|
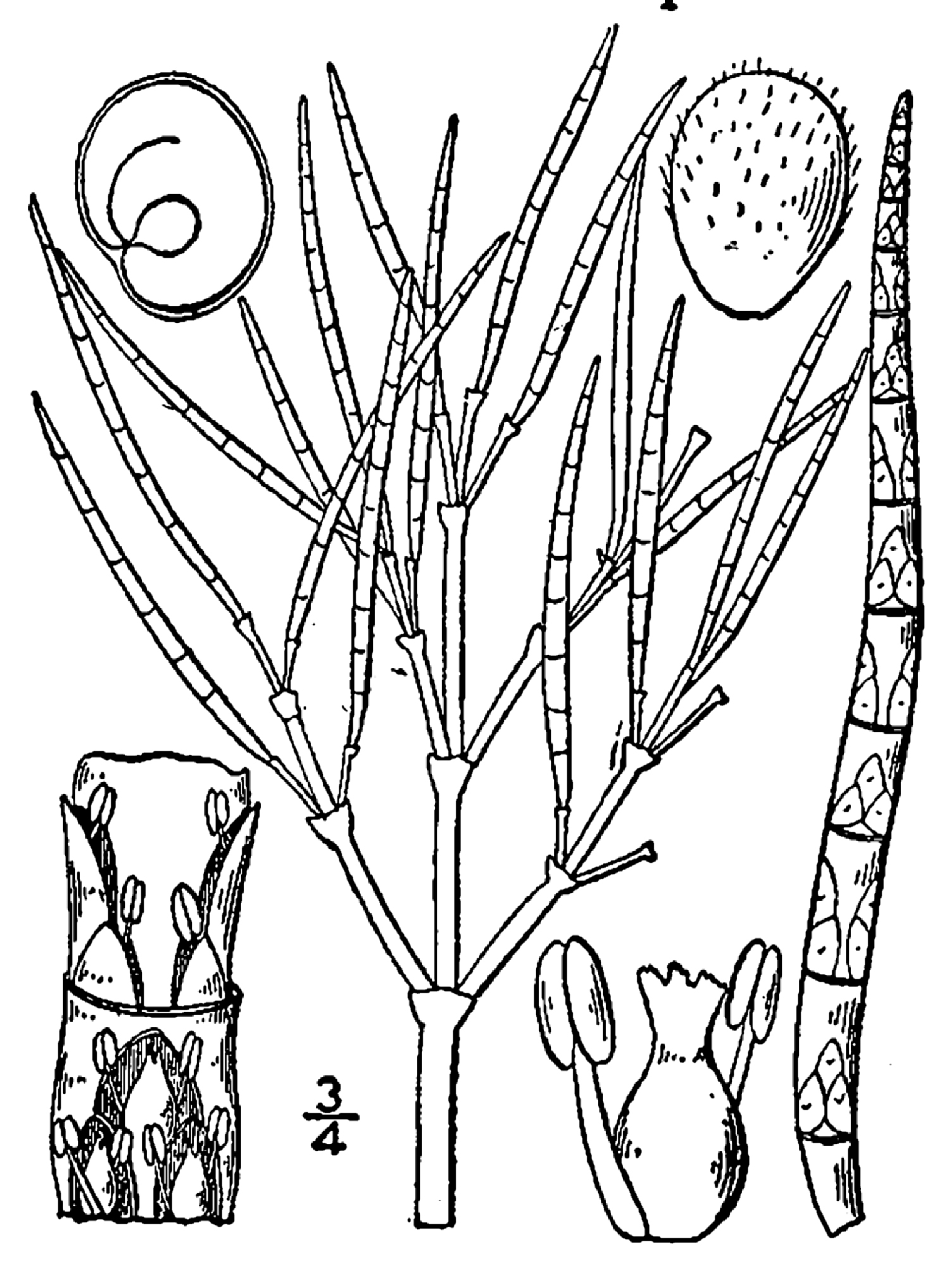
Salicornia
''Salicornia'' is a genus of succulent, halophytic (salt tolerant) flowering plants in the family Amaranthaceae that grow in salt marshes, on beaches, and among mangroves. ''Salicornia'' species are native to North America, Europe, central Asia, and southern Africa. Common names for the genus include glasswort, pickleweed, picklegrass, and marsh samphire; these common names are also used for some species not in ''Salicornia''. To French speakers in Atlantic Canada, they are known colloquially as ('mouse tits'). The main European species is often eaten, called marsh samphire in Britain, and the main North American species is occasionally sold in grocery stores or appears on restaurant menus as sea beans, samphire greens or sea asparagus. Description The ''Salicornia'' species are small annual herbs. They grow prostrate to erect, their simple or branched stems are succulent, hairless, and appear to be jointed. The opposite leaves are strongly reduced to small fleshy scales with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salicornia Europaea
''Salicornia europaea'', known as marsh samphire, common glasswort or just glasswort, is a halophytic annual dicot flowering plant. Other common names include pickle weed, saltwort, and chicken toe (due to the shape). It is a succulent plant with high water content, accounting for its slightly translucent look (the source of the name 'glasswort'). It is found near saline water in Europe and is edible both raw and cooked. Description Glasswort plants are relatively small and have jointed, bright green stems. During the fall, these plants turn red or purple. Their leaves are small and scale like, and they produce fleshy fruits that contain a single seed. Like most members of the subfamily Salicornioideae, ''Salicornia'' species use the C3 carbon fixation pathway to take in carbon dioxide from the surrounding atmosphere. Distribution and habitat It is found on most coastlines in Europe. It grows in various zones of intertidal salt marshes, on beaches, and among mangroves. Cul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glasswort
The glassworts are various succulent, annual halophytic plants, that is, plants that thrive in saline environments, such as seacoasts and salt marshes. The original English glasswort plants belong to the genus '' Salicornia'', but today the glassworts include halophyte plants from several genera, some of which are native to continents unknown to the medieval English, and growing in ecosystems, such as mangrove swamps, never envisioned when the term glasswort was coined. The common name "glasswort" came into use in the 16th century to describe plants growing in England whose ashes could be used for making soda-based (as opposed to potash-based) glass.Turner, William (1995). ''A New Herball: Parts II and III'', edited by George T. L. Chapman, Frank McCombie, and Anne U. Wesencraft (Cambridge University Press, ). This book contains a facsimile of Turner's original 1562 and 1568 volumes, along with an edited transcript. The transcript of Turner's article on Kali (p. 673) includes t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salicornia Maritima
''Salicornia maritima'', the sea glasswort, is a succulent, salt-tolerant plant found along the eastern coast of North America, including Maine and New Brunswick New Brunswick is a Provinces and Territories of Canada, province of Canada, bordering Quebec to the north, Nova Scotia to the east, the Gulf of Saint Lawrence to the northeast, the Bay of Fundy to the southeast, and the U.S. state of Maine to .... It produces flowers towards late summer or beginning of fall. This plant is sometimes mistaken for '' Salicornia depressa''. Description ''Salicornia maritima'' has terminal spikes and branches that are swollen and rounded at the tips. Fertile segments grow thicker and become reddish towards the end of the year. References maritima Flora of Newfoundland Flora of Labrador {{Amaranthaceae-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salicornioideae
The Salicornioideae are a subfamily of the flowering plant family Amaranthaceae (''sensu lato'', including the Chenopodiaceae). Important characters are succulent, often articulated stems, strongly reduced leaves, and flowers aggregated in thick, dense spike-shaped thyrses. These halophyte, halophytic plants are distributed worldwide. Many are edible (see Samphire) Description The Salicornioideae are Annual plant, annual or Perennial plant, perennial herbs, subshrubs, or low shrubs. Their stems are glabrous and often apparently jointed. The alternate or opposite leaf, leaves are fleshy, glabrous, often basally connate and stem-clasping (thus forming the joints), with missing or short free leaf blades. The spike-shaped inflorescences consist of alternate or opposite bracts, these are often connate and stem-clasping, sometimes free. In the axil of each bract, there are one to five (rarely to twelve) flowers, free or sometimes fused to each other, to the bract, and to the inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samphire
Samphire is a name given to a number of succulent salt-tolerant plants (halophytes) that tend to be associated with water bodies. * Rock samphire ('' Crithmum maritimum'') is a coastal species with white flowers that grows in Ireland, the United Kingdom and the Isle of Man. This is probably the species mentioned by Shakespeare in ''King Lear''. * Golden samphire (''Limbarda crithmoides'') is a coastal species with yellow flowers that grows across Eurasia. * Several species in the genus ''Salicornia'', known as "marsh samphire" in Britain. * '' Blutaparon vermiculare'', Central America, southeastern North America * '' Tecticornia'', Australia * '' Sarcocornia'', cosmopolitan Following the construction of the Channel Tunnel, the nature reserve created on new land near Folkestone made from excavated rock was named " Samphire Hoe", a name coined by Mrs Gillian Janaway. Etymology Originally "sampiere", a corruption of the French "Saint Pierre" (Saint Peter), samphire was named af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halophytic
A halophyte is a salt-tolerant plant that grows in soil or waters of high salinity, coming into contact with saline water through its roots or by salt spray, such as in saline semi-deserts, mangrove swamps, marshes and sloughs, and seashores. The word derives from Ancient Greek ἅλας (halas) 'salt' and φυτόν (phyton) 'plant'. Halophytes have different anatomy, physiology and biochemistry than glycophytes.Physiology of halophytes, T. J. FLOWERS, Plant and Soil 89, 41–56 (1985) An example of a halophyte is the salt marsh grass ''Spartina alterniflora'' (smooth cordgrass). Relatively few plant species are halophytes—perhaps only 2% of all plant species. Information about many of the earth's halophytes can be found in thhalophytedatabase. The large majority of plant species are glycophytes, which are not salt-tolerant and are damaged fairly easily by high salinity. Classification Halophytes can be classified in many ways. According to Stocker (1933), it is mainly of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
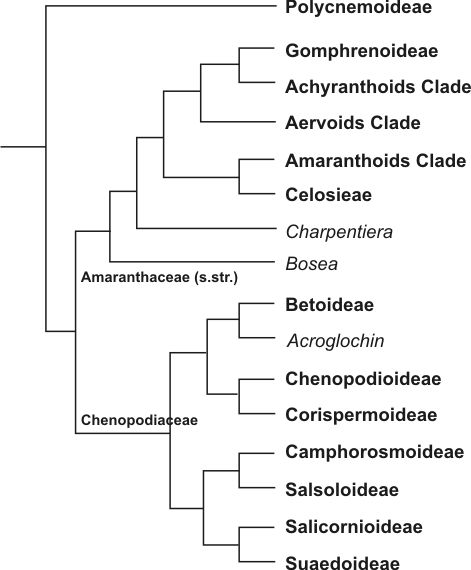
Amaranthaceae
Amaranthaceae ( ) is a family of flowering plants commonly known as the amaranth family, in reference to its type genus '' Amaranthus''. It includes the former goosefoot family Chenopodiaceae and contains about 165 genera and 2,040 species, making it the most species-rich lineage within its parent order, Caryophyllales. Description Most species in the Amaranthaceae are annual or perennial herbs or subshrubs; others are shrubs; very few species are vines or trees. Some species are succulent. Many species have stems with thickened nodes. The wood of the perennial stem has a typical "anomalous" secondary growth; only in subfamily Polycnemoideae is secondary growth normal. The leaves are simple and mostly alternate, sometimes opposite. They never possess stipules. They are flat or terete, and their shape is extremely variable, with entire or toothed margins. In some species, the leaves are reduced to minute scales. In most cases, neither basal nor terminal aggregations of leav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt Marsh
A salt marsh, saltmarsh or salting, also known as a coastal salt marsh or a tidal marsh, is a coastal ecosystem in the upper coastal intertidal zone between land and open saltwater or brackish water that is regularly flooded by the tides. It is dominated by dense stands of salt-tolerant plants such as herbs, grasses, or low shrubs. These plants are terrestrial in origin and are essential to the stability of the salt marsh in trapping and binding sediments. Salt marshes play a large role in the aquatic food web and the delivery of nutrients to coastal waters. They also support terrestrial animals and provide coastal protection. Salt marshes have historically been endangered by poorly implemented coastal management practices, with land reclaimed for human uses or polluted by upstream agriculture or other industrial coastal uses. Additionally, sea level rise caused by climate change is endangering other marshes, through erosion and submersion of otherwise tidal marshes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Succulent
In botany, succulent plants, also known as succulents, are plants with parts that are thickened, fleshy, and engorged, usually to retain water in arid climates or soil conditions. The word ''succulent'' comes from the Latin word ''sucus'', meaning "juice" or "sap". Succulents may store water in various structures, such as leaves and stems. The water content of some succulent organs can get up to 90–95%, such as '' Glottiphyllum semicyllindricum'' and '' Mesembryanthemum barkleyii''. Some definitions also include roots, thus geophytes that survive unfavorable periods by dying back to underground storage organs (caudex) may be regarded as succulents. The habitats of these water-preserving plants are often in areas with high temperatures and low rainfall, such as deserts, but succulents may be found even in alpine ecosystems growing in rocky or sandy soil. Succulents are characterized by their ability to thrive on limited water sources, such as mist and dew, which makes them ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pickleweed
Pickleweed is a common name used for two unrelated genera of flowering plants: *'' Batis'', family Bataceae *''Salicornia ''Salicornia'' is a genus of succulent, halophytic (salt tolerant) flowering plants in the family Amaranthaceae that grow in salt marshes, on beaches, and among mangroves. ''Salicornia'' species are native to North America, Europe, central Asia, ...'', family Amaranthaceae {{Short pages monitor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and means "less recent" because it has 18% fewer modern marine invertebrates than the Pliocene has. The Miocene followed the Oligocene and preceded the Pliocene. As Earth went from the Oligocene through the Miocene and into the Pliocene, the climate slowly cooled towards a series of ice ages. The Miocene boundaries are not marked by distinct global events but by regionally defined transitions from the warmer Oligocene to the cooler Pliocene Epoch. During the Early Miocene, Afro-Arabia collided with Eurasia, severing the connection between the Mediterranean and Indian Oceans, and allowing the interchange of fauna between Eurasia and Africa, including the dispersal of proboscideans and Ape, hominoids into Eurasia. During the late Miocene, the conn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |