|
Salal Creek
''Gaultheria shallon'' is an evergreen shrub in the heather family (Ericaceae), native to western North America. Common names include salal (), shallon, or (mainly in Britain) gaultheria. Description ''Gaultheria shallon'' is tall, sprawling to erect. It is loosely to densely branched and often forms dense, nearly impenetrable thickets. The twigs are reddish-brown, with shredding bark. Twigs can live up to 16 years or more, but bear leaves only the first few years. The leaves are alternate, evergreen, leathery, thick and egg shaped. They are shiny and dark green on the upper surface, and rough and lighter green on the lower. Each finely and sharply serrate leaf is long. Each leaf generally lives for 2 to 4 years before it is replaced. The inflorescence of flowers consists of a bracteate raceme, one-sided, with 5–15 flowers at the ends of branches. Each flower is composed of a deeply five-parted, glandular-haired calyx and an urn-shaped pink to white, glandular to hairy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick Traugott Pursh
Frederick Traugott Pursh (or Friedrich Traugott Pursch) (February 4, 1774 – July 11, 1820) was a German people, German–United States, American botanist. Born in Großenhain, in the Electorate of Saxony, under the name Friedrich Traugott Pursh, he was educated at Dresden Botanical Gardens, and emigrated to the United States in 1799. From 1802 to 1805, he worked in Philadelphia as the botanical manager of the extensive gardens of William Hamilton, Esq., "The Woodlands (Philadelphia), The Woodlands." By 1805, he was working for Benjamin Smith Barton on a new Flora (publication), flora of North America, under whom he studied the plants collected on the Lewis and Clark Expedition. His work with Barton allowed him to travel farther afield. In 1805, he traveled south from Maryland to the Carolinas and, in 1806, he traveled north from the mountains of Pennsylvania to New Hampshire. He made both trips principally on foot, with only his dog and a gun, covering over three thousand miles e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seed
In botany, a seed is a plant structure containing an embryo and stored nutrients in a protective coat called a ''testa''. More generally, the term "seed" means anything that can be Sowing, sown, which may include seed and husk or tuber. Seeds are the product of the ripened ovule, after the embryo sac is fertilization, fertilized by Pollen, sperm from pollen, forming a zygote. The embryo within a seed develops from the zygote and grows within the mother plant to a certain size before growth is halted. The formation of the seed is the defining part of the process of reproduction in seed plants (spermatophytes). Other plants such as ferns, mosses and marchantiophyta, liverworts, do not have seeds and use water-dependent means to propagate themselves. Seed plants now dominate biological Ecological niche, niches on land, from forests to grasslands both in hot and cold climates. In the flowering plants, the ovary ripens into a fruit which contains the seed and serves to disseminate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oregon
Oregon ( , ) is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is a part of the Western U.S., with the Columbia River delineating much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of its eastern boundary with Idaho. The 42nd parallel north, 42° north parallel delineates the southern boundary with California and Nevada. The western boundary is formed by the Pacific Ocean. Oregon has been home to many Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous nations for thousands of years. The first European traders, explorers, and settlers began exploring what is now Oregon's Pacific coast in the early to mid-16th century. As early as 1564, the Spanish expeditions to the Pacific Northwest, Spanish began sending vessels northeast from the Philippines, riding the Kuroshio Current in a sweeping circular route across the northern part of the Pacific. In 1592, Juan de Fuca undertook detailed mapping a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Washington (state)
Washington, officially the State of Washington, is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is often referred to as Washington State to distinguish it from Washington, D.C., the national capital, both named after George Washington (the first President of the United States, U.S. president). Washington borders the Pacific Ocean to the west, Oregon to the south, Idaho to the east, and shares Canada–United States border, an international border with the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of British Columbia to the north. Olympia, Washington, Olympia is the List of capitals in the United States, state capital, and the most populous city is Seattle. Washington is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 18th-largest state, with an area of , and the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 13th-most populous state, with a population of just less than 8 million. The majority of Washington's residents live ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, forests, lakes, mountains, inland deserts and grassy plains. British Columbia borders the province of Alberta to the east; the territories of Yukon and Northwest Territories to the north; the U.S. states of Washington (state), Washington, Idaho and Montana to the south, and Alaska to the northwest. With an estimated population of over 5.7million as of 2025, it is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, third-most populous province. The capital of British Columbia is Victoria, British Columbia, Victoria, while the province's largest city is Vancouver. Vancouver and its suburbs together make up List of census metropolitan areas and agglomerations in Canada, the third-largest metropolit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the northernmost, westernmost, and easternmost (the Aleutian Islands cross the 180th meridian into the eastern hemisphere) state in the United States. It borders the Canadian territory of Yukon and the province of British Columbia to the east. It shares a western maritime border, in the Bering Strait, with Russia's Chukotka Autonomous Okrug. The Chukchi and Beaufort Seas of the Arctic Ocean lie to the north, and the Pacific Ocean lies to the south. Technically, it is a semi-exclave of the U.S., and is the largest exclave in the world. Alaska is the largest U.S. state by area, comprising more total area than the following three largest states of Texas, California, and Montana combined, and is the seventh-largest subnational division i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saanich Dialect
Saanich (also Sənčáθən, written as in Saanich orthography, ) is the language of the First Nations Saanich people in the Pacific Northwest region of northwestern North America. Saanich is a Coast Salishan language in the Northern Straits dialect continuum, the varieties of which are closely related to the Klallam language. Language revitalization efforts "The School Board, together with the FirstVoices program for revitalizing Aboriginal languages, is working to teach a new generation to speak " at the ȽÁU¸WELṈEW̱ Tribal School. The first Grade 12 class is scheduled to graduate in June 2026. SENĆOŦEN texting, mobile app and portal A Saanich texting app was released in 2012. A SENĆOŦEN iPhone app was released in October 2011. An online dictionary, phrasebook, and language learning portal is available at the First Voices SENĆOŦEN Community Portal. Phonology Vowels Saanich has no rounded vowels in native vocabulary. As in many languages, vowels are s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamish Language
Squamish ( ; ', ''sníchim'' meaning "language") is a Coast Salish language spoken by the Squamish people of the Pacific Northwest. It is spoken in southwestern British Columbia, Canada, centred on their reserve communities in Squamish, North Vancouver, and West Vancouver. An archaic historical rendering of the native ' is ''Sko-ko-mish'' but this should not be confused with the name of the Skokomish people of Washington state. Squamish is most closely related to the Sechelt, Halkomelem, and Nooksack languages. The Squamish language was first documented in the 1880s by a German anthropologist;; however the grammar of the language was documented by the Dutch linguist Aert Kuipers in the 1960s. The orthography or spelling system of the language came about in the 1960s, while the first Squamish dictionary was published only in 2011. The language shares certain similarities with languages like Sechelt and Halkomelem which are spoken in similar regions. Documentation A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dictionary Of Canadian Biography
The ''Dictionary of Canadian Biography'' (''DCB''; ) is a dictionary of biographical entries for individuals who have contributed to the history of Canada. The ''DCB'', which was initiated in 1959, is a collaboration between the University of Toronto and Laval University. Fifteen volumes have so far been published with more than 8,400 biographies of individuals who died or whose last known activity fell between the years 1000 and 1930. The entire print edition is online, along with some additional biographies to the year 2000. Establishment of the project The project was undertaken following a bequest to the University of Toronto from businessman James Nicholson for the establishment of a Canadian version of the United Kingdom's ''Dictionary of National Biography''. In the spring of 1959, George Williams Brown was appointed general editor and the University of Toronto Press, which had been named publisher, sent out some 10,000 announcements introducing the project. Work started in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean François Gaultier
Jean François Gaultier (6 October 1708 in La Croix-Avranchin – 10 July 1756 in Quebec) was a French physician and botanist. He was the king's physician for New France and was the regular physician at the Hôtel-Dieu de Québec. Gaultier, being one of the leading naturalists in Canada, supported Swedish botanist Pehr Kalm Pehr Kalm (6 March 1716 – 16 November 1779), also known as Peter Kalm, was a Swedish-Finnish List of explorers, explorer, botany, botanist, natural history, naturalist, and Agricultural economics, agricultural economist. He was one of the most ... in his 1749 exploring voyage of Quebec. Jean-François Gaultier married Madeleine-Marie-Anne on 12 March 1752. References 18th-century French botanists People from the Province of Normandy 1708 births 1756 deaths 18th-century French physicians People of New France {{France-botanist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pehr Kalm
Pehr Kalm (6 March 1716 – 16 November 1779), also known as Peter Kalm, was a Swedish-Finnish List of explorers, explorer, botany, botanist, natural history, naturalist, and Agricultural economics, agricultural economist. He was one of the most important Apostles of Linnaeus, apostles of Carl Linnaeus. In 1747, he was commissioned by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences to travel to the North American colonies in order to bring back seeds and plants that might be useful to agriculture. Among his many scientific accomplishments, Kalm can be credited with the first description of Niagara Falls written by a trained scientist. In addition, he published the first scientific paper on the North American 17-year periodical cicada, ''Magicicada septendecim.'' Kalm wrote an account of his travels that was translated into numerous European languages; a 20th-century translation remains in print in English as ''Peter Kalm's Travels in North America: The English Version of 1770,'' translated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
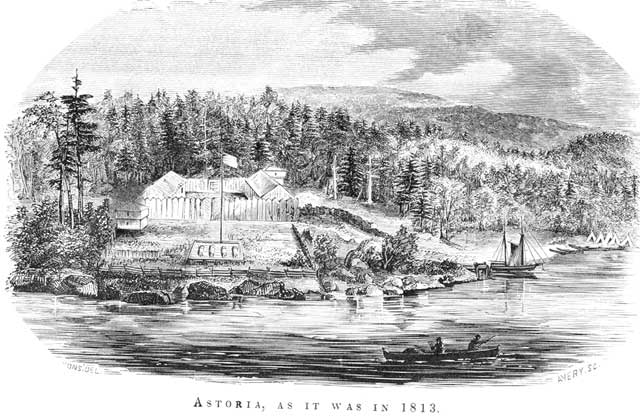
Fort George, Oregon
Fort Astoria (also named Fort George) was the primary fur trading post of John Jacob Astor's Pacific Fur Company (PFC). A maritime contingent of PFC staff was sent on board the '' Tonquin'', while another party traveled overland from St. Louis. This land based group later became known as the Astor Expedition. Built at the entrance of the Columbia River in 1811, Fort Astoria was the first American-owned settlement on the Pacific coast of North America. The inhabitants of the fort differed greatly in background and position, and were structured into a corporate hierarchy. The fur trading partners of the company were at the top, with clerks, craftsmen, hunters, and laborers in descending order. Nationalities included Americans, Scots, French Canadian voyageurs, Native Hawaiian Kanakas, and various indigenous North Americans, including Iroquois and others from Eastern Canada. They found life quite monotonous, with the fish and vegetable diet boring. Venereal diseases were problemati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |