquest of Constantinople **Modern Greek, varieties spoken in the modern era (from 1453 AD) *Greek alphabet, script used to write the Greek language *Greek Orthodox Church, several Churches of the Eastern Orthodox Church *Ancient Greece, the ancient civilization before the end of Antiquity * Old Greek, the language as spoken from Late Antiquity to around 1500 AD *Greek mythology, a body of myths o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsade
Tsade (also spelled , , , , tzadi, sadhe, tzaddik) is the eighteenth Letter (alphabet), letter of the Semitic abjads, including Phoenician alphabet, Phoenician ''ṣādē'' 𐤑, Hebrew alphabet, Hebrew ''ṣādī'' , Aramaic alphabet, Aramaic ''ṣāḏē'' 𐡑, Syriac alphabet, Syriac ''ṣāḏē'' ܨ, Ge'ez script, Ge'ez ''ṣädäy'' ጸ, and Arabic alphabet, Arabic ''ṣād'' . It is related to the Ancient North Arabian 𐪎, Ancient South Arabian script, South Arabian , and Geʽez script, Ge'ez . The corresponding letter of the Ugaritic alphabet is 𐎕 ''ṣade''. Its oldest phonetic value is debated, although there is a variety of pronunciations in different modern Semitic languages and their dialects. It represents the coalescence of three Proto-Semitic "emphatic consonants" in Canaanite language, Canaanite. Arabic language, Arabic, which kept the phonemes separate, introduced variants of and to express the three (see , ). In Aramaic, these emphatic consonants c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenician Sade
Phoenician may refer to: * Phoenicia, an ancient civilization * Phoenician alphabet **Phoenician (Unicode block) * Phoenicianism, a form of Lebanese nationalism * Phoenician language * List of Phoenician cities See also * Phoenix (mythology) * Phoenix (other) * Phoenicia (other) Phoenicia, or Phœnicia, was an ancient civilization in the north of Canaan in parts of Lebanon, Syria, and Palestine. Phoenicia may also refer to: Historical places *Phoenice (Roman province), a province of the Roman Empire encompassing the reg ... * {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeta (letter)
Zeta (, ; uppercase Ζ, lowercase ζ; , , classical or ''zē̂ta''; ''zíta'') is the sixth letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 7. It was derived from the Phoenician letter zayin . Letters that arose from zeta include the Roman Z and Cyrillic З. Name Unlike the other Greek letters, this letter did not take its name from the Phoenician letter from which it was derived; it was given a new name on the pattern of beta, eta and theta. The word ''zeta'' is the ancestor of ''zed'', the name of the Latin letter Z in Commonwealth English. Swedish and many Romance languages (such as Italian and Spanish) do not distinguish between the Greek and Roman forms of the letter; "''zeta''" is used to refer to the Roman letter Z as well as the Greek letter. Uses Letter The letter ζ represents the voiced alveolar fricative in Modern Greek. The sound represented by zeta in Greek before 400 BC is disputed. See Ancient Greek pho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Zeta Archaic
Greek may refer to: Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe: *Greeks, an ethnic group *Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family **Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all known varieties of Greek **Mycenaean Greek, most ancient attested form of the language (16th to 11th centuries BC) **Ancient Greek, forms of the language used c. 1000–330 BC **Koine Greek, common form of Greek spoken and written during Classical antiquity **Medieval Greek or Byzantine Language, language used between the Middle Ages and the Ottoman conquest of Constantinople **Modern Greek, varieties spoken in the modern era (from 1453 AD) *Greek alphabet, script used to write the Greek language *Greek Orthodox Church, several Churches of the Eastern Orthodox Church *Ancient Greece, the ancient civilization before the end of Antiquity * Old Greek, the language as spoken from Late Antiquity to around 1500 AD *Greek mythology, a body of myths o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zayin
Zayin (also spelled zain or zayn or simply zay) is the seventh letter of the Semitic abjads, including Phoenician ''zayn'' 𐤆, Hebrew ''zayīn'' , Aramaic ''zain'' 𐡆, Syriac ''zayn'' ܙ, and Arabic ''zāy'' . It represents the sound . It is also related to the Ancient North Arabian 𐪘, South Arabian , and Ge'ez . The Phoenician letter gave rise to the Greek zeta (Ζ), Etruscan ''z'' , Latin Z, and Cyrillic Ze З, as well as Ж. Origin The Proto-Sinaitic glyph may have been called , may not have been based on a hieroglyph, and may have depicted a " fetter". An alternative view is that it is based on the " copper ingot" hieroglyph ( 𓈔) in the form of an axeblade, after noting that the name "zayin" has roots in Aramaic to refer to "Arms," "Armor," and " Metal used for arms."Cross, F. M. (1980) Newly Found Inscriptions in Old Canaanite and Early Phoenician Scripts. Bulletin of the American Schools of Oriental Research, 238, 1–20. https://doi.org/10.2307/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoenician Zayin
Phoenician may refer to: * Phoenicia, an ancient civilization * Phoenician alphabet **Phoenician (Unicode block) * Phoenicianism, a form of Lebanese nationalism * Phoenician language * List of Phoenician cities See also * Phoenix (mythology) * Phoenix (other) * Phoenicia (other) Phoenicia, or Phœnicia, was an ancient civilization in the north of Canaan in parts of Lebanon, Syria, and Palestine. Phoenicia may also refer to: Historical places *Phoenice (Roman province), a province of the Roman Empire encompassing the reg ... * {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xi (letter)
Xi ( or ; uppercase Ξ, lowercase ξ; ) is the fourteenth letter of the Greek alphabet, representing the voiceless consonant cluster . Its name is pronounced in Modern Greek. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 60. Xi was derived from the Phoenician letter samekh . Xi is distinct from the letter chi, which gave its form to the Latin letter X. Greek Both in classical Ancient Greek and in Modern Greek, the letter Ξ represents the consonant cluster /ks/. In some archaic local variants of the Greek alphabet, this letter was missing. Instead, especially in the dialects of most of the Greek mainland and Euboea, the cluster /ks/ was represented by Χ (which in classical Greek is chi, used for ). Because this variant of the Greek alphabet was used in Magna Graecia (the Greek colonies in Sicily and the southern part of the Italian peninsula), the Latin alphabet borrowed Χ rather than Ξ as the Latin letter that represented the /ks/ cluster that was also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |