|
Samanar
Tamil Jains (Tamil Samaṇar, from Prakrit '' samaṇa'' "wandering renunciate") are ethnic-Tamils from the Indian state of Tamil Nadu, who practice Jainism (Tamil ). The Tamil Jain is a microcommunity of around 85,000 (around 0.13% of the population of Tamil Nadu). They are predominantly scattered in northern Tamil Nadu, largely in the districts of Tiruvannamalai, Kanchipuram, Vellore, Villupuram, Ranipet and Kallakurichi. Early Tamil-Brahmi inscriptions in Tamil Nadu date to the third century BCE and describe the livelihoods of Tamil Jains. ''Samaṇar'' wrote much Tamil literature, including the important Sangam literature, such as the ''Nālaṭiyār'', the ''Cilappatikaram'', the ''Valayapathi'' and the '' Civaka Cintamani''. Three of the five great epics of Tamil literature are attributed to Jains. History Origins Some scholars believe that Jain philosophy must have entered South India some time in the sixth century BCE. According to other scholars, Jainism must have e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
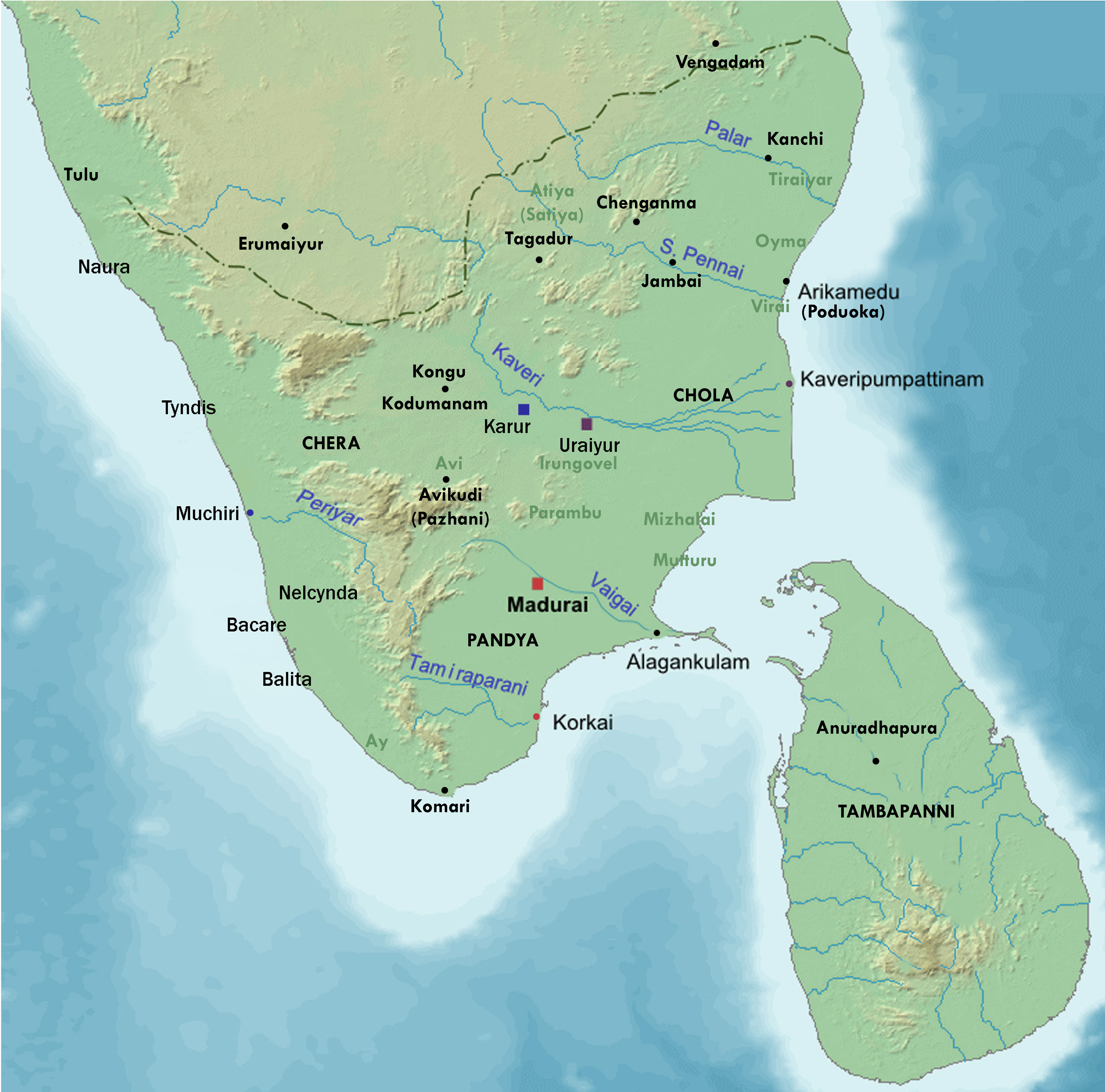
Madurai
Madurai ( , , ), formerly known as Madura, is a major city in the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is the cultural capital of Tamil Nadu and the administrative headquarters of Madurai District, which is governed by the Madurai Municipal Corporation established on 1 November 1866. As of the 2011 Census of India, 2011 census, it is the List of cities in India by population, third largest metropolis in Tamil Nadu after Chennai and Coimbatore in terms of population and 27th largest List of million-plus urban agglomerations in India, urban agglomeration in India. Located on the banks of River Vaigai, Madurai has been a major settlement for two millennia and has a documented history of more than 2500 years. It is often referred to as "Thoongatha Nagaram", meaning "the city that never sleeps". Madurai is closely associated with the Tamil language. The third Tamil Sangam, a major congregation of Tamil scholars, is said to have been held in the ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhattaraka
A Bhaṭṭāraka (; ) heads traditional Digambara Jain institutions. He is responsible for training scholars, maintenance of libraries, managing endowments, presiding over installation ceremonies and running Jain institutions. Overview The term ''bhaṭṭāraka'' was used for Virasena, Bhadrabahu and other notables. It has also been used for the Tirthankaras. It was in the past used for leaders of religious orders in Shaivism, Buddhism and other groups, but currently it is applied to heads of Digambara Jain institutions. Unlike a Digambara monk, a bhaṭṭāraka wears an orange robe, stays in a single place and is involved in management of assets of the institution. Several of the Bhattarak seats were termed "Vidyasthana" i.e. centers of learning. These include Jaipur, Delhi, Gwalior, Ajmer, Nagaur, Rampur-Bhanpura, Karanaja, Surat, Kolhapur, Jinakanchi, Penukonda, Malkhed, Vijayanagara, Varanga and Hummacha. The role of a bhaṭṭāraka is described by Brahm Gyansag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kallakurichi
Kallakurichi is a Municipality in the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Tamil Nadu and the administrative headquarters of Kallakurichi district in Tamil Nadu. As of 2019, the town had a population of 73528. Member of the Legislative Assembly (India), Member of the Legislative Assembly (Tamil Nadu) is M. Senthilkumar Demographics According to 2011 census of India, 2011 census, Kallakurichi had a population of 52,508 with a sex-ratio of 984 females for every 1,000 males, much above the national average of 929. A total of 5,541 were under the age of six, constituting 2,914 males and 2,627 females. Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes accounted for 15.49% and .27% of the population respectively. The average literacy of the town was 77.08%, compared to the national average of 72.99%. The town had a total of 12801 households. There were a total of 19,013 workers, comprising 471 cultivators, 840 main agricultural labourers, 537 in house hold industries, 14,673 o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thanjavur
Thanjavur (), also known as Thanjai, previously known as Tanjore, Pletcher 2010, p. 195 is a city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is the 12th biggest city in Tamil Nadu. Thanjavur is an important center of southern Indian religion, art, and architecture. Most of the Great Living Chola Temples, which are UNESCO World Heritage Monuments, are located in and around Thanjavur. The foremost among these, the Brihadisvara Temple, built by the Chola emperor Rajaraja I, is located in the centre of the city. This temple has one of the largest bull statues (called Nandi) in India carved out of a single granite rock. Thanjavur is also home to Tanjore painting, a painting style unique to the region. Thanjavur is the headquarters of the Thanjavur District. The city is an important agricultural centre located in the Kaveri Delta and is known as the ''Rice bowl of Tamil Nadu''. Thanjavur is administered by a municipal corporation covering an area of and had a population of 222,943 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanyakumari
Kanyakumari (Tamil; / kəɳjɑkʊmɑɾiː/; referring to Devi Kanya Kumari, officially known as Kanniyakumari, formerly known as Cape Comorin) is a town and a municipality in Kanyakumari district in the state of Tamil Nadu, India. It is the southernmost tip of the contiguous Indian subcontinent and the southernmost city in mainland India, and thus it is informally referred to as "The Land's End". Kanyakumari town is about from Thiruvananthapuram and south of Nagercoil, the headquarters of Kanyakumari district. Kanyakumari is a popular tourist destination and pilgrimage centre in India. Notable tourist spots include its unique sunrise and sunset points, the '' Thiruvalluvar Statue'', and Vivekananda Rock Memorial off the coast. Lying at the tip of peninsular India, the town is bordered on the west, south, and east by the Laccadive Sea. It has a coastline of stretched along these three sides. On the shores of the city is a temple dedicated to the goddess Kanya Kumari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiruchirappalli
Tiruchirappalli (), also known as Trichy, is a major tier II city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu and the administrative headquarters of Tiruchirappalli district. The city is credited with being the best livable and the cleanest city of Tamil Nadu, as well as the fifth safest city for women in India. It is the fourth largest city as well as the fourth largest urban agglomeration in the state. Located south of Chennai and north of Kanyakumari, Tiruchirappalli sits almost at the geographic centre of Tamil Nadu. The Cauvery Delta begins west of the city where the Kaveri river splits into two, forming the island of Srirangam which is now incorporated into the Tiruchirappalli City Municipal Corporation. The city occupies an area of and had a population of 916,857 in 2011. Tiruchirappalli's recorded history begins under Chola rule in the 3rd century BC. The city has also been ruled by the Pallavas, Pandyas, Vijayanagar Empire, Nayak Dynasty, the Carnatic state and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South India
South India, also known as Southern India or Peninsular India, is the southern part of the Deccan Peninsula in India encompassing the states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu and Telangana as well as the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry, occupying 19.31% of India's area () and 20% of India's population. It is bound by the Bay of Bengal in the east, the Arabian Sea in the west and the Indian Ocean in the south. The geography of the region is diverse, with two mountain ranges, the Western and Eastern Ghats, bordering the plateau heartland. The Godavari, Krishna, Kaveri, Penna, Tungabhadra and Vaigai rivers are important non-perennial sources of water. Chennai, Bengaluru, Hyderabad, Coimbatore and Kochi are the largest urban areas in the region. The majority of the people in South India speak at least one of the four major Dravidian languages: Telugu, Tamil, Kannada and Malayalam. During its history, a number of dynastic kingdoms ruled ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jambai Tamil Brahmi
Jambai is a panchayat town in Bhavani Taluk Erode district in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. Demographics India census A census (from Latin ''censere'', 'to assess') is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording, and calculating population information about the members of a given Statistical population, population, usually displayed in the form of stati ..., Jambai had a population of 14,999. Males constitute 51% of the population and females 49%. Jambai has an average literacy rate of 54%, lower than the national average of 59.5%: male literacy is 63%, and female literacy is 45%. In Jambai, 9% of the population is under 6 years of age. Pincode is 638312. Villages * Amman Kovil Pudur * Chinnamolapalayam * Chinnavadamalaipalayam * Chinniyampalayam * Jambai Pudur * Karukkuppalayam * Muthukoundanoor * Nallipalayam * Periyavadamalaipalayam * Periyamolapalayam * Perumapalayam * Pilagiri Naickenpalayam * Thalavaipettai * Thurusampalayam * Seethapalayam * Vaaikaalpal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valayapathi
''Valaiyapadhi'' (; ), also spelled ''Valayapathi'', is one of the five great Tamil epics, but one that is almost entirely lost. It is a story of a father who has two wives, abandons one who gives birth to their son, and the son grows up and seeks his real father. The dominant emotion of this epic is love, and its predominant object is the inculcation of Jain principles and doctrines. Palm-leaf manuscripts of the epic likely existed until the 19th-century, but presently only uncertain fragments of the epic are known from commentaries and the 14th-century anthology ''Purattirattu''. Based on these fragments, the epic appears to be the story of a merchant with an overseas trading business who married two women. He abandoned one, who later gives birth to his son. He has children with the other wife too. The abandoned son is bullied by overseas kids for not knowing the name of his father. His mother then discloses the father's name. The son travels and confronts his father, who f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silappatikaram
''Cilappatikāram'' ( IPA: ʧiləppət̪ikɑːrəm, ''lit.'' "the Tale of an Anklet"), also referred to as ''Silappathikaram'' or ''Silappatikaram'', is the earliest Tamil epic. It is a poem of 5,730 lines in almost entirely ''akaval'' (''aciriyam'') meter. The epic is a tragic love story of an ordinary couple, Kaṇṇaki and her husband Kōvalaṉ. The ''Cilappatikāram'' has more ancient roots in the Tamil bardic tradition, as Kannaki and other characters of the story are mentioned or alluded to in the Sangam literature such as in the '' Natṟiṇai'' and later texts such as the ''Kovalam Katai''. It is attributed to a prince-turned-jain-monk Iḷaṅkō Aṭikaḷ, and was probably composed in the 5th century CE (although estimates range from 2nd to 6th century CE). The ''Cilappatikāram'' is an ancient literary masterpiece. It is to the Tamil culture what the ''Iliad'' is to the Greek culture, states R. Parthasarathy. It blends the themes, mythologies and theologica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nālaṭiyār
The Nālaṭiyār () is a Tamil poetic work of didactic nature belonging to the Eighteen Lesser Texts (''Patiṉeṇkīḻkaṇakku'') anthology of Tamil literature. This belongs to the post Sangam period corresponding to between 100 and 500 CE. ''Nālaṭiyār'' contains 400 poems, each containing four lines. Every poem deals with morals and ethics, extolling righteous behaviour. Etymology The term ''Naladiyar'' is derived from the Tamil terms ''Naalu'', a colloquial form of ''Naangu'' meaning “four”, ''adi'' meaning metrical feet or poetic metre, and ''aar'' referring to a honorific suffix. Thus ''Naladiyar'' refers to the work that contains four-lined verse. The work is also termed ''Naaladi Naanooru'', sometimes spelled ''Naladi Nannurru'', meaning "four hundred quatrains," since it has 400 verses in total. Didactic nature ''Nālaṭiyār'' was composed by Jain monks. It is an anthology in the venba metre and is pessimistic in its outlook. It is divided into three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |