|
Samuel Hodge
Samuel Hodge, VC ( 1840 – 14 January 1868) was a West Indian soldier in the British Army and a recipient of the Victoria Cross, the highest award for gallantry in the face of the enemy that can be awarded to British and Commonwealth soldiers. From the island of Tortola in the British Virgin Islands, he was the second black man to be awarded the Victoria Cross after William Hall. Details Samuel Hodge was one of the West Indian soldiers who garrisoned British positions on the West coast of Africa during the 19th century. White troops suffered terribly from malaria, blackwater fever and dysentery, and the War Office addressed the problem by using troops of the West India Regiments. In 1866, Lieutenant Colonel George Abbas Kooli D'Arcy, commanding officer of the 3rd West India Regiment and Governor of The Gambia, marched to confront a rebellious Marabout leader named Amar Faal at (also known as Tubab Kolon), a stockaded town on the northern bank of the River Gambia; taking w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis William Desanges
Louis William Desanges; Chevalier Desanges (1822–1905) was an English artist of French background, known today for his paintings of Victoria Cross winners. Life Born in Bexley, Kent, he was the great grandson of a French nobleman who had settled in England 80 years before and, as a consequence, the artist used the title 'Chevalier'. He travelled in France and Italy before settling in London in 1845; he later travelled to India. At first his pictures were of an historical nature, but he turned more to portrait painting as it was more lucrative. While painting a portrait of Lieut. Col. Robert Lindsay (created Baron Wantage in 1885) who had won the Victoria Cross at the Battle of the Alma at his home in Wantage, the two men came up with idea of creating a series of paintings containing portraits of the various soldiers winning their V.C. medals. Many of these were exhibited at the Egyptian Gallery in Piccadilly, and 47 of the paintings were exhibited at the Crystal Palace a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Abbas Kooli D'Arcy
George Abbas Kooli D'Arcy (30 July 1818 – 22 October 1885) was a British soldier and colonial administrator. He was governor of the Gambia from 1859 to 1866, and governor of the Falkland Islands from 1870 to 1876. Early life D'Arcy was born in London, the son of Lt Col Joseph D'Arcy and Lady Catherine Georgiana West (daughter of the 4th Earl De La Warr). D'Arcy's father was a Major (25/11/1813) in the Royal Artillery who arrived in Persia in with the Ambassador, Sir Gore Ouseley, to reform and equip the Persian Army, the British Mission to Herat, and as a result D'Arcy was named in honour of the Shah of Persia. The Shah had requested that Joseph name his eldest son after him. Joseph being of modest mind named the child Abbas Kooli, not liking to take the title of the Shah as well as the name "Khan" signifying Highness, whereas "Kooli" meant ordinary. Career D'Arcy became a Colonel in the 3rd West India Regiment. In 1859, he was appointed governor of The Gambia. A yellow fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British West Indies Recipients Of The Victoria Cross
British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. * British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture * British English, the English language as spoken and written in United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and, more broadly, throughout the British Isles * Celtic Britons, an ancient ethno-linguistic group * Brittonic languages, a branch of the Insular Celtic language family (formerly called British) ** Common Brittonic, an ancient language Other uses *People or things associated with: ** Great Britain, an island ** British Isles, an island group ** United Kingdom, a sovereign state ** British Empire, a historical global colonial empire ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922) * British Raj, colonial India under the British Empire * British Hong Kong, colonial H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1868 Deaths
Events January * January 2 – British Expedition to Abyssinia: Robert Napier leads an expedition to free captive British officials and missionaries. * January 3 – The 15-year-old Mutsuhito, Emperor Meiji of Japan, declares the ''Meiji Restoration'', his own restoration to full power, under the influence of supporters from the Chōshū and Satsuma Domains, and against the supporters of the Tokugawa shogunate, triggering the Boshin War. * January 5 – Paraguayan War: Brazilian Army commander Luís Alves de Lima e Silva, Duke of Caxias, enters Asunción, Paraguay's capital. Some days later he declares the war is over. Nevertheless, Francisco Solano López, Paraguay's president, prepares guerrillas to fight in the countryside. * January 7 – The Arkansas constitutional convention meets in Little Rock. * January 9 – Penal transportation from Britain to Australia ends, with arrival of the convict ship ''Hougoumont'' in Western Australia, after a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1840s Births
__NOTOC__ Year 184 ( CLXXXIV) was a leap year starting on Wednesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Eggius and Aelianus (or, less frequently, year 937 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 184 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place China * The Yellow Turban Rebellion and Liang Province Rebellion break out in China. * The Disasters of the Partisan Prohibitions ends. * Zhang Jue leads the peasant revolt against Emperor Ling of Han of the Eastern Han dynasty. Heading for the capital of Luoyang, his massive and undisciplined army (360,000 men), burns and destroys government offices and outposts. * June – Ling of Han places his brother-in-law, He Jin, in command of the imperial army and sends them to attack the Yellow Turban rebels. * Winter – Zhang Jue dies of illness while his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacis
A glacis (, ) in military engineering is an artificial slope as part of a medieval castle or in early modern fortresses. They may be constructed of earth as a temporary structure or of stone in more permanent structure. More generally, a glacis is any slope, natural or artificial, which fulfils the above requirements. The etymology of this French word suggests a slope made dangerous with ice, hence the relationship with ''glacier''. A ''glacis plate'' is the sloped front-most section of the hull of a tank or other armoured fighting vehicle. Ancient fortifications A glacis could also appear in ancient fortresses, such as the one the ancient Egyptians built at Semna in Nubia. Here it was used by them to prevent enemy siege engines from weakening defensive walls. Hillforts in Britain started to incorporate glacis around 350 BC. Those at Maiden Castle, Dorset were high. Medieval fortifications Glacises, also called taluses, were incorporated into medieval fortifications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pioneer (military)
A pioneer () is a soldier employed to perform engineering and construction tasks. The term is in principle similar to sapper or combat engineer. Pioneers were originally part of the artillery branch of European armies. Subsequently, they formed part of the military engineering, engineering branch, the military logistics, logistic branch, part of the infantry, or even comprised a branch in their own right. Historically, the primary role of pioneer units was to assist other arms in tasks such as the construction of trench warfare#Field works, field fortifications, military camps, bridges and roads. Prior to and during the First World War, pioneers were often engaged in the construction and repair of military railways. During World War II, pioneer units were used extensively by all major forces, both on the front line and in supporting roles. During the 20th century, British Commonwealth military forces came to distinguish between small units of "assault pioneers" belonging to infan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belize
Belize is a country on the north-eastern coast of Central America. It is bordered by Mexico to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and Guatemala to the west and south. It also shares a maritime boundary with Honduras to the southeast. Part of the Caribbean region, Belize is a member of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM) and the Commonwealth Caribbean, the historical British West Indies. The Maya civilization spread into the area of Belize between 1500 BCE and 300 CE and flourished until about 1200. European contact began in 1502–04 when Christopher Columbus sailed along the Gulf of Honduras. European exploration was begun by English settlers in 1638. Spanish Empire, Spain and Kingdom of Great Britain, Britain both laid claim to the land until Britain defeated the Spanish in the Battle of St. George's Caye (1798). It became British Honduras, a British colony in 1840, and a Crown colony in 1862. Belize achieved its independence from the United Kingdom on 21 September ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lance Corporal
Lance corporal is a military rank, used by many English-speaking armed forces worldwide, and also by some police forces and other uniformed organisations. It is below the rank of corporal. Etymology The presumed origin of the rank of lance corporal derives from an amalgamation of "corporal" from the Italian phrase ''capo corporale'' ("head of the body") with the now-archaic ''wikt:lancepesade, lancepesade'', which in turn derives from the Italian ''lancia spezzata'', which literally means "broken lance" or "broken spear", formerly a non-commissioned officer of the lowest rank. It can be translated as "one who has broken a lance in combat", and is therefore a leader. Other sources claim that it referred to a knight who had broken his lance and lost his horse, and thus had to join a foot company temporarily; or to gendarmerie who could no longer afford to fight on horseback and formed a foot unit. "Lance" or "lances fournies" was also a term used in medieval Europe to denote a uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Private (rank)
A private is a soldier, usually with the lowest Military rank, rank in many armies. Soldiers with the rank of private may be conscription, conscripts or they may be professional (career) soldiers. The term derives from the term "private soldier". "Private" comes from the Latin word ''privus'' or perhaps ''privo'' that meant an individual person and later an individual without an Official (other), office. Asia Indonesia In Indonesia, this rank is referred to as ''Tamtama'' (specifically ''Prajurit'' which means soldier), which is the lowest rank in the Indonesian National Armed Forces. In the Indonesian Army, Indonesian Marine Corps, and Indonesian Air Force, "Private" has three levels, which are: Private (''Prajurit Dua''), Private First Class (''Prajurit Satu''), and Chief Private (''Prajurit Kepala''). After this rank, the next promotion is to Corporal. File:prada pdh ad.png, Private (''Prajurit Dua'') File:pratu pdh ad.png, Private First Class (''Prajurit Satu'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
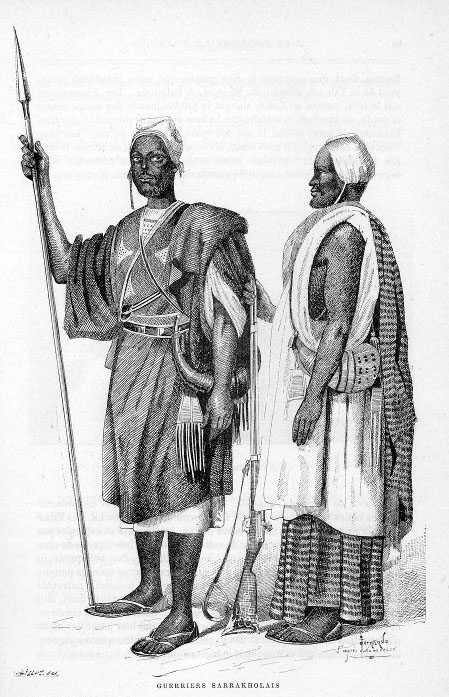
Soninke People
The Soninke (Sarakolleh) people are a West African Mande languages, Mande-speaking ethnic group found in Mali, southern Mauritania, eastern Senegal, The Gambia, and Guinea (especially Fouta Djallon). They speak the Soninke language, also called the Serakhulle or Azer language, which is one of the Mande languages. Soninke people were the founders of the ancient Ghana Empire, empire of Ghana or Wagadou c. 200–1240 CE, Subgroups of Soninke include the Jakhanke, Maraka and Soninke Wangara, Wangara. When the Ghana empire was destroyed, the resulting diaspora brought Soninkes to Mali, Mauritania, Senegal, Gambia, Burkina Faso, Côte d'Ivoire, Guinée-Conakry, modern-day Republic of Ghana, Kano in Nigeria, and Guinea-Bissau where some of this trading diaspora was called Wangara, leading to the saying “when Americans landed on the moon, a Soninke was already there” in Senegal, with other versions across West Africa. Predominantly Muslims, the Soninke were one of the early ethnic gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
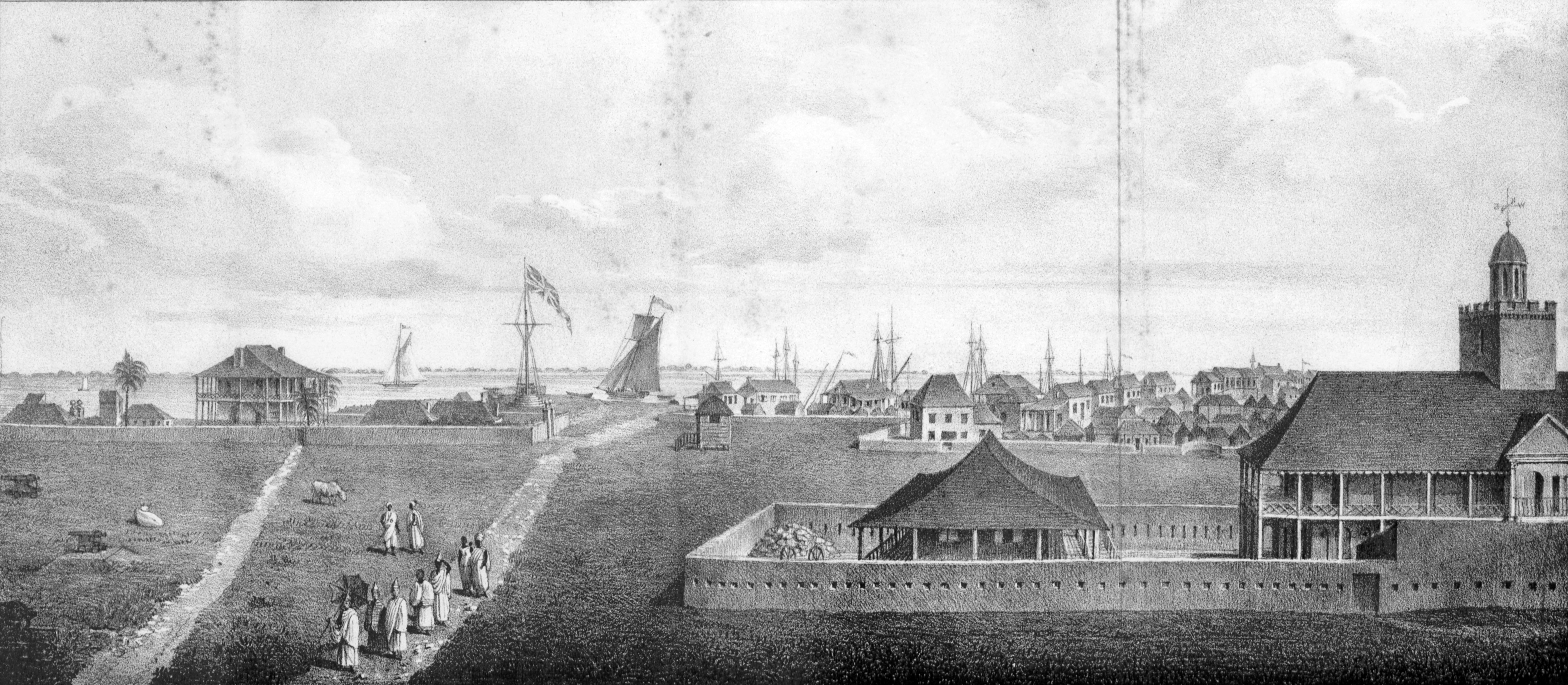
Banjul
Banjul (, (US) and ), officially the City of Banjul, is the capital city of The Gambia. It is the centre of the eponymous administrative division which is home to an estimated 400,000 residents, making it The Gambia's largest and most densely populated metropolitan area. The city Banjul is located on St Mary's Island (Banjul Island), where the Gambia River enters the Atlantic Ocean. The population of the city proper is 31,301, with the Greater Banjul Area, which includes the City of Banjul and the Kanifing Municipal Council, at a population of 413,397 (2013 census). The island is connected to the mainland to the west and the rest of Greater Banjul Area via bridges. There are also ferries linking Banjul to the mainland at the other side of the river. From the 19th century until 24 April 1973, the city was known as Bathurst. Etymology There are several etymologies for 'Banjul.' One traditional history recounts that Bandjougou, son of Barafin, came to the island after fleeing t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |