|
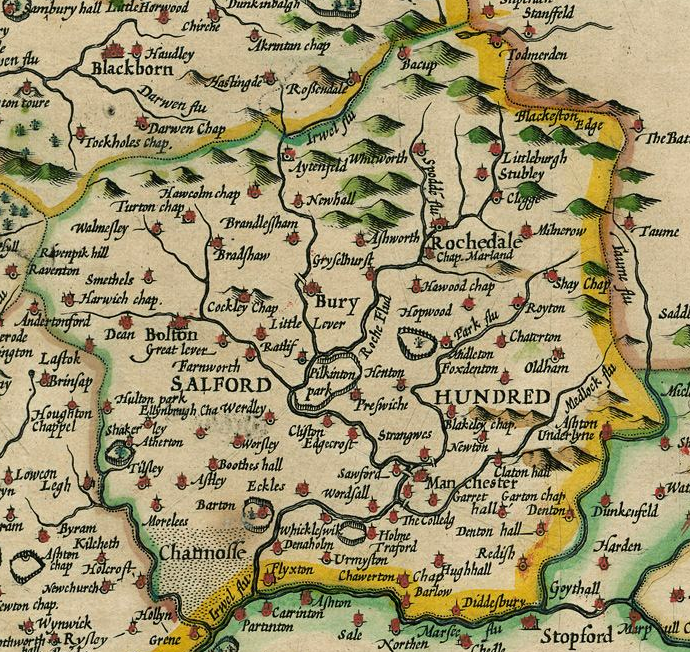
Salford Hundred
The Salford Hundred (also known as Salfordshire) was one of the subdivisions (a hundred) of the historic county of Lancashire in Northern England. Its name alludes to its judicial centre being the township of Salford (the suffix ''-shire'' meaning the territory was appropriated to the prefixed settlement). It was also known as the Royal Manor of Salford and the Salford wapentake.. Origins The Manor or Hundred of Salford had Anglo-Saxon origins. The ''Domesday Book'' recorded that the area was held in 1066 by Edward the Confessor. Salford was recorded as part of the territory of ''Inter Ripam et Mersam'' or "Between Ribble and Mersey", and it was included with the information about Cheshire, though it cannot be said clearly to have been part of Cheshire. The area became a subdivision of the County Palatine of Lancaster (or Lancashire) on its creation in 1182. Salford Hundred Court In spite of its incorporation into Lancashire, Salford Hundred retained a separate jurisdiction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salford, Greater Manchester
Salford ( ) is a City status in the United Kingdom, city in Greater Manchester, England, on the western bank of the River Irwell which forms its boundary with Manchester city centre. Landmarks include the former Salford Town Hall, town hall, Salford Cathedral, Salford Lads' Club and St Philip's Church, Salford, St Philip's Church. In 2021 it had a population of 129,794. The demonym for people from Salford is ''Salfordian''. Salford is the main settlement of the wider City of Salford metropolitan borough, which incorporates Eccles, Greater Manchester, Eccles, Pendlebury, Swinton, Greater Manchester, Swinton and Walkden. Salford was named in the Early Middle Ages, though evidence exists of settlement since Neolithic times. It was the seat of the large Hundred of Salford in the Historic counties of England, historic county of Lancashire and was granted a market charter in about 1230, which gave it primary cultural and commercial importance in the region.. It was eventually overt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reeve (England)
In Anglo-Saxon England, a reeve (Old English: ) was an administrative official serving the king or a lesser lord in a variety of roles. After the Norman Conquest, it was an office held by a man of lower rank, appointed as manager of a manor and overseer of the peasants. In this later role, historian H. R. Loyn observes, "he is the earliest English specialist in estate management." Types ''Reeve'' is a general term that could refer to a variety of administrative officials. Royal reeves worked for the king, but nobles and bishops also employed reeves. Some reeves served as estate managers, while others held positions in towns and boroughs. Royal reeves In the late 7th and early 8th centuries, royal reeves oversaw royal estates. By the 10th century, royal reeves performed a variety duties in shires and hundreds. They enforced legislation and royal decrees. They presided over local courts, carried out police functions, and witnessed sales. A royal reeve's authority often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peterloo Poster
The Peterloo Massacre took place at St Peter's Field, Manchester, Lancashire, England, on Monday 16 August 1819. Eighteen people died and 400–700 were injured when the cavalry of the Yeomen charged into a crowd of around 60,000 people who had gathered to demand the reform of parliamentary representation. After the end of the Napoleonic Wars in 1815, there was an acute economic slump, accompanied by chronic unemployment and harvest failure due to the Year Without a Summer, and worsened by the Corn Laws, which kept the price of bread high. At that time, only around 11 percent of adult males had the right to vote, very few of them in the industrial north of England, which was worst hit. Radicals identified parliamentary reform as the solution, and a mass campaign to petition parliament for manhood suffrage gained three-quarters of a million signatures in 1817 but was flatly rejected by the House of Commons. When a second slump occurred in early 1819, Radicals sought to mob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solicitor
A solicitor is a lawyer who traditionally deals with most of the legal matters in some jurisdictions. A person must have legally defined qualifications, which vary from one jurisdiction to another, to be described as a solicitor and enabled to practise there as such. For example, in England and Wales a solicitor is admitted to practise under the provisions of the Solicitors Act 1974. With some exceptions, practising solicitors must possess a practising certificate. There are many more solicitors than barristers in England; they undertake the general aspects of giving legal advice and conducting legal proceedings. In the jurisdictions of England and Wales and in Northern Ireland, in the Australian states of New South Wales, Victoria, and Queensland, Hong Kong, South Africa (where they are called '' attorneys'') and the Republic of Ireland, the legal profession is split between solicitors and barristers (called ''advocates'' in some countries, for example Scotland), and a lawye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weights And Measures Acts Of The United Kingdom
Weights and Measures Acts are acts of the British Parliament determining the regulation of weights and measures. It also refers to similar royal and parliamentary acts of the Kingdoms of England and Scotland and the medieval Welsh states. The earliest of these were originally untitled but were given descriptive glosses or titles based upon the monarch under whose reign they were promulgated. Several omnibus modern acts have the short title " Weights and Measures Act" and are distinguished by the year of their enactment. Background There have been many laws concerned with weights and measures in the United Kingdom or parts of it over the last 1,000 or so years. The acts may catalogue lawful weights and measures, prescribe the mechanism for inspection and enforcement of the use of such weights and measures and may set out circumstances under which they may be amended. Modern legislation may, in addition to specific requirements, set out circumstances under which the incumbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Court Leet
The court leet was a historical court baron (a type of manorial court) of England and Wales and Ireland that exercised the "view of frankpledge" and its attendant police jurisdiction, which was normally restricted to the hundred courts. Etymology The word "leet", as used in reference to special court proceedings, dates from the late 13th century, from Anglo-French ''lete'' and Anglo-Latin ''leta'' of unknown origin, with a possible connection to the verb " let". Early history At a very early time in medieval England, the lord of the manor exercised or claimed certain feudal rights over his serfs and feudal tenants. The exercise of those rights was combined with manorial administrative concerns, in his court baron. However this court had no power to deal with criminal acts. Criminal jurisdiction was held by the hundred courts; the country was divided into hundreds, and there was a hundred court for each of them. Each hundred comprised 100 hides, with each hide being an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Improvement Commissioners
Boards of improvement commissioners were ''ad hoc'' urban local government boards created during the 18th and 19th centuries in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and its predecessors the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Kingdom of Ireland. Around 300 boards were created, each by a local act of Parliament, typically termed an Improvement Act.Ed. Juliet Gardiner, ''The Penguin Dictionary of English History'' The powers of the boards varied according to the acts which created them. They often included street paving, cleansing, lighting, providing watchmen or dealing with various public nuisances. Those with restricted powers might be called lighting commissioners, paving commissioners, police commissioners, etc. Older urban government forms included the corporations of ancient boroughs, vestries of parishes, and in some cases the lord of the manor. These were ill-equipped for the larger populations of the Industrial Revolution: the most powerful in theory, the corporat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earl Of Sefton
Earl of Sefton was a title in the Peerage of Ireland created in 1771 for the 8th Viscount Molyneux. The Earls of Sefton held the subsidiary titles Viscount Molyneux, of Maryborough (modern day Portlaoise) in the Queen's County (created 1628), in the Peerage of Ireland, and (from the 2nd Earl onwards) Baron Sefton, of Croxteth in the County Palatine of Lancaster (created 1831), in the Peerage of the United Kingdom. All three titles became extinct upon the death of the 7th Earl in 1972. The Molyneux family's powerful allegiances led to an acquisition of lands and wealth throughout the period 1100–1700, when members of the family were lords of the manor at Sefton. The seat of the Earls of Sefton was Croxteth Hall near (now in) Liverpool. It was bequeathed to the City of Liverpool by the 7th and last Earl of Sefton and his wife, the former Josephine Gwynne Armstrong (1903–1980), who was the final member of the Molyneux family to live at Croxteth. The American-born Countess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Lancaster
The Duchy of Lancaster is an estate of the British sovereign. The estate has its origins in the lands held by the medieval Dukes of Lancaster, which came under the direct control of the monarch when Henry Bolingbroke, the then duke of Lancaster, ascended the throne in 1399. In 1461 King Edward IV confirmed that the Duchy would be inherited by the monarch, but held separately from the Crown Estate, the other assets which belong to the monarch. The Duchy consists of a portfolio of lands, properties, and assets held in trust for the sovereign. The principal purpose of the estate is to provide a source of independent income. The Duchy consists of of land holdings, including rural estates and farmland, urban developments, historic buildings, and commercial properties across England and Wales, particularly in Cheshire, Staffordshire, Derbyshire, Lincolnshire, Yorkshire, Lancashire, and the Savoy Estate in London. As of the financial year ending 31 March 2022, the estate was va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hundred Court
A hundred is an administrative division that is geographically part of a larger region. It was formerly used in England, Wales, some parts of the United States, Denmark, Sweden, Finland, Norway, and in Cumberland County in the British Colony of New South Wales. It is still used in other places, including in Australia (in South Australia and the Northern Territory). Other terms for the hundred in English and other languages include ''wapentake'', ''herred'' (Danish and Bokmål Norwegian), ''herad'' ( Nynorsk Norwegian), ''härad'' or ''hundare'' (Swedish), ''Harde'' (German), ''hiird'' ( North Frisian), ''kihlakunta'' (Finnish), and ''cantref'' (Welsh). In Ireland, a similar subdivision of counties is referred to as a barony, and a hundred is a subdivision of a particularly large townland (most townlands are not divided into hundreds). Etymology The origin of the division of counties into hundreds is described by the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') as "exceedingly obscu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longman
Longman, also known as Pearson Longman, is a publisher, publishing company founded in 1724 in London, England, which is owned by Pearson PLC. Since 1968, Longman has been used primarily as an imprint by Pearson's Schools business. The Longman brand is also used for the Longman Schools in China and the ''Longman Dictionary of Contemporary English, Longman Dictionary''. History Beginnings The Longman company was founded by Thomas Longman (1699–1755), Thomas Longman (1699 – 18 June 1755), the son of Ezekiel Longman (died 1708), a gentleman of Bristol. Thomas was apprenticed in 1716 to John Osborn, a London bookseller, and at the expiration of his apprenticeship married Osborn's daughter. In August 1724, he purchased the stock and household goods of William Taylor (bookseller), William Taylor, the first publisher of ''Robinson Crusoe'', for 9s 6d. Taylor's two shops in Paternoster Row, London, were known respectively as the ''Black Swan (St. Paul's Churchyard), Bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
View Of Frankpledge
Frankpledge was a system of joint suretyship common in England throughout the Early Middle Ages and High Middle Ages. The essential characteristic was the compulsory sharing of responsibility among persons connected in tithings. This unit, under a leader known as the chief-pledge or tithing-man, was then responsible for producing any man of that tithing suspected of a crime. If the man did not appear, the entire group could be fined. While women, clergy, and the richer freemen were exempt, otherwise all men over 12 years of age were organised in the system for mutual surety. Origins The first mention of frankpledge comes in 1114–1118, with the '' Leges Henrici Primi''; but 12th-century figures like William of Malmesbury were keen to link it to pre-Norman times, and to the laws of Canute the Great. Some historians have indeed seen in the Anglo-Saxon frith-borh (literally "peace-pledge") the clear anticipation of frankpledge; others consider the 12th-century commentators were re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |