|
Samuel Selvon
Samuel Dickson Selvon (20 May 1923 – 16 April 1994)"Samuel Selvon" ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. was a -born writer, who moved to London, England, in 1950. His 1956 novel '' The Lonely Londoners'' is groundbreaking in its use of creolised English, or " nation language", for narrative as well as dialogue. Life and work Samuel Dickson Selvon was born in[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naparima College
Naparima College (informally known as Naps) is a public secondary school for boys in Trinidad and Tobago. Located in San Fernando, Trinidad and Tobago, San Fernando, the school was founded in 1894 but received official recognition in 1900. It was established by Dr. Kenneth J. Grant, a Canadians, Canadian Presbyterian missionary working among the Indian population in Trinidad. The school was one of the first to educate Indo-Trinidadian people, Indo-Trinidadians and played an important and crucial role in the development of an Indo-Trinidadian and Tobagonian professional class. Naparima is derived from the Arawak word (A) naparima, meaning ‘large water’, or from Nabarima, Warao language, Warao, for ‘Father of the waves.’ The school was founded in the churchyard of Susamachar Presbyterian Church in San Fernando as the ''Canadian Mission Indian School''. In 1899, the Mission Council petitioned the Board of Queen's Royal College in Port of Spain for affiliation with it. In 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Fernando, Trinidad And Tobago
San Fernando, officially the City of San Fernando, is the most populous city and second most populous municipality in Trinidad and Tobago, after Chaguanas. Sando, as it is known to many local Trinidadians, occupies 19 km2 and is located in the southwestern part of the island of Trinidad. It is bounded to the north by the Guaracara River, the south by the Oropouche River, the east by the Sir Solomon Hochoy Highway, and the west by the Gulf of Paria. The former borough was elevated to the status of a city corporation on 18 November 1988. The motto of San Fernando is: ''"Sanitas Fortis"'' - ''In a Healthy Environment We Will Find Strength''. San Fernando is called Trinidad and Tobago's "industrial capital" because of its proximity to the Pointe-à-Pierre oil refinery and many other petrochemical, LNG, iron and steel and aluminium smelters in places such as Point Lisas in Couva, Point Fortin, and La Brea. Geography Of Trinidad and Tobago San Fernando is a coastal city. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Of Spain
Port of Spain ( ; Trinidadian and Tobagonian English, Trinidadian English: ''Port ah Spain'' ) is the capital and chief port of Trinidad and Tobago. With a municipal population of 49,867 (2017), an urban population of 81,142 and a transient daily population of 250,000, it is Trinidad and Tobago's third largest municipality, after Chaguanas and San Fernando, Trinidad and Tobago, San Fernando. Port of Spain is located on the Gulf of Paria, on the northwest coast of the island of Trinidad and is part of East–West Corridor, a larger conurbation stretching from Chaguaramas, Trinidad, Chaguaramas in the west to Arima in the east with an estimated population of 600,000. The city serves primarily as a retail and administrative centre and it has been the capital of the island since 1757. It is also an important financial services centre for the Caribbean [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
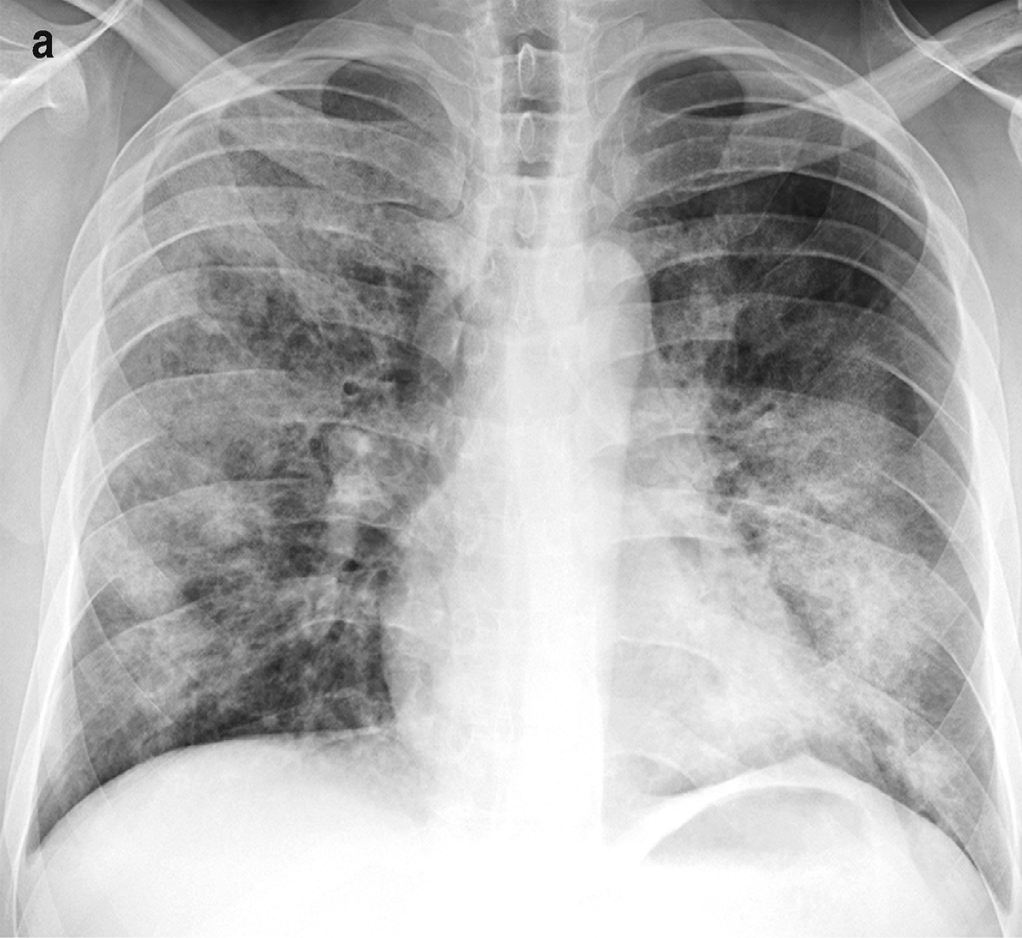
Bronchopneumonia
Bronchopneumonia is a subtype of pneumonia. It is the acute inflammation of the Bronchus, bronchi, accompanied by inflamed patches in the nearby lobules of the lungs. citing: Webster's New World College Dictionary, Fifth Edition, Copyright 2014 It is often contrasted with lobar pneumonia; but, in clinical practice, the types are difficult to apply, as the patterns usually overlap. Topic Completed: 1 August 2011 Bronchopneumonia (lobular) often leads to lobar pneumonia as the infection progresses. The same organism may cause one type of pneumonia in one patient, and another in a different patient. Causes It is more commonly a hospital-acquired pneumonia than a community-acquired pneumonia, in contrast to lobar pneumonia. Bronchopneumonia is less likely than lobar pneumonia to be associated with ''Streptococcus pneumoniae''. Rather, the bronchopneumonia pattern has been associated mainly with the following: ''Staphylococcus aureus'', ''Klebsiella'', ''Escherichia coli, E. coli'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Respiratory Failure
Respiratory failure results from inadequate gas exchange by the respiratory system, meaning that the arterial oxygen, carbon dioxide, or both cannot be kept at normal levels. A drop in the oxygen carried in the blood is known as hypoxemia; a rise in arterial carbon dioxide levels is called hypercapnia. Respiratory failure is classified as either Type 1 or Type 2, based on whether there is a high carbon dioxide level, and can be acute or chronic. In clinical trials, the definition of respiratory failure usually includes increased respiratory rate, abnormal blood gases (hypoxemia, hypercapnia, or both), and evidence of increased work of breathing. Respiratory failure causes an altered state of consciousness due to ischemia in the brain. The typical partial pressure reference values are oxygen Pa more than 80 mmHg (11 kPa) and carbon dioxide Pa less than 45 mmHg (6.0 kPa). Cause A variety of conditions that can potentially result in respiratory failure. The etiologie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Calgary
{{Infobox university , name = University of Calgary , image = University of Calgary coat of arms without motto scroll.svg , image_size = 150px , caption = Coat of arms , former_name = Normal School (1905–1913)Calgary Normal School (1913–1945)Calgary Branch of the Faculty of Education of the University of Alberta (1945–1958)University of Alberta in Calgary (1958–1966){{efn, The following are names of the predecessor institution which the University of Calgary originates from, prior to its reorganization as a standalone university. , motto = {{Lang, gd, Mo Shùile Togam Suas (Canadian Gaelic, Gaelic) , mottoeng = I will lift up my eyes , established = {{Start date and age, 1966, 04, 26, df=yes, p=yes, br=yes , type = Public university, Public , endowment = {{CAD, 1.176 billion (2023) , chancellor = J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Victoria
The University of Victoria (UVic) is a public research university located in the municipalities of Oak Bay, British Columbia, Oak Bay and Saanich, British Columbia, Canada. Established in 1903 as Victoria College, British Columbia, Victoria College, the institution was initially an affiliated college of McGill University until 1915. From 1921 to 1963, it functioned as an affiliate of the University of British Columbia. In 1963, the institution was reorganized into an independent university. History The University of Victoria is the oldest post-secondary institution in British Columbia. First established in 1903 as Victoria College, an affiliated college of McGill University, it gained full autonomy and degree-granting status through a charter on July 1, 1963. Between 1903 and 1915, Victoria College offered first- and second-year McGill courses in the arts and sciences. Administered locally by the Victoria School Board, the college was an adjunct to Victoria High School (British ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, second-largest country by total area, with the List of countries by length of coastline, world's longest coastline. Its Canada–United States border, border with the United States is the world's longest international land border. The country is characterized by a wide range of both Temperature in Canada, meteorologic and Geography of Canada, geological regions. With Population of Canada, a population of over 41million people, it has widely varying population densities, with the majority residing in List of the largest population centres in Canada, urban areas and large areas of the country being sparsely populated. Canada's capital is Ottawa and List of census metropolitan areas and agglomerations in Canada, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberta
Alberta is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Canada. It is a part of Western Canada and is one of the three Canadian Prairies, prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to its west, Saskatchewan to its east, the Northwest Territories to its north, and the U.S. state of Montana to its south. Alberta and Saskatchewan are the only two landlocked Canadian provinces. The eastern part of the province is occupied by the Great Plains, while the western part borders the Rocky Mountains. The province has a predominantly humid continental climate, continental climate, but seasonal temperatures tend to swing rapidly because it is so arid. Those swings are less pronounced in western Alberta because of its occasional Chinook winds. Alberta is the fourth largest province by area, at , and the fourth most populous, with 4,262,635 residents. Alberta's capital is Edmonton; its largest city is Calgary. The two cities are Alberta's largest Census geographic units ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Dundee
The University of Dundee is a public research university based in Dundee, Scotland. It was founded as a university college in 1881 with a donation from the prominent Baxter family of textile manufacturers. The institution was, for most of its early existence, a constituent college of the University of St Andrews alongside United College and St Mary's College located in the town of St Andrews itself. Following significant expansion, the University of Dundee gained independent university status by royal charter in 1967 while retaining elements of its ancient heritage and governance structure. The main campus of the university is located in Dundee's West End, which contains many of the university's teaching and research facilities; the Duncan of Jordanstone College of Art and Design, Dundee Law School and the Dundee Dental Hospital and School. The university has additional facilities at Ninewells Hospital, containing its School of Medicine; Perth Royal Infirmary, which hous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Statesman
''The New Statesman'' (known from 1931 to 1964 as the ''New Statesman and Nation'') is a British political and cultural news magazine published in London. Founded as a weekly review of politics and literature on 12 April 1913, it was at first connected with Sidney Webb, Sidney and Beatrice Webb and other leading members of the socialist Fabian Society, such as George Bernard Shaw, who was a founding director. The longest-serving editor was Kingsley Martin (1930–1960), and the most recent editor was Jason Cowley (journalist), Jason Cowley, who assumed the post in 2008 and left in 2024. Today, the magazine is a print–digital hybrid. According to its present self-description, it has a modern Liberalism in the United Kingdom, liberal and Independent progressive, progressive political position. Jason Cowley (journalist), Jason Cowley, the magazine's editor, has described the ''New Statesman'' as a publication "of the left, for the left" but also as "a political and literary magaz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Magazine
''The London Magazine'' is the title of six different publications that have appeared in succession since 1732. All six have focused on the arts, literature and poetry. A number of Nobel Laureates, including Annie Ernaux, Albert Camus, Doris Lessing and Nadine Gordimer have been published in its pages. It is England's oldest literary journal. 1732–1785 ''The London Magazine, or, Gentleman's Monthly Intelligencer'' was founded in 1732 in political opposition and rivalry to the Tory-supporting '' Gentleman's Magazine'' and ran for 53 years until its closure in 1785. Edward Kimber became editor in 1755, succeeding his father Isaac Kimber. Henry Mayo was editor from 1775 to 1783. Publishers included Thomas Astley. 1820–1829 In 1820 the ''London Magazine'' was resurrected by the publishers Baldwin, Craddock & Joy under the editorship of John Scott who formatted the magazine along the lines of the Edinburgh publication '' Blackwood's Magazine''. It was during this time tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |