|
Sampit Conflict
The Sampit conflict, Sampit war or Sampit riots was an outbreak of inter-ethnic violence in Indonesia, beginning in February 2001 and lasting through the year. The conflict started in the town of Sampit, Central Kalimantan, and spread throughout the province, including the capital Palangka Raya. The conflict took place between the indigenous Dayak people and the migrant Madurese people from the island of Madura off Java. The exact origin of the conflict is disputed, but it eventually culminated in hundreds of deaths, with at least one hundred Madurese being decapitated. Background The 2001 Sampit conflict was not an isolated incident, as there had been previous incidents of violence between the Dayak and the Madurese. The last major conflict occurred between December 1996 and January 1997, and resulted in more than 600 deaths. The Madurese first arrived in Borneo in 1930 under the transmigration program initiated by the Dutch colonial administration, and continued by the Indones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-Suharto Era
The Post-Suharto era () is the contemporary history in Indonesia, which began with fall of Suharto, the resignation of authoritarian President of Indonesia, president Suharto on 21 May 1998. Since his resignation, the country has been in a period of transition, colloquially known as the Reform era (). This period has been characterised by a more open political-social environment and grassroots economic improvement. Issues over this period have included a push for a stronger democracy and civilian rule, elements of the Indonesian National Armed Forces, military trying to retain their influence, a growing Islamism in Politics of Indonesia, politics and Islam in Indonesia, society, and demands for greater regional autonomy. The process of has resulted in a higher degree of freedom of speech, in contrast to the pervasive censorship under the New Order (Indonesia), New Order. This has led to a more open political debate in the news media and increased expression in the arts. Events ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arson
Arson is the act of willfully and deliberately setting fire to or charring property. Although the act of arson typically involves buildings, the term can also refer to the intentional burning of other things, such as motor vehicles, watercraft, or forests. The crime is typically classified as a felony, with instances involving risk to human life or property carrying a stricter penalty. Arson that results in death can be further prosecuted as manslaughter or murder. A common motive for arson is to commit insurance fraud. In such cases, a person destroys their own property by burning it and then lies about the cause in order to collect against their insurance policy. Arson is also often committed to conceal another crime, such as murder or burglary. A person who commits arson is referred to as an arsonist, or a serial arsonist if the person has committed arson several times. Arsonists normally use an accelerant (such as gasoline or kerosene) to ignite, propel, and direct fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conflicts In 2001
Conflict may refer to: Social sciences * Conflict (process), the general pattern of groups dealing with disparate ideas * Conflict continuum from cooperation (low intensity), to contest, to higher intensity (violence and war) * Conflict of interest, involvement in multiple interests which could possibly corrupt the motivation or decision-making * Cultural conflict, a type of conflict that occurs when different cultural values and beliefs clash * Ethnic conflict, a conflict between two or more contending ethnic groups * Group conflict, conflict between groups * Intragroup conflict, conflict within groups * Organizational conflict, discord caused by opposition of needs, values, and interests between people working together * Role conflict, incompatible demands placed upon a person such that compliance with both would be difficult * Social conflict, the struggle for agency or power in something * Work–family conflict, incompatible demands between the work and family roles of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmigration Program
The transmigration program (, from Dutch language, Dutch, ''transmigratie'') was an initiative of the Netherlands, Dutch Dutch East Indies, colonial government and later continued by the government of Indonesia, Indonesian government to move landless people from densely populated areas of Indonesia to less populous areas of the country. This involved moving people permanently from the island of Java (island), Java, but also to a lesser extent from Bali and Madura Island, Madura to less densely populated areas including Kalimantan, Sumatra, Sulawesi, Maluku Islands, Maluku and Western New Guinea, Papua. The program is currently coordinated by Ministry of Transmigration. The stated purpose of this program was to reduce the considerable poverty and Human overpopulation, overpopulation on Java, to provide opportunities for hard-working poor people, and to provide a workforce to utilize better the natural resources of the outer islands. The program, however, has been controversial as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarakan
Tarakan is an island and co-extensively the sole city within the Indonesian province of North Kalimantan. The island city is the largest urban area in North Kalimantan population-wise and is located in northern Borneo, midway along the coast of the province. The city boundaries are co-extensive with the island (including a couple of small islands off the coast of the Tarakan Barat District). Once a major oil-producing region during the colonial period, Tarakan had great strategic importance during the Pacific War and was among the first Japanese targets early in the conflict. It is the sole city within the Indonesian province of North Kalimantan (established in 2012). According to Statistics Indonesia, the city had a population of 193,370 at the 2010 CensusBiro Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2011. and 242,786 inhabitants at the 2020 Census;Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2021. the official estimate as at mid 2024 was 255,310 (comprising 132,175 males and 123,135 females).Badan Pusat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bugis
The Bugis people, also known as Buginese, are an Austronesian ethnic groupthe most numerous of the three major linguistic and ethnic groups of South Sulawesi (the others being Makassarese and Torajan), in the south-western province of Sulawesi, third-largest island of Indonesia. The Bugis in 1605 converted to Islam from Animism. Although the majority of Bugis are Muslim, a small minority adhere to Christianity as well as a pre-Islamic indigenous belief called ''Tolotang''. The Bugis, whose population numbers around six million and constitutes less than 2.5% of the Indonesian population, are influential in the politics in the country; and historically influential on the Malay Peninsula, Sumatra, Borneo, Lesser Sunda Islands and other parts of the archipelago where they have migrated en masse, starting in the late seventeenth century. The third president of Indonesia, B. J. Habibie, and a former vice president of Indonesia, Jusuf Kalla, are Bugis descent. In Malaysia, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tidung
The Tidung, Tidong ( Jawi: تيدوڠ) are a native group originating from northeastern part of Borneo and surrounding small islands. They live on both sides of the border of Malaysia and Indonesia. Tidung speak Tidong language, a North Bornean language. The Tidong are traditionally farmers practising slash-and-burn agriculture. Some are ocean fishermen. They grow sweet potatoes, cassava, lentils, fruits, and vegetables. Their farming methods are often accused of being the main cause of forest fires in Kalimantan. The rise of the Muslim Tidung Sultanate molded the ethnogenesis character of the Tidung people. They collectively known as a Malayised Dayak (Indonesian: ''Dayak berbudaya Melayu'' or ''Dayak-Melayu'') people of Kalimantan similar to other native Muslim coastal Borneo groups, such as the Bulungan, Kutainese, Banjarese and Paserese people. Nonetheless, the Tidung people maintain historical connections with the Murut community. Despite following distinct cultural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarakan Riot
The Tarakan riot was an ethnic riot which occurred between September 27 and September 29, 2010 in the city of Tarakan, East Kalimantan (now part of North Kalimantan), Indonesia. The riot pitched native Tidung people against Bugis migrants. It was triggered by the death of a Tidung elder in a scuffle with a youth gang. During the ensuing riot four people were killed and thousands of civilians were displaced, before a peace agreement was made between the communities. Background Tarakan, located on Tarakan Island, is one of the major cities in eastern Borneo (now Northern Borneo). It had a population of 178,111 in 2008. Native residents are the Tidung, a subgroup of the Dayak people. The city also has a multi-ethnic population from other parts of Indonesia, such as Bugis, Javanese and Chinese Indonesians. The Tidung are a group of Malayised Dayak people who live in the north-eastern part of Borneo and surrounding small islands. They live on both sides of the border of Malays ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sambas Riots
The Sambas riots were an outbreak of inter-ethnic violence in Indonesia, in 1999 in the regency of Sambas, West Kalimantan Province and involved the Madurese on one side and an alliance of the indigenous Dayak people and Sambas Malays on the other. The Madurese and Dayak were inspired by their respective traditions of violence: ''carok'' for the Madurese and ''ngayau'' or headhunting for the Dayak. The Dayak attempt to settle disputes first by means of a peaceful agreement and only practice "ngayau" when they are violently attacked, while the Madurese practice "carok" as a first measure. In this case, the Madurese aggressively murdered some Dayak by using a sickle (celurit), so the Dayak responded out of self-defense. As for the Malays, they do not have a tradition of violence but allied with the Dayak due to harassment of the migrant Madurese over the course of many decades. Background The Sambas riots in 1999 were not an isolated incident, as there had been previous inciden ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
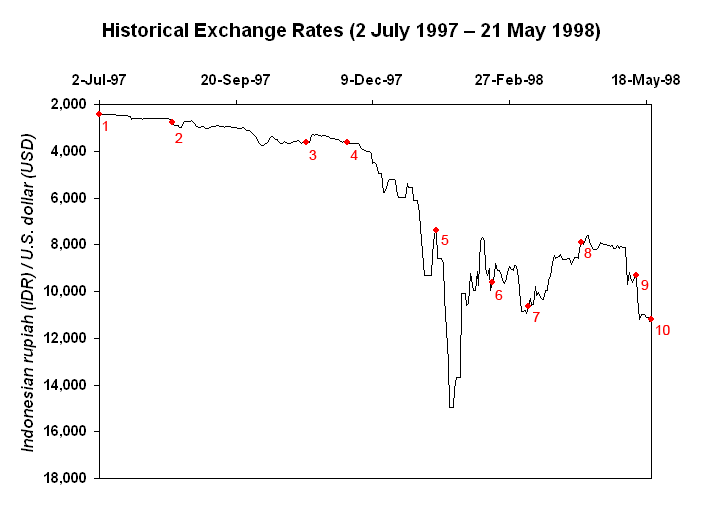
Fall Of Suharto
On 21 May 1998, Suharto resigned as president of Indonesia following protests and riots across the country against his regime. His vice president, B. J. Habibie, took over the presidency. Suharto's grip on power weakened following severe economic and political crises stemming from the 1997 Asian financial crisis. The economy suffered a flight of foreign capital, leading to a drastic drop in the value of the Indonesian rupiah, which severely impacted the economy and people's livelihoods. Suharto was re-elected to his seventh term by the People's Consultative Assembly in March 1998. Increasing political unrest and violence undermined his previously firm political and military support, leading to his May 1998 resignation. Initially under newly installed President Habibie, a period of political reform ('' Reformasi'') followed. Historical background Dissent during the New Order Having consolidated power in 1967 in the aftermath of the attempted coup in 1965 which wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Of Indonesia
The asterisk ( ), from Late Latin , from Ancient Greek , , "little star", is a typographical symbol. It is so called because it resembles a conventional image of a heraldic star. Computer scientists and mathematicians often vocalize it as star (as, for example, in ''the A* search algorithm'' or ''C*-algebra''). An asterisk is usually five- or six-pointed in print and six- or eight-pointed when handwritten, though more complex forms exist. Its most common use is to call out a footnote. It is also often used to censor offensive words. In computer science, the asterisk is commonly used as a wildcard character, or to denote pointers, repetition, or multiplication. History The asterisk was already in use as a symbol in ice age cave paintings. There is also a two-thousand-year-old character used by Aristarchus of Samothrace called the , , which he used when proofreading Homeric poetry to mark lines that were duplicated. Origen is known to have also used the asteriskos to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Cannibalism
Human cannibalism is the act or practice of Human, humans eating the Meat, flesh or internal organs of other human beings. A person who practices cannibalism is called a cannibal. The meaning of "cannibalism" has been extended into zoology to describe animals consuming parts of individuals of the same species as food. Early modern human, Anatomically modern humans, Neanderthals, and ''Homo antecessor'' are known to have practised cannibalism to some extent in the Pleistocene. Cannibalism was occasionally practised in Egypt during ancient Egypt, ancient and Roman Egypt, Roman times, as well as later during severe famines. The Island Caribs of the Lesser Antilles, whose name is the origin of the word ''cannibal'', acquired a long-standing reputation as eaters of human flesh, reconfirmed when their legends were recorded in the 17th century. Some controversy exists over the accuracy of these legends and the prevalence of actual cannibalism in the culture. Reports describing cannib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |