|
Sakkara
Saqqara ( ar, سقارة, ), also spelled Sakkara or Saccara in English , is an Egyptian village in Giza Governorate, that contains ancient burial grounds of Egyptian royalty, serving as the necropolis for the ancient Egyptian capital, Memphis. Saqqara contains numerous pyramids, including the Step pyramid of Djoser, sometimes referred to as the Step Tomb, and a number of mastaba tombs. Located some south of modern-day Cairo, Saqqara covers an area of around . Saqqara contains the oldest complete stone building complex known in history, the Pyramid of Djoser, built during the Third Dynasty. Another sixteen Egyptian kings built pyramids at Saqqara, which are now in various states of preservation. High officials added private funeral monuments to this necropolis during the entire Pharaonic period. It remained an important complex for non-royal burials and cult ceremonies for more than 3,000 years, well into Ptolemaic and Roman times. North of the area known as Saqqara l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyramid Of Unas
The pyramid of Unas ( Egyptian: ''Nfr swt Wnjs'' "Beautiful are the places of Unas") is a smooth-sided pyramid built in the 24th century BC for the Egyptian pharaoh Unas, the ninth and final king of the Fifth Dynasty. It is the smallest Old Kingdom pyramid, but significant due to the discovery of Pyramid Texts, spells for the king's afterlife incised into the walls of its subterranean chambers. Inscribed for the first time in Unas's pyramid, the tradition of funerary texts carried on in the pyramids of subsequent rulers, through to the end of the Old Kingdom, and into the Middle Kingdom through the Coffin Texts that form the basis of the ''Book of the Dead''. Unas built his pyramid between the complexes of Sekhemket and Djoser, in North Saqqara. Anchored to the valley temple at a nearby lake, a long causeway was constructed to provide access to the pyramid site. The causeway had elaborately decorated walls covered with a roof which had a slit in one section allowing light t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serapeum Of Saqqara
The Serapeum of Saqqara was the ancient Egyptian burial place for sacred bulls of the Apis cult at Memphis. It was believed that the bulls were incarnations of the god Ptah, which would become immortal after death as ''Osiris-Apis''. a name which evolved to ''Userhapi'' () in Coptic, and ''Serapis (''), in the Hellenistic period. Over a timespan of approximately 1400 years, from the New Kingdom of Egypt to the Ptolemaic Period, at least sixty Apis are attested to have been interred at the Serapeum. The earliest burials are found in isolated tombs, as the cult gained importance underground galleries were dug that connected subsequent burial chambers. One of the cult practices involved the dedication of commemorative stone tablets with dates relating to the life and death of the Apis. This data was crucial for the establishment of an Egyptian chronology in the 19th century. It is part of the Saqqara necropolis, which includes several animal catacombs, notably the burial vault ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
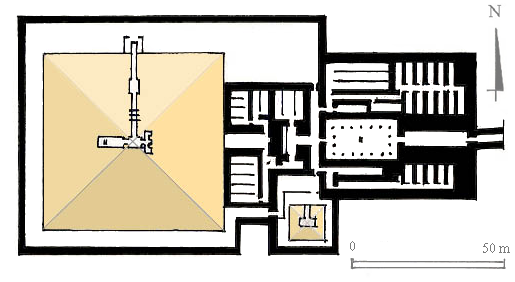
Pyramid Of Teti
The pyramid of Teti is a smooth-sided pyramid situated in the pyramid field at Saqqara in Egypt. It is the second known pyramid containing pyramid texts. Excavations have revealed a satellite pyramid, two pyramids of queens accompanied by cult structures, and a funerary temple. The pyramid was opened by Gaston Maspero in 1882 and the complex explored during several campaigns ranging from 1907 to 1965. It was originally called ''Teti's Places Are Enduring''. The preservation above ground is very poor, and it now resembles a small hill. Below ground the chambers and corridors are very well preserved. The funerary complex The pyramid complex of Teti follows a model established during the reign of Djedkare Isesi, the arrangement of which is inherited from the funerary complexes of Abusir. A valley temple, now lost, was probably destroyed in antiquity due to the place of an Old Kingdom temple dedicated to Anubis constructed there. A better known funerary temple, revealed by James ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
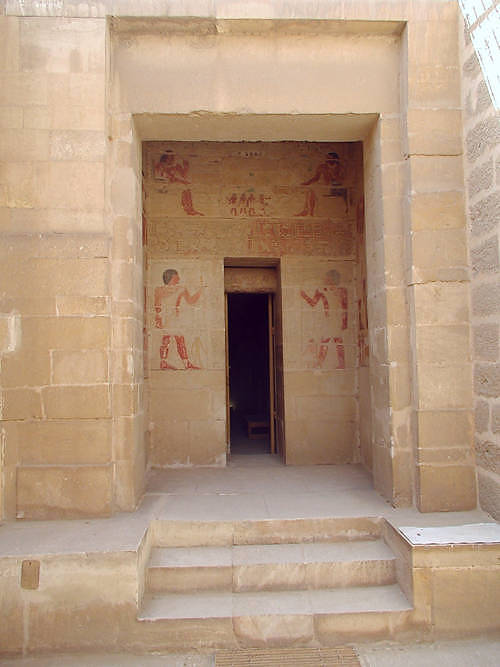
Khnumhotep And Niankhkhnum
Khnumhotep ( egy, ẖnm.w-ḥtp(.w)) and Niankhkhnum ( egy, nj-ꜥnḫ-ẖnm.w) were ancient Egyptian royal servants. They shared the title of Overseer of the Manicurists in the Palace of King Nyuserre Ini, sixth pharaoh of the Fifth Dynasty, reigning during the second half of the 25th century BC. They were buried together at Saqqara and are listed as "royal confidants" in their joint tomb. They are notable for their unusual depiction in Egyptian records, often interpreted as the first recorded same-sex couple,. Family Khnumhotep and Niankhkhnum are believed by scholars, including Thomas Dowson, and Greg Reeder, to be the first recorded same-sex couple in ancient history. The assumed romantic relationship between Khnumhotep and Niankhkhnum is based on depictions of the two men standing nose to nose and embracing. Niankhkhnum's wife, depicted in a banquet scene, was almost completely erased in antiquity, and in other pictures Khnumhotep occupies the position usually designated fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyramid Of Userkaf
The pyramid complex of Userkaf was built c. 2490 BC for the pharaoh Userkaf (reigned 2494–2487 BC), founder of the 5th Dynasty of Egypt (c. 2494–2345 BC). It is located in the pyramid field at Saqqara, on the north-east of the step pyramid of Djoser (reigned c. 2670 BC). Constructed in dressed stone with a core of rubble, the pyramid is now ruined and resembles a conical hill in the sands of Saqqara.Mark Lehner, ''The Complete Pyramids'', Thames & Hudson, , p. 140 For this reason, it is known locally as ''El-Haram el-Maharbish'', the "Heap of Stone",Jean-Phillipe Lauer (in French): ''Saqqarah, Une vie, Entretiens avec Phillipe Flandrin'', Petite Bibliotheque Payot 107, 1988, and was recognized as a royal pyramid by western archaeologists in the 19th century. Userkaf's pyramid is part of a larger mortuary complex comprising a mortuary temple, an offering chapel and a cult pyramid as well as separate pyramid and mortuary temple for Userkaf's wife, queen Neferhete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Necropolis
A necropolis (plural necropolises, necropoles, necropoleis, necropoli) is a large, designed cemetery with elaborate tomb monuments. The name stems from the Ancient Greek ''nekropolis'', literally meaning "city of the dead". The term usually implies a separate burial site at a distance from a city, as opposed to tombs within cities, which were common in various places and periods of history. They are different from grave fields, which did not have structures or markers above the ground. While the word is most commonly used for ancient sites, the name was revived in the early 19th century and applied to planned city cemeteries, such as the Glasgow Necropolis. Necropoli in the ancient world Egypt Ancient Egypt is noted for multiple necropoleis. Ancient Egyptian funerary practices and beliefs about the afterlife led to the construction of several extensive necropoleis to secure and provision the dead in the hereafter. These necropoleis are therefore major archaeological si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomb Of Perneb
The Tomb of Perneb is a mastaba-style tomb from ancient Egypt, built during the reigns of Djedkare Isesi and Unas (ca. 2381 BC to 2323 BC), in the necropolis of Saqqara, north of Pharaoh Djoser's Step Pyramid and about 30 kilometers south of Giza, Egypt. It was the tomb of Perneb, and from the size and placement of the tomb he might have been a court official or royal family member. The tomb was erected during the 5th Dynasty in the Old Kingdom. It was discovered in 1907, purchased from the Egyptian government in 1913 and given to the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York City, by Edward S. Harkness. Perneb was a court official in the royal household who had a role in the robing and crowning of the king. His name means "my Lord has come forth to me". His tomb was attached to the larger tomb of the vizier Shepsesre, who may have been Perneb's father. Description The tomb consists of an underground burial chamber and a limestone mastaba above ground. The mastaba is div ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyramid Of Khendjer
The pyramid of Khendjer was a pyramid built for the burial of the 13th dynasty pharaoh Khendjer, who ruled Egypt c. 1760 BC during the Second Intermediate Period. The pyramid, which is part of larger complex comprising a mortuary temple, a chapel, two enclosure walls and a subsidiary pyramid, originally stood around high and is now completely ruined. The pyramidion was discovered during excavations under the direction of Gustave Jéquier in 1929, indicating that the pyramid was finished during Khendjer's lifetime. It is the only pyramid known to have been completed during the 13th Dynasty. Excavations The first investigations of the pyramid of Khendjer were undertaken in the mid 19th century by Karl Richard Lepsius, who included the pyramid in his list under the number XLIV. The pyramid was excavated by Gustave Jéquier from 1929 until 1931 with the excavation report published two years later in 1933.Gustave Jéquier: ''Deux pyramides du Moyen Empire'', Cairo 1933, pp. 3-35 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mortuary Complex Of Pepi I
The pyramid of Pepi I (in ancient Egyptian Men-nefer-Pepi meaning Pepi's splendour is enduring) is the pyramid complex built for the Egyptian pharaoh Pepi I of the Sixth Dynasty in the 24th or 23rd century BC. The complex gave its name to the capital city of Egypt, Memphis. As in the pyramids of his predecessors, Pepi I's substructure was filled with vertical columns of hieroglyphic texts, Pyramid Texts. It was in Pepi I's pyramid that these texts were initially discovered in 1880 by Gaston Maspero, though they originated in the pyramid of Unas. The corpus of Pepi I's texts is also the largest from the Old Kingdom, comprising 2,263 columns and lines of hieroglyphs. Pepi I sited his pyramid complex in South Saqqara an approximate north of Djedkare Isesi's pyramid. It is unclear why Pepi I relocated to South Saqqara. Perhaps Pepi I had moved the royal palace south and away from the city, or perhaps no viable sites were left in North and Central Saqqara after Teti built his py ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memphis, Egypt
, alternate_name = , image = , alt = , caption = Ruins of the pillared hall of Ramesses IIat Mit Rahina , map_type = Egypt#Africa , map_alt = , map_size = , relief = , coordinates = , location = Mit Rahina, Giza Governorate, Egypt , region = Lower Egypt , type = Settlement , part_of = , length = , width = , area = , height = , builder = Unknown, was already in existence during Iry-Hor's reignP. Tallet, D. Laisnay: ''Iry-Hor et Narmer au Sud-Sinaï (Ouadi 'Ameyra), un complément à la chronologie des expéditios minière égyptiene'', in: BIFAO 112 (2012), 381–395available online/ref> , material = , built = Earlier than 31st century BC , abandoned = 7th century AD , epochs = Early Dynastic Period to Early Middle Ages , cultures = , dependency_of = , occupants = , event ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mastaba
A mastaba (, or ), also mastabah, mastabat or pr- djt (meaning "house of stability", " house of eternity" or "eternal house" in Ancient Egyptian), is a type of ancient Egyptian tomb in the form of a flat-roofed, rectangular structure with inward sloping sides, constructed out of mudbricks. These edifices marked the burial sites of many eminent Egyptians during Egypt's Early Dynastic Period and Old Kingdom. In the Old Kingdom epoch, local kings began to be buried in pyramids instead of in mastabas, although non-royal use of mastabas continued for over a thousand years. Egyptologists call these tombs ''mastaba'', from the Arabic word (maṣṭaba) "stone bench". History The afterlife was important in the religion of ancient Egyptians. Their architecture reflects this, most prominently by the enormous amounts of time and labour involved in building tombs. Ancient Egyptians believed the soul could live only if the body was fed and preserved from corruption and depredation. St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |